
Design Data - Information flow
RH-1 Introductions for technological details at realisations
RH-1.1 Contents
⚙ RH-1.1.1 Looking forward - paths by seeing directions
A reference frame in mediation innovation

When the image link fails,
🔰 click
here.
There is a revert to main topic in a shifting frame.
Contexts:
◎ r-steer the business
↖ r-shape mediation change
↗ r-serve split origin
↙ data values stream
↘ functional details
Fractal focus in technology for functionality
The cosmos is full of systems and we are not good in understanding what is going on.
In a ever more complex and fast changing world we are searching for more certainties and predictabilities were we would better off in understanding the choices in uncertainties and unpredictability's.
Combining:
- Systems Thinking, decisions, ViSM (Viable Systems Model) good regulator
- Lean as the instantiation of identification systems
- The Zachman 6*6 reference frame principles
- Information processing, the third wave
- Value Stream (VaSM) Pull-Push cycle
- Improvement cycles : PDCA DMAIC SIAR OODA
- Risks and uncertainties for decisions in the now near and far future, VUCA BANI
The additional challenge with all complexities is that this is full of dualities - dichotomies.
⚙ RH-1.1.2 Local content
⚖ RH-1.1.3 Guide reading this page
The position of this pages in the whole
This page is positioned as the
technology details that are a split from the concepts in the Zarf JAbes technology idea for enabling a realisation.
The technology concepts page is a split from the generic technology page (r-serve). That page is part of the generic 6*6 reference frame.
There is no intention to have all chapters completely filled ar achieve a belanced load in the content.
The goal is a collection of what I have in a more understandable strcuture than beig spread all over many pages.
| | | | Details |
| | | | Technology |
| Context | r-serve: SDLC DevOps | Concepts | 🕳 |
| | | | Functional |
| | | | Details |
The entry anchor will be the RH-2 chapters.
An introdcution when appplicable RH-1
The impact when applicable in RH-3
The quest for methodlogies and practices
These are mostly well known might be forgotten, but they are keeping coming back although in new boundaries new options.
It is the same questions: what is possible now, at what cost and for what kind of impact.
⚒ RH-1.1.4 Progress
done and currently working on:
- 2026 week 4
- Starting to refill this page in a new structure
The topics that are unique on this page

RH-1.2 Basics performance processing in flow lines
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
⟲ RH-1.2.1 The technological approach in performance
Tuning performance basics.
Solving performance problems requires understanding of the operating system and hardware.
That architecture was set by von Neumann (see design-math).
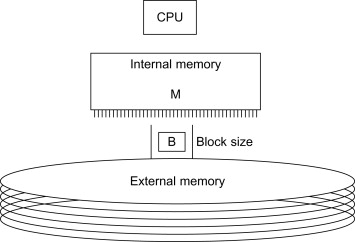
A single CPU, limited Internal Memory and the external storage.
The time differences between those resources are in magnitudes (factor 100-1000).
Optimizing is balancing between choosing the best algorithm and the effort to achieve that algorithm.
That concept didn´t change. The advance in hardware made it affordable to ignore the knowledge of tuning.
The Free Lunch Is Over
A Fundamental Turn Toward Concurrency in Software, By Herb Sutter (march 2008, februari 2005).
"Welcome to the jungle" Herb sutters blog
If you haven´t done so already, now is the time to take a hard look at the design of your application, determine what operations are CPU-sensitive now or are likely to become so soon,
and identify how those places could benefit from concurrency. Now is also the time for you and your team to grok concurrent programming´s requirements, pitfalls, styles, and idioms.
Additional component, the connection from machine, multiple cpu´s - several banks internal memory, to multiple external storage boxes by a network.
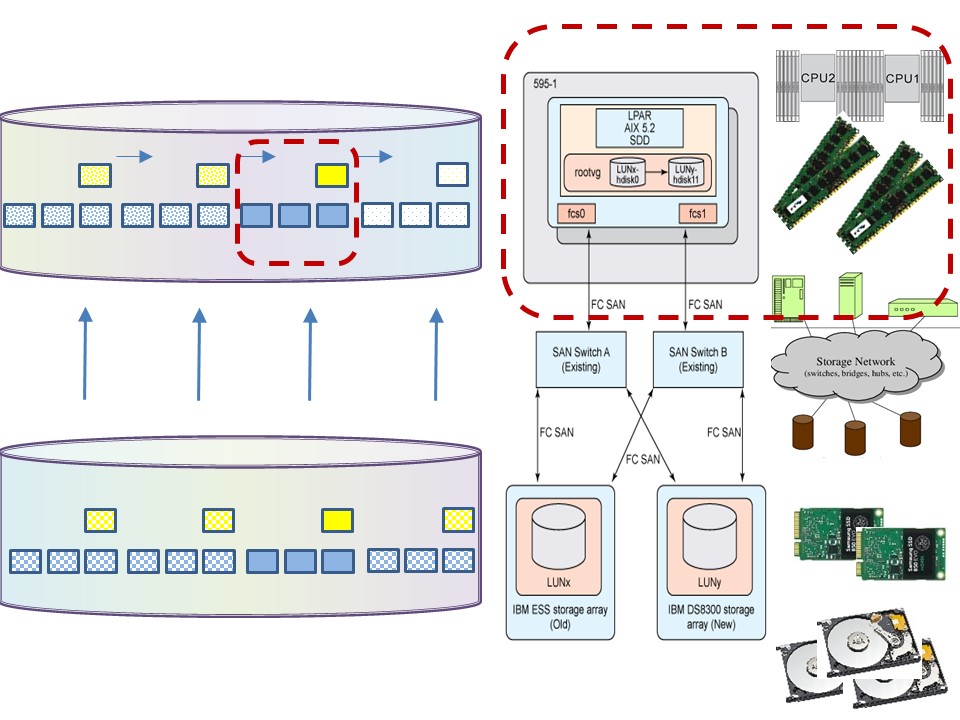
Tuning cpu - internal memory.
Minimize resource usage:
- use data records processing in serial sequence. (blue)
- indexes bundled (yellow).
- Allocate correct size and correct number of buffers.
- Balance buffers between operating system (OS) and DBMS. A DBMS normally is optimal without OS buffering (DIO).
❗ The
"balance line" algorithm is the best.
A DBMS will do that when possible.
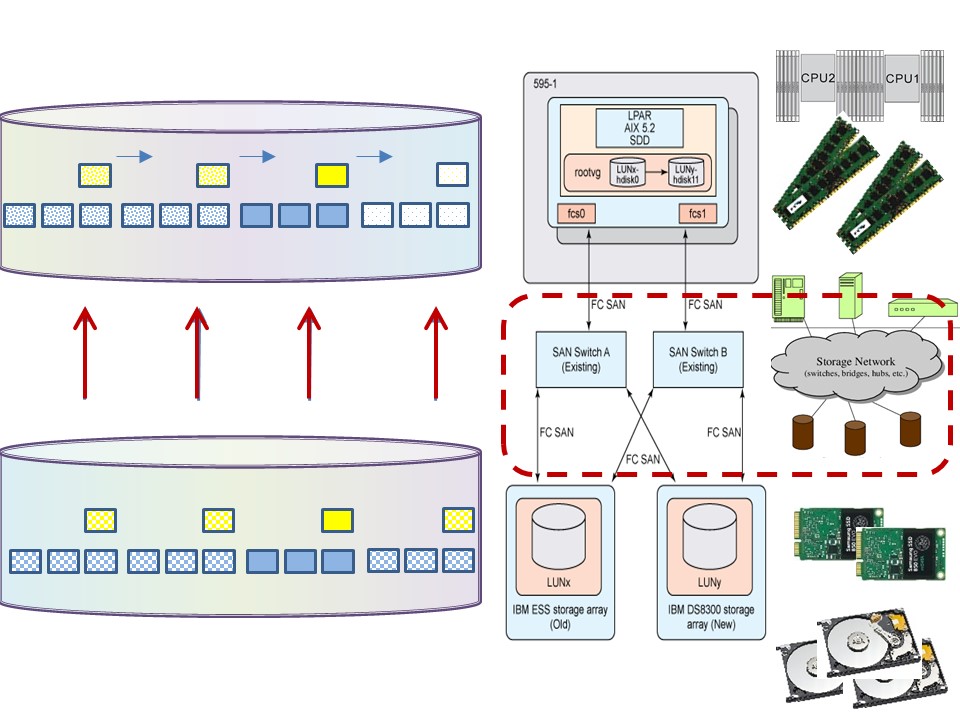
Network throughput.
Minimize delays, use parallelization:
- Stripe logical volumes (OS).
- Parallelize IO, transport lines.
- Optimize buffer transport size.
- Compress - decompress data at CPU can decrease elapse time.
- Avoid locking caused by: shared storage - clustered machines.
⚠ Transport buffer size is a coöperation between remote server and local driver. The local optimal buffer size can be different.
Resizing data in buffers a cause of performance problems.
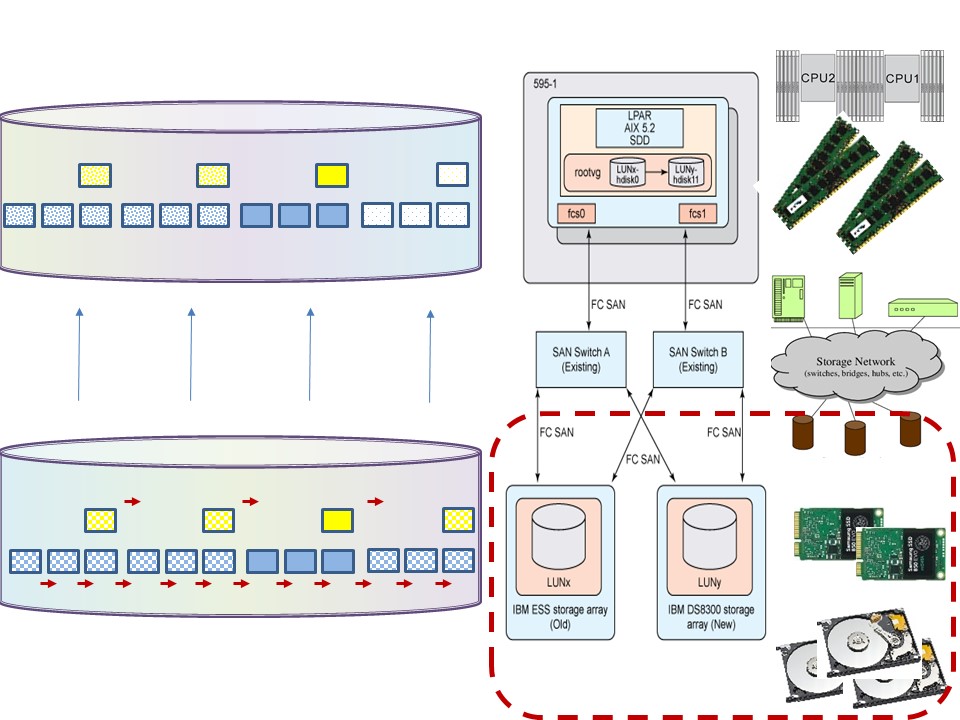
Minize delays in the storage system.
- Multi tiers choice SSD- Harddisk -Tape, Local unshared - remote shared.
- Prefered: sequential or skipped sequential.
- tuning with Analytics is big block bulk sequential instead of random small block transactional usage.
⚠ Using Analtyics, tuning IO is quite different to transactional DBMS usage.
💣 This different non standard approach must be in scope with service management. The goal of sizing capacity is better understood than Striping for IO perfromance.
⚠ DBMS changing types, the best one in a situation
A mix of several DBMS are allowed in a EDWH 3.0. The speed of transport and retentionperiods are important considerations.
Technical engineering for details and limitations to state of art and cost factors.
⟲ RH-1.2.2 The why of using dashboards
Anti-buzz hype simplified dashboard distinctions
Transformational
The anti-buzz hype data strategy, a strategy is not:
- a fancy story about data strategy,
- a long document full of definitions,
- an "inspiring" deck without actions, choices, priorities, or ownership.
A data strategy is, however, a set of explicit choices that:
- provides direction (what to do/not to do, why),
- is manageable (who does what, decides, how to measure),
- is executable (capacity, roadmap, preconditions).
Where do "theorists" typically get stuck?
The theory of data strategy is confused with strategy.
This mainly occurs at these intersections:
- Goals without prioritization ➡ "we want to be data-driven" (no choices)
- Governance without a mandate ➡ roles on paper, no one decides
- Roadmap without capacity ➡ list of actions, no feasibility
- Values without management measures ➡ ethics/GDPR mentioned, no controls/KPIs
- Data as a concept, not master data ➡ unclear what constitutes "truth"
What's needed at a minimum to make this a "strategy" (the smallest upgrade):
| | Goals | information capability |
| 1 | Goal & focus | 3-5 priority data domains + 10 "don'ts" |
| 2 | Starting position | 1-page baseline (maturity + top bottlenecks + risks) |
| 3 | Organizational model | decision path + ownership + portfolio board (who decides what) |
| 4 | Management measures | KPI set (quality/delivery/value/compliance) + rhythm + interventions |
| 5 | Master data | top 15 objects + source agreements + definitions + management process |
| 6 | Capacity | roles/FTEs/skills + budget bandwidth + 12-month roadmap |
| 7 | Transformational options | |
Anti-buzz hype simplified dashboard distinctions
Complexity is simplicity gone wrong.
No bottom-up approach, no raising awareness, no building support, no nonsense following over-the-top, no-nonsense catch-all terms.
"Simply" knowing how governance works is the best starting point.
A GOOD dashboard consists of at least six components.
| | Goals | information capability |
| 1 | The goal | |
| 2 | situation awareness | |
| 3 | Model of the system | |
| 4 | Options for influence | |
| 5 | Masterdata | |
| 6 | capacity & capabilities | |
| 7 | Transformational options | |

RH-1.3 Competing functionality vs safety to realisation
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
⟲ RH-1.3.1 Info
butics
Auditing monitoring.
For legal requirements there are standards by auditors. When they follow their checklist a list of &best practices"e are verified.
The difference with "good practice" is the continous improvement (PDCA) cycle.
| Procedures , organisational. |
| People , personal. |
| Products, physical & cyber. |
| Security Operations Center. |
| Infrastructure building blocks- DevOps. |
| Auditing & informing management. |
Audit procedure processing.
The situation was: Infrastructure building blocks- DevOps Leading. Auditing and informing management on implementations added for control.
Added is: Security Operations Centre, leading for evaluating security risk. Auditing and informing management on implementations added for control.
The ancient situation was: Application program coding was mainly done in house. This had changed into using public and commercial retrieved software when possible.
⚠ Instead of having a software crisis in lines of code not being understood (business rules dependency).
It has changed in used software libraries not being understood (vulnerabilities) and not understood how to control them by the huge number of used copied software libraries.
⚠ Instead of having only an simple infrastructure stack to evaluate it has become a complicated infrastructure stack with an additional involved party into a triad to manage.
Penetration testing,
also called pen testing or ethical hacking, is the practice of testing a computer system, network or web application to find security vulnerabilities that an attacker could exploit.
Penetration testing can be automated with software applications or performed manually. Either way, the process involves gathering information about the target before the test, identifying possible entry points,
attempting to break in -- either virtually or for real -- and reporting back the findings.
It will only notify what is visible to the tester, using tools only what is commonly known. There is nog warrant that it is not vulnerable after "ecorrections" are made.
It is well posible there is no security risk at all by the way the system is used and being managed.
logging monitoring.
Logging events when processing information is generating new information. The goal in using those logging informations has several goals.
Some loginformation is related to the product and could also become new operational information.
💣 When there are different goals an additional copy of the information is an option but introduces an option of integrity mismatches.
Data classification.
Information security
The CIA triad of confidentiality, integrity, and availability is at the heart of information security.
(The members of the classic InfoSec triad confidentiality, integrity and availability are interchangeably referred to in the literature as security attributes, properties, security goals, fundamental aspects, information criteria, critical information characteristics and basic building blocks.)
However, debate continues about whether or not this CIA triad is sufficient to address rapidly changing technology and business requirements,
with recommendations to consider expanding on the intersections between availability and confidentiality, as well as the relationship between security and privacy.
Other principles such as "accountability" have sometimes been proposed; it has been pointed out that issues such as non-repudiation do not fit well within the three core concepts.
😉 Two additionals are:
- Undisputable When the information itself is in dispute that is a serious problem. Needed is the source and time / period relevance of the information.
- Verifiability When not able to that there is no underpinning on usage and any risks.
Negelected attentions points:
- An important logical control that is frequently overlooked is the principle of least privilege, which requires that an individual, program or system process not be granted any more access privileges than are necessary to perform the task.
- An important physical control that is frequently overlooked is separation of duties, which ensures that an individual can not complete a critical task by himself.
An important aspect of information security and risk management is recognizing the value of information and defining appropriate procedures and protection requirements for the information.
Not all information is equal and so not all information requires the same degree of protection. This requires information to be assigned a security classification.
Classified information
When labelling information in a categories an approach is:
- Public / unclassified
- Confidential, intended for circulation in the internal organisation and authorized third parties at owners discretion.
- Restricted, information that should not into disclosure outside a defined group.
- Secret, strategical sensitive information only shared between a few individuals.
butics
Turing thesis
The data explosion. The change is the ammount we are collecting measuring processes as new information (edge).
📚 Information questions.
⚙ measurements data figures.
🎭 What to do with new data?
⚖ legally & ethical acceptable?

📚 Information questions.
⚙ measurements data figures.
🎭 What to do with new data?
⚖ legally & ethical acceptable?
BISL Business Information Services Library.
Bisl is used for a demand supply chain. Often going along with internal business and external outsourcec IT services. Nice to see is a seperation of concerns in a similar way, placing the high level drivers in the center.
The framework describes a standard for processes within business information management at the strategy, management and operations level.
BiSL is closely related to the ITIL and ASL framework, yet the main difference between these frameworks is that ITIL and ASL focus on the supply side of information (the purpose of an IT organisation), whereas BiSL focuses on the demand side (arising from the end-user organisation
The demand side focus for some supply is a solution for the supposed mismatch business & ICT. The approach for that mismatch is an external supplier.

RH-1.4 Defining taxonomies - concepts - ontology
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
⟲ RH-1.4.1 Info
Changing the way of informing.
Combining the data transfer, microservices, archive requirement, security requirements and doing it like the maturity of physical logistics.
It goes into the direction of a centralized managed approach while doing as much as possible decentralised.
Decoupling activities when possible to get popping up problems human manageable small.
Combining information connections.
There are a lot of ideas giving when combined another situation:
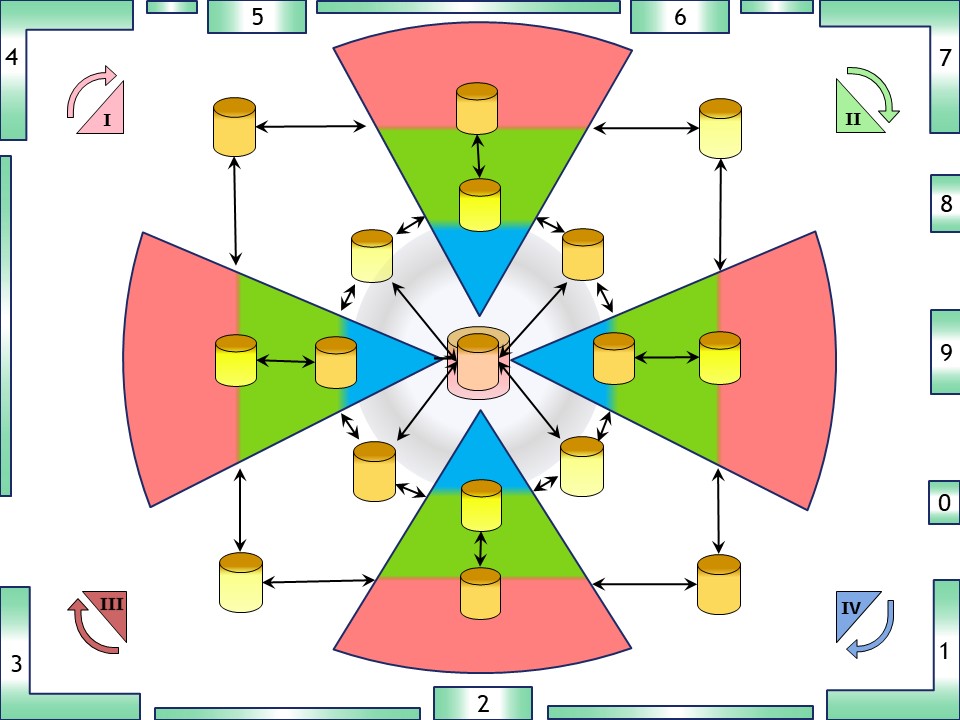 💡
💡 Solving gaps between silos supporting the values stream.
Those are the rectangular positioned containers connecting between the red/green layers. (total eight internal - intermediates)
💡 Solving management information into the green/blue layers in every silo internal.
These are the second containers in every silo. (four: more centralised)
💡 Solving management information gaps between the silos following the value stream at a higher level .
These are the containers at the circle (four intermediates).
Consolidate that content to a central one.
🎭 The result is Having the management information supported in nine (9) containers following the product flow at strategic level. Not a monolithic central management information system but one that is decentralised and delegate as much as possible in satellites.
💡 The outer operational information rectangle is having a lot of detailed information that is useful for other purposes. One of these is the integrity processes.
A SOC (Security Operations Centre) is an example for adding another centralised one.
🎭 The result is Having the management information supported in nine (9) containers following the product flow at strategic level. Another eight (8) at the operational level another and possible more.
Not a monolithic central management information system but one that is decentralised and delegate as much as possible in satellites.
🤔 Small is beautiful, instead of big monolithic costly systems, many smaller ones can do the job better an more efficiënt. The goal: repeating a pattern instead of a one off project shop.
The duality when doing a change it will be like a project shop.

Containerization.
We are used to the container boxes as used these days for all kind of transport.
The biggest of the containerships are going over the world reliable predictable affordable.
Normal economical usage, load - reload, returning, many predictable reliable journeys.
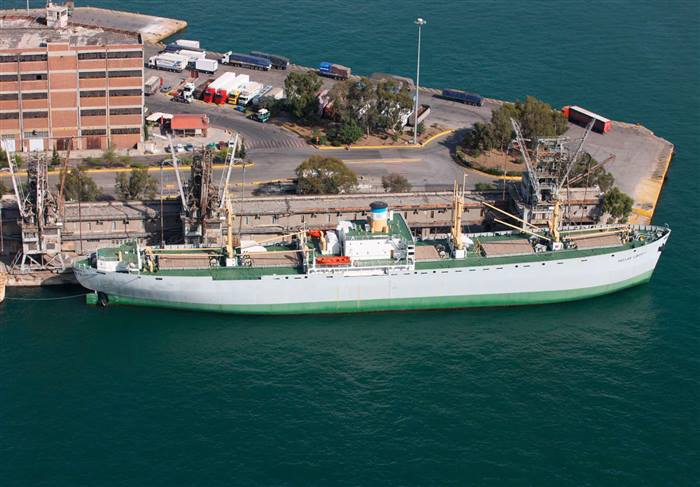

The first containerships where these liberty ships. Fast and cheap to build. The high loss rate not an problem but solved by building many of those.
They were build as project shops but at many locations. The advantage of a known design to build over and over again.
They were not designed for many journeys, they were designed for the deliveries in war conditions.

project shop.
to cite:
This approach is most often used for very large and difficult to move products in small quantities.
...
There are cases where it is still useful, but most production is done using job shops or, even better, flow shops.
💣 The idea is that everything should become a flow shop even when not applicable. At ICT delivering software in high speed is seen as a goal, that idea is missing the data value stream as goal.
Containerization.
Everybody is using a different contact to the word "data". That is confusing when trying to do something with data. A mind switch is seeing it as information processing in enterprises.
As the datacentre is not a core business activity for most organisations there is move in outsourcing (cloud SAAS).
Engineering a process flow, then at a lot of point there will be waits.
At the starting and ending point it goes from internal to external where far longer waits to get artefacts or product deliveries will happen.
Avoiding fluctuations having a predictable balanced workload is the practical solution to become effciënt.
Processing objects, collecting information and delivering goes along with responsibilities.
It is not sexy, infact rather boring. Without good implementation all other activities are easily getting worthless. The biggest successed like Amazon are probably more based in doing this very well than something else.
The Inner Workings of Amazon Fulfillment Centers
Common used ICT patterns processing information.
For a long time the only delivery of an information process was a hard copy paper result.
Deliveries of results has changed to many options. The storing of information has changed also.
Working on a holistic approach on information processing starting at the core activities can solve al lot of problems. Why just working on symptoms and not on root causes?
💡 Preparing data for BI, Analytics has become getting an unnecessary prerequisite. Build a big design up front: the enterprise data ware house (EDWH 3.0).
Data Technical - machines oriented
The technical machines oriënted approach is about machines and the connections between them (network).
The service of delivering Infrastructure (IAAS) is limited to this kind of objects. Not how they are inter related.
The problem to solve behind this are questions of:
- Any machine has limitations with performance.
❓ Consideration question: is it cheaper to place additional machines (* default action) or analysing performance issues by human experts.
- Confidentiality and Availability.
The data access has to be managed, backups and software upgrades (PAAS). All with planned outage times. Planning and coordination involved parties.
❓ Consideration question: is it cheaper to place additional machines (* default action) or manage additional complexity by human experts for machine support.
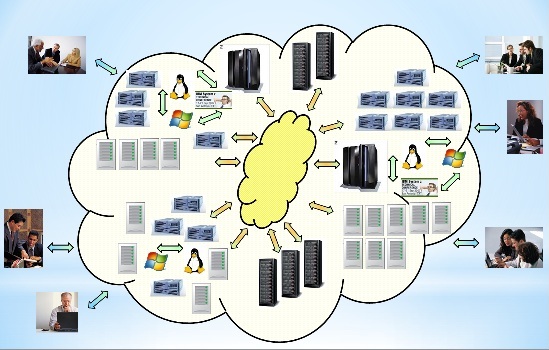
🤔 A bigger organisations has several departments. Expectations are that their work has interactions and there are some central parts.
Sales, Marketing, Production lines, bookkeeping, payments, accountancy.
🤔 Interactions with actions between all those departments are leading to complexity.
🤔 The number of machines and the differnces in stacks are growing fast. No matter where these logical machines are.
For every business service an own dedicated number of machines will increase complexity.
The information process flow has many interactions, inputs, tranformtions and outputs.
- ⚠ No relationsship machines - networking. The problem to solve that will popup at some point.
- ⚠ Issues by datatype conversions, integrity validation when using segragated sources (machines).
💡 Reinvention of a pattern. The physical logistic warehouse approach is well developed and working well. Why not copy that pattern to ICT? (EDWH 3.0)

What is delivered in a information process?
The mailing print processing is the oldest Front-end system using Back-end data. The moment of printing not being the same of the manufactured information.
Many more frontend deliveries have been created recent years. The domiant ones becoming webpages and apps on smartphones.
A change in attitude is needed bu still seeing it as a delivery needed the quality of infomration by the process.
Change data - Transformations
A data strategy helping the business should be the goal. Processing information as "documents" having detailed elements encapsulated.
Transport & Archiving aside producing it as holistic approach.

Logistics using containers.
The standard approach in information processing is focussing on the most detailed artefacts trying to build a holistic data model for all kind of relationships.
This is how goods were once transported as single items (pieces). That has changed into: containers having encapsulated good.
💡 Use of labelled information containers instead of working with detailed artefacts.
 💡
💡 Transport of containers is requiring some time. The required time is however predictable.
Trusting that the delivery is in time, the quality is conform expectations, is more efficiënt than trying to do everything in real time.

Informations containers have arrived almost ready for delivery having a more predictable moment for deliveriy to the customer.
💡 The expected dleivery notice is becoming standard in physical logistics. Why not doing the same in adminsitrative processes?

RH-1.5 Defining temporal boundaries dependencies
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
⟲ RH-1.5.1 Info
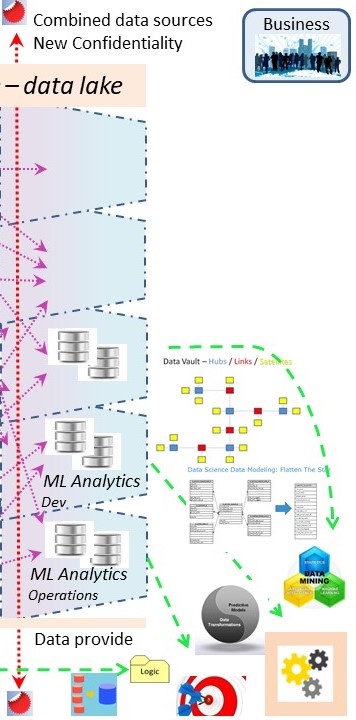
Applied Machine learning (AI), operations.
Analytics, Machine Learning, is changing the way of inventing rules to only human invented to helping humans with machines.
💡 The biggest change is the ALC type3 approach. This fundamentally changes the way how release management should be implemented.
ML is exchanging some roles in coding and data to achieve results at development but not in other life cycle stages.
When only a research is done for a report being made only once, the long waiting on data deliveries of the old DWH 2.0 methodology is acceptable.
⚠ Having a (near) real time operational process the data has to be correct when the impact on the scoring is important.
Using that approach, at least two data streams are needed:
- ML model Development: accept delays information delivery.
- ML exploitation (operations): No delay in deliveries.
🤔 The analytics AI ML machine learning has a duality in the logics definition.
The modelling stage (develop) is using data, that data is not the same, although similar, as in the operational stage.
Developing is done with operational production data. The sizing of this data can be much bigger than that of what is needed at operations due to the needed history.
The way of developping is ALC type3.
❗ The results of what an operational model is generating should be well monitored for many reasons. That is new information to process.
Some mismatches in a value stream.
Aside all direct questions from the organisation many external requirements are coming in.
A limited list to get en idea on regulations having impact on the adminsitrative information processing.
business flow & value stream.
Having a main value stream from left to right, the focus can be top down with the duality of processes - transformations and the product - information.
Complicating factor is that:
✅ Before external can be retrieved the agreement on wat is to retrieve must be on some level.
✅ Before the delivery can be fulfilled the request on what tot deliver must be there.
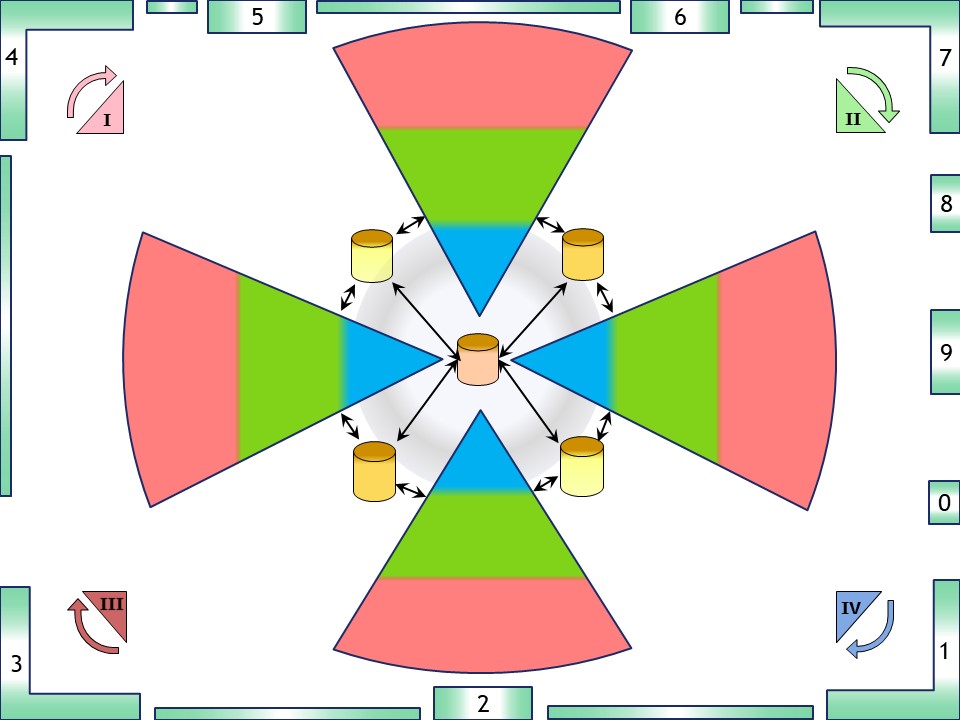
Having the same organisation, the focus can be bottom up with the layers in silos and separation of concerns.
Complicating factor is that:
❓ In the centre needed government information is not coming in by default. The request for that information is not reaching the operational floor.
😲 cooperation between the silos responsible for a part of the operating process are not exchanging needed information on the most easy way by default.
EDW development approach and presetation
BI DWH, datavirtualization.
Once upon a time there were big successes using BI and Analytics. The success were achieved by the good decisions, not best practices, made in those projects.
To copy those successes the best way would be understanding those decisions made. As a pity these decisions and why the were made are not published.
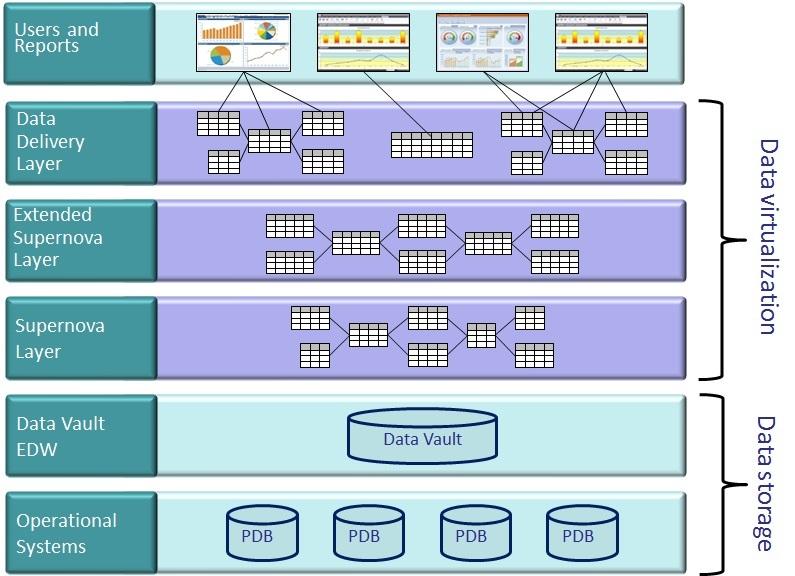
The focus for achieving success changed in using the same tools with those successes.
BI Business Intelligence has for long claiming being the owner of the E-DWH.
Typical in BI is almost all data is about periods. Adjusting data matching the differences in periods is possible in a standard way.
The data virtualization is build on top of the "data vault" DWH 2.0 dedicated build for BI reporting usage.
It is not virtualization on top of the ODS or original data sources (staging).
Presenting data using figures as BI.
The information for managers commonly is presented in easily understandable figures.
When used for giving satisfying messages or escalations for problems there is bias to prefer the satisfying ones over the ones alerting for possible problems.
😲 No testing and validation processes being necessary as nothing is operational just reporting to managers.
 💡
💡 The biggest change for a DWH 3.0 approach is the shared location of data information being used for the whole organisation, not only for BI.
The Dimensional modelling and the Data Vault for building up a dedicated storage as seen as the design pattern solving all issues.
OLap modelling and reporting on the production data for delivery new information for managers to overcome performance issues.
A more modern approach is using in memory analytics. In memory analytics is still needing a well designed data structure (preparation).
😱 Archiving historical records that may be retrieved is an option that should be regular operations not a DWH reporting solution.
The operations (value stream) process is sometimes needing information of historical records.
That business question is a solution for limitations in the operational systems. Those systems were never designed and realised with archiving and historical information.
⚠ Storing data in a DWH is having many possible ways. The standard RDBMS dogma has been augmented with a lot of other options.
Limitations: Technical implementations not well suited because the difference to an OLTP application system.
Reporting Controls (BI)
The understandable goal of BI reporting and analytics reporting is rather limited, that is:
📚 Informing management with figures,
🤔 so they can make up their mind on their actions - decisions.
The data explosion. The change is the ammount we are collecting measuring processes as new information (edge).
📚 Information questions.
⚙ measurements data figures.
🎭 What to do with new data?
⚖ legally & ethical acceptable?
Adding BI (DWH) to layers of enterprise concerns.
Having the three layers, separation of concern :
- operations , business values stream (red)
- documentation (green)
- part of the product describing it for longer period
- related to the product for temporary flow reasons
- control strategy (blue))
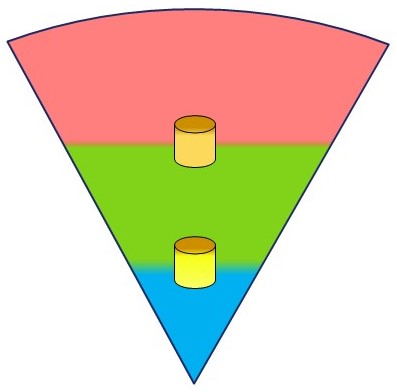
At the edges of those layers inside the hierarchical pyramid interesting information to collect for controlling & optimising the internal processes.
For strategic information control the interaction with the documentational layer is the first one being visible.
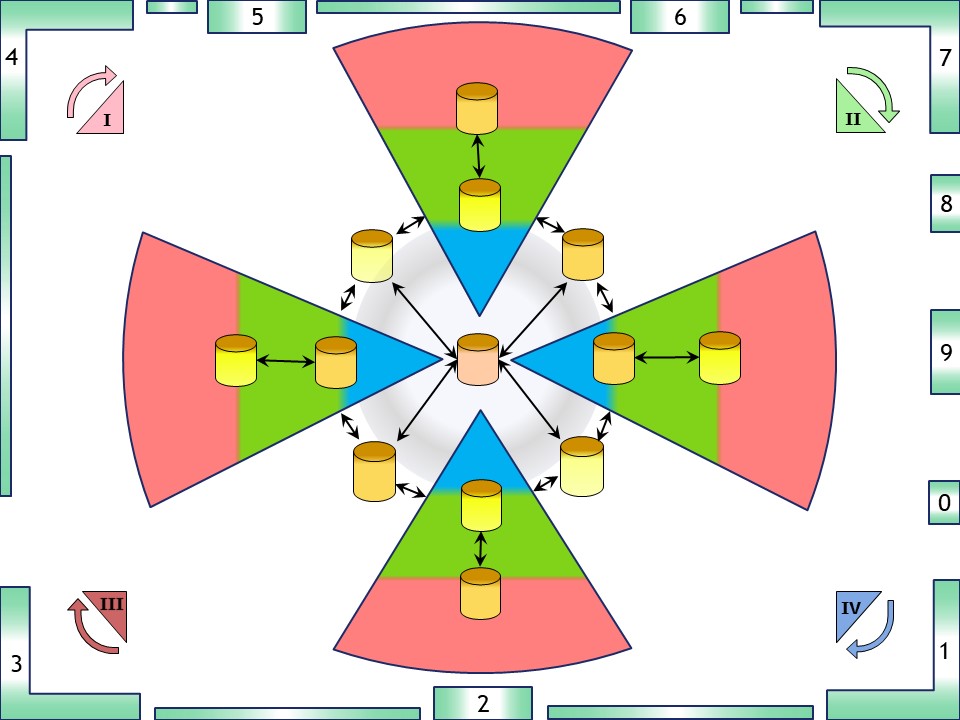
Having the four basic organisational lines that are assumed to cooperate as a single enterprise in the operational product value stream circle, there are gaps between those pyramids.
Controlling them at a higher level is using information the involved parties two by two, are in agreement. This is adding another four points of information.
Consolidating those four interactions point to one central point makes the total number of strategic information containers nine.
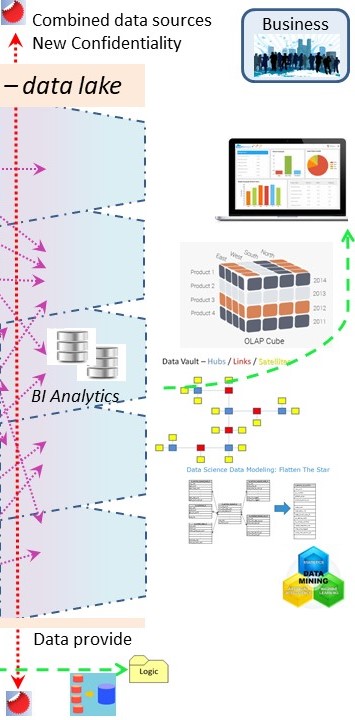
Classic DataWareHousing: EDWH 3.0 - Data Lake - Data Mesh
Processing objects, processing information goes along with responsibilities. There is an origin of the information and a consumer of combined information lines.
⚠ A data warehouse is at the moment siloed to reporting tasks. Reporting in dashboards and reports so managers are making up their mind with those reports as the "data".
Other usage for a data warehouse is seen as problematic when it used for operational informational questions may be involved with AI better Machine learning bypassing those managers as the decision makers.
❓
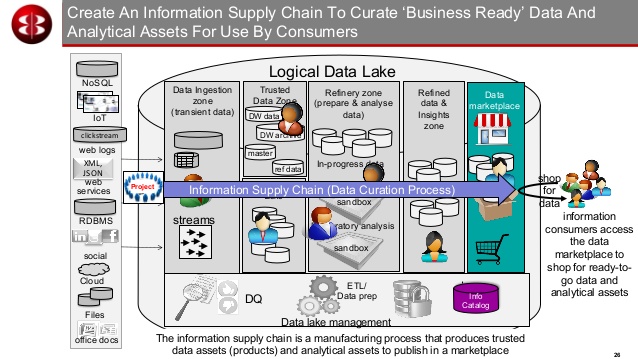
👓
DWH -data lake example (Slideshare: M.Ferguson LDN 2018)
- The technology question wat kind of DBMS should be uses in a monolithic system for management reporting is a strategy question asked.
- Data curation before being used in a monolithic system for management reporting is a strategy question asked.
- Historical information in this monolithic system for management reporting is a question.
- Connecting to analytical usage in an operational flow in this monolithic system for management reporting is a question. <

RH-1.6 Defining what is learned for systems maturity
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
⟲ RH-1.6.1 Attempts for defining maturity classifications
butics
Maturtity Level 1-5
A history of strategic alignment:
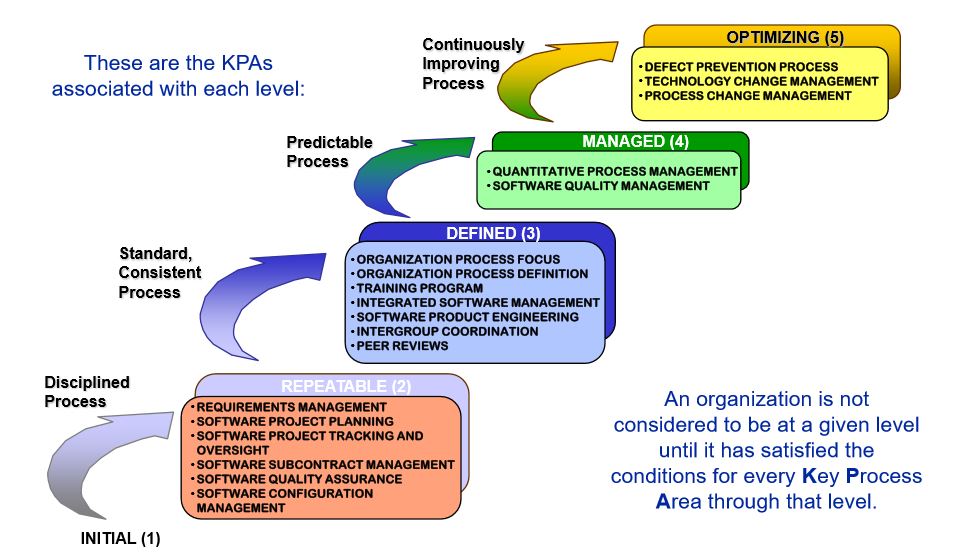
SAM Maturity (J.Luftman 2011)
Why -still- discuss IT-business alignment?
4. In search of mythical silver bullet
5. Focusing on infrastructure/architecture
7 Can we move from a descriptive vehicle to a prescriptive vehicle?
(see link with figure 👓)
💣 This CMM level is going on since 1990. Little progress in results are made. those can be explained by the document analyses and the listed numbers.
Going on the way to achieve the levels by fullfilling some action list as having done is a way to not achieve those goals. Cultural behanvior is very difficult to measure. Missing in IT is te C for communication: ICT.
⟲ RH-1.6.2 Info
⚠ ETL ELT - No Transformation.
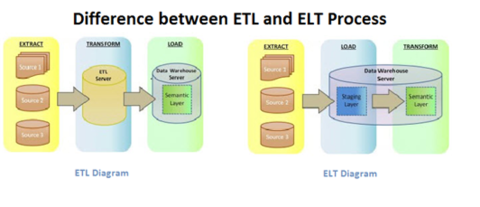
Classic is the processing order:
⌛ Extract, ⌛ Transform, ⌛ Load.
For segregation from the operational flow a technical copy is required.
Issues are:
- Every Transform is adding logic that can get very complicated. Unnecesary complexity is waste to be avoided.
- The technical copy involves conversions between technical systems when they are different. Also introduce integrity questions by synchronisation. Unnecesary copies are waste to be avoided.
- Transforming (manufacturing) data should be avoided, it is the data-consumer process that should do logic processing.
Translating the physical warehouse to ICT.
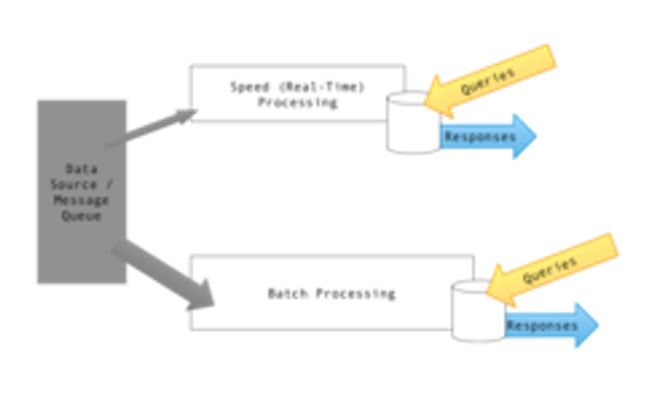
All kind of data (technical) should get support for all types of information (logical) at all kinds of speed.
Speed, streaming, is bypassing (duplications allowed) the store - batch for involved objects. Fast delivery (JIT Just In Time).
💣 The figure is what is called lambda architecture in data warehousing.
lambda architecture. (wikipedia).
With physical warehouses logistics this question for a different architecture is never heard of.
The warehouse is supposed to support the manufacturing process.
For some reason the data warehouse has got reserved for analytics and not supporting the manufacturing process.
The technical solutions as first process option.
Sometimes a simple paper note will do, sometimes an advanced new machine is needed.
It depends on the situation. A simple solution avoiding the waste is lean - agile
 Optimization Transactional Data.
Optimization Transactional Data.
An warehouse does not content structuring it must be able to locate the wanted content structured. Delivering the labelled containers efficient >
Optimization Transactional Data.
The way of processing information was in the old day using flat files in the physical way. Still very structured stored and labelled.
In the modern approach these techniques still are applicable although automated hidden in a RDBMS .
Analytics & reporting.
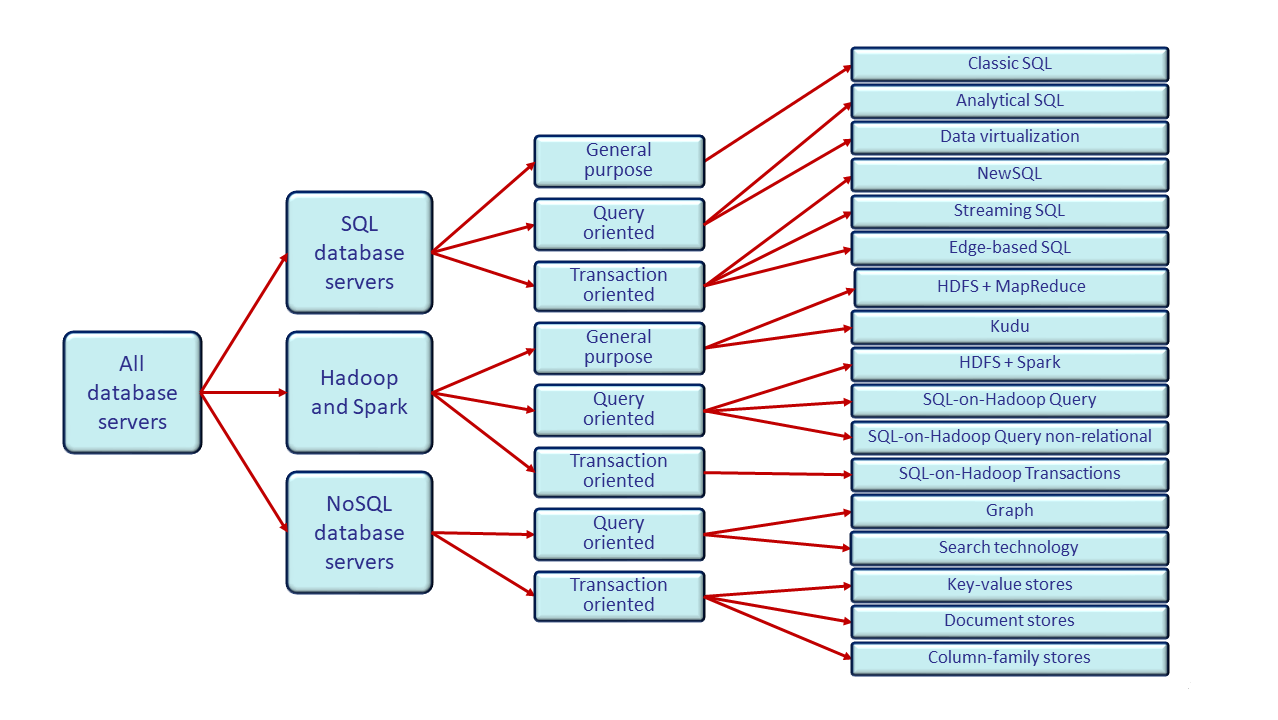
The "NO SQL" hype is a revival of choosing more applicable techniques.
It is avoiding the transactional RDBMS approach as the single possible technical solution.
Information process oriented, Process flow.
The information process in an internal flow has many interactions input, transformations and output in flows.
⚠ There is no relationship to machines and networking. The problem to solve those interactions will popup at some point.
⚠ Issues by conversions in datatypes, validations in integrity when using segregated sources (machines) will popup at some point.
The service bus (SOA).
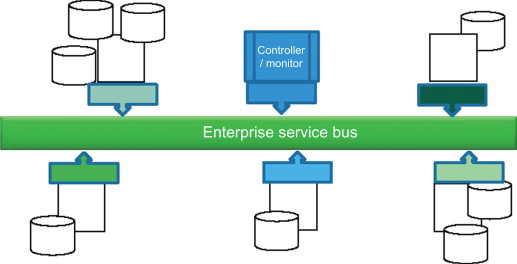
ESB enterprise service bus
The technical connection for business applications is preferable done by a an enterprise service bus.
The goal is normalized systems.
Changing replacing one system should not have any impact on others.
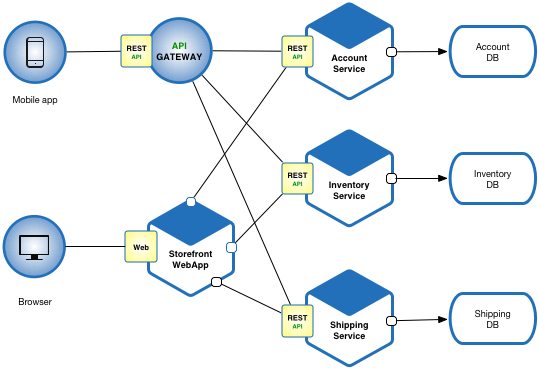
Microservices with api´s
Microservices (Chris Richardson):
Microservices - also known as the microservice architecture - is an architectural style that structures an application as a collection of services that are:
- Highly maintainable and testable.
- Loosely coupled.
- Independently deployable/
- Organized around business capabilities.
The microservice architecture enables the continuous delivery/deployment of large, complex applications. It also enables an organization to evolve its technology stack.
Data in containers.
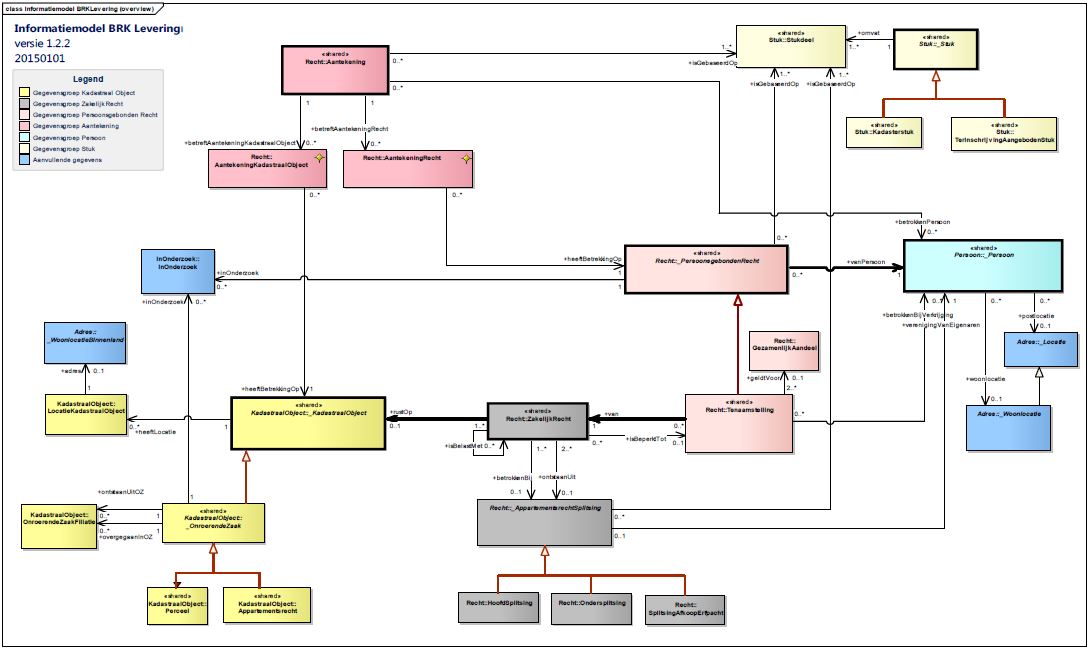
Data modelling using the relational or network concepts is based on basic elements (artefacts).
An information model can use more complex objects as artefacts. In the figure every object type has got different colours.
The information block is a single message describing complete states before and after a mutation of an object. The Life Cycle of a data object as new metainformation.
Any artefact in the message following that metadata information.
⚠ This is making a way to process a chained block of information. It is not following the blockchain axioma´s.
The real advantage of a chain of related information is detecting inter-relationships with the possible not logical or unintended effects.
Optimization OLTP processes.
The relational SQL DBMS replaced codasyl network databases (see math).
The goal is simplification of online transaction processing (oltp) data by deduplication and
normalization (techtarget)
using DBMS systems supporting ACID
ACID properties of transactions (IBM).
These approaches are necessary doing database updates with transactional systems. Using this type of DBMS for analytics (read-only) was not the intention.
normalization (techtarget, Margaret Rouse )
Database normalization is the process of organizing data into tables in such a way that the results of using the database are always unambiguous and as intended.
Such normalization is intrinsic to relational database theory.
It may have the effect of duplicating data within the database and often results in the creation of additional tables.
ACID properties of transactions (IBM)
- Atomicity
All changes to data are performed as if they are a single operation. That is, all the changes are performed, or none of them are.
For example, in an application that transfers funds from one account to another, the atomicity property ensures that, if a debit is made successfully from one account, the corresponding credit is made to the other account.
- Consistency
Data is in a consistent state when a transaction starts and when it ends.
For example, in an application that transfers funds from one account to another, the consistency property ensures that the total value of funds in both the accounts is the same at the start and end of each transaction.
- Isolation
The intermediate state of a transaction is invisible to other transactions. As a result, transactions that run concurrently appear to be serialized.
For example, in an application that transfers funds from one account to another, the isolation property ensures that another transaction sees the transferred funds in one account or the other, but not in both, nor in neither.
- Durability
After a transaction successfully completes, changes to data persist and are not undone, even in the event of a system failure.
For example, in an application that transfers funds from one account to another, the durability property ensures that the changes made to each account will not be reversed.
⟲ RH-1.6.3 Info
⟲ RH-1.6.4 Info
RH-2 Anchorpoints of technological details at realisations
RH-2.1 Using standard patterns for component in lines
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
⟲ RH-2.1.1 Info
Administrative Value Stream Mapping Symbol Patterns.
Help in abstracting ideas is not by long text but using symbols and figures.
A blueprint is the old name for doing a design before realisation.
- Value stream mapping has symbols to help in abstracting ideas.
- Structured Program, coding, has the well known flow symbols.
- Demo has a very detailed structure on interactions with symbols.
What is missing is something in between that is helping in the value stream of administrative processing.
Input processing:
 Retrieve multiple well defined resources.
Retrieve multiple well defined resources.
Transform into a data model around a subject.
The result is similar to a star model. The differenes are that is lacking some integrity and constraint definitions.  Retrieve a data model around a subject.
Retrieve a data model around a subject.
Transform this in a denormalised one with possible logical adjustments.
Moving to in memory processing for analytics & reporting, denormalisation is the way to achieve workable solutions.  Retrieve multiple unstructured resources.
Retrieve multiple unstructured resources.
Transform (transpose) into multiple well defined resource.
A well defined resource is one that can be represented in rows columns. The columns are identifiers for similar logical information in some context.
Execute Business Logic (score):
 Retrieve a data model around a subject.
Retrieve a data model around a subject.
Execute business logic generating some result.
This type of processing is well known for RDBMS applications. The denormalisation is done by the application.  Retrieve denormalised data for subject.
Retrieve denormalised data for subject.
Execute business logic generating some result.
Moving to in memory processing for analytics & reporting, denormalisation is the way to achieve workable solutions.  Retrieve historical results (business) what has been previous scored. Execute business logic generating some result.
Retrieve historical results (business) what has been previous scored. Execute business logic generating some result.
The is monitoring block generates a log-file (technical), historical results (business) and does a halt of the flow when something is wrong.
Logging: / Monitoring:
-
 Retrieve a data model around a subject. Apply businsess rules for assumed validity.
Retrieve a data model around a subject. Apply businsess rules for assumed validity.
This logging block generates a log-file. The period is limited, only technicial capacity with possible restarts to show.
Does a line-halt of the flow when something is wrong.
-
 Retrieve a result from an executed business logic process. Apply businsess rules for assumed validity.
Retrieve a result from an executed business logic process. Apply businsess rules for assumed validity.
This monitoring block generates a log-file (technical), historical results (business).
Does a line-halt of the flow when something is wrong.
Output, delivery:
-
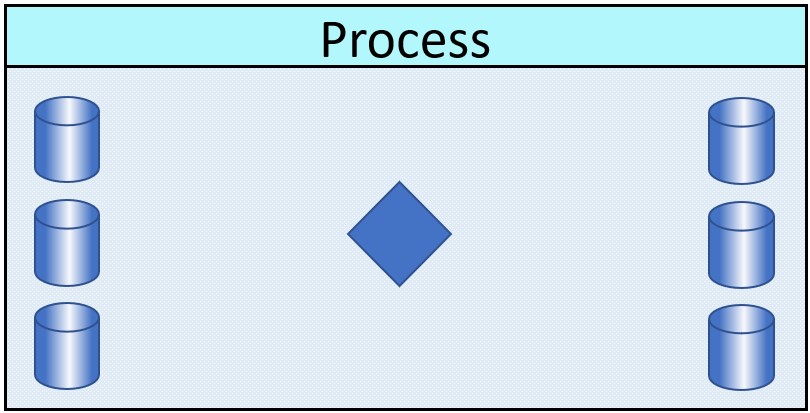 From a weel defined resource, propagate to, from this processing context, external one.
From a weel defined resource, propagate to, from this processing context, external one.
A logical switch is included with the goal of preventing sending out information when that is not applicable for some reason.
RH-2.2 Performance of the processing for flow
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
⟲ RH-2.2.1 Info
Archiving, Retention policies.
Information is not only active operational but also historical what has happened, who has execute, what was delivered, when was the delivery when was the purchase etc.
That kind of information is often very valuable but at the same time it is not well clear how to organize that and who is responsible.
💣 Retention policies, archiving information is important do it well, the financial and legal advantages are not that obvious visible. Only when problems are escalating to high levels it is clear but too late to solve.
When being in some financial troubles, cost cutting is easily done.
Historical and scientific purposes, moved out off any organisational process.
An archive is an accumulation of historical records in any media or the physical facility in which they are located.
Archives contain primary source documents that have accumulated over the course of an individual or organization's lifetime, and are kept to show the function of that person or organization.
Professional archivists and historians generally understand archives to be records that have been naturally and necessarily generated as a product of regular legal, commercial, administrative, or social activities.
The word record and word document is having a slightly different meaning in this context than technical ICT staff is used to.
In general, archives consist of records that have been selected for permanent or long-term preservation on grounds of their enduring cultural, historical, or evidentiary value.
Archival records are normally unpublished and almost always unique, unlike books or magazines of which many identical copies may exist.
This means that archives are quite distinct from libraries with regard to their functions and organization, although archival collections can often be found within library buildings.
Additional information container attributes.
😉 EDW 3.0 Every information container must be fully identifiable. Minimal by:
- a logical context key
- moment of relevance
- moment received, available at the ware house
- source received information container.
When there are compliancy questions on information with this kind of compliancy questions it is often assumed to be an ICT problem only. Classic applications are lacking thes kind of attributes with information.
 💡
💡 Additional information container attributes supporting implementations defined retention policies.
Every information container must have for applicable retention references :
- Normal operational visibility moments:
- registered in the system
- information validity start
- information validity end
- registration in system to end
- Legal change relevance:
- legal case registered in system started
- registration for legal case in system to end
- Internal extended archive for purposes:
- registration for archiving purposes in system to end
Common issues when working for retention periods.
⚠ An isolated archive system in complexity reliability and availability being a big hurdle, high impact.
⚠ Relevant information for legal purposes, moved out from manufacturing process and not being available anymore in legal cases, is problematic.
⚠ Impact by cleaning as soon as possible is having high impact. The GDPR states it should be deleted as soon as possible.
This law is getting much attention and is having regulators. Archiving information for longer periods is not directly covered by laws, only indirect.
Government Information Retention.
Instead of a fight how it should be solved there is a fight somebody else is to blame for missing information.

Different responsible parties have their own opinion how conflict in retention policies should get solved.
🤔 Having information deleted permanent there is no way to recover when that decision is wrong.
🤔 The expectation it would be cheaper and having better quality is a promise without warrrants.
RH-2.3 Tradeoffs in achieving functionality vs safety
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
⟲ RH-2.3.1 Info
Change data - Transformations
Seeing the values stream within an administrative product is a different starting point for completely new approaches.
The starting point is redesigning what is not working well. Not automatically keeping things doing as always have been done. Also not changing things because of wanting to change something.
Design thinking.
It is a common misconception that design thinking is new. Design has been practiced for ages: monuments, bridges, automobiles, subway systems are all end-products of design processes.
Throughout history, good designers have applied a human-centric creative process to build meaningful and effective solutions.
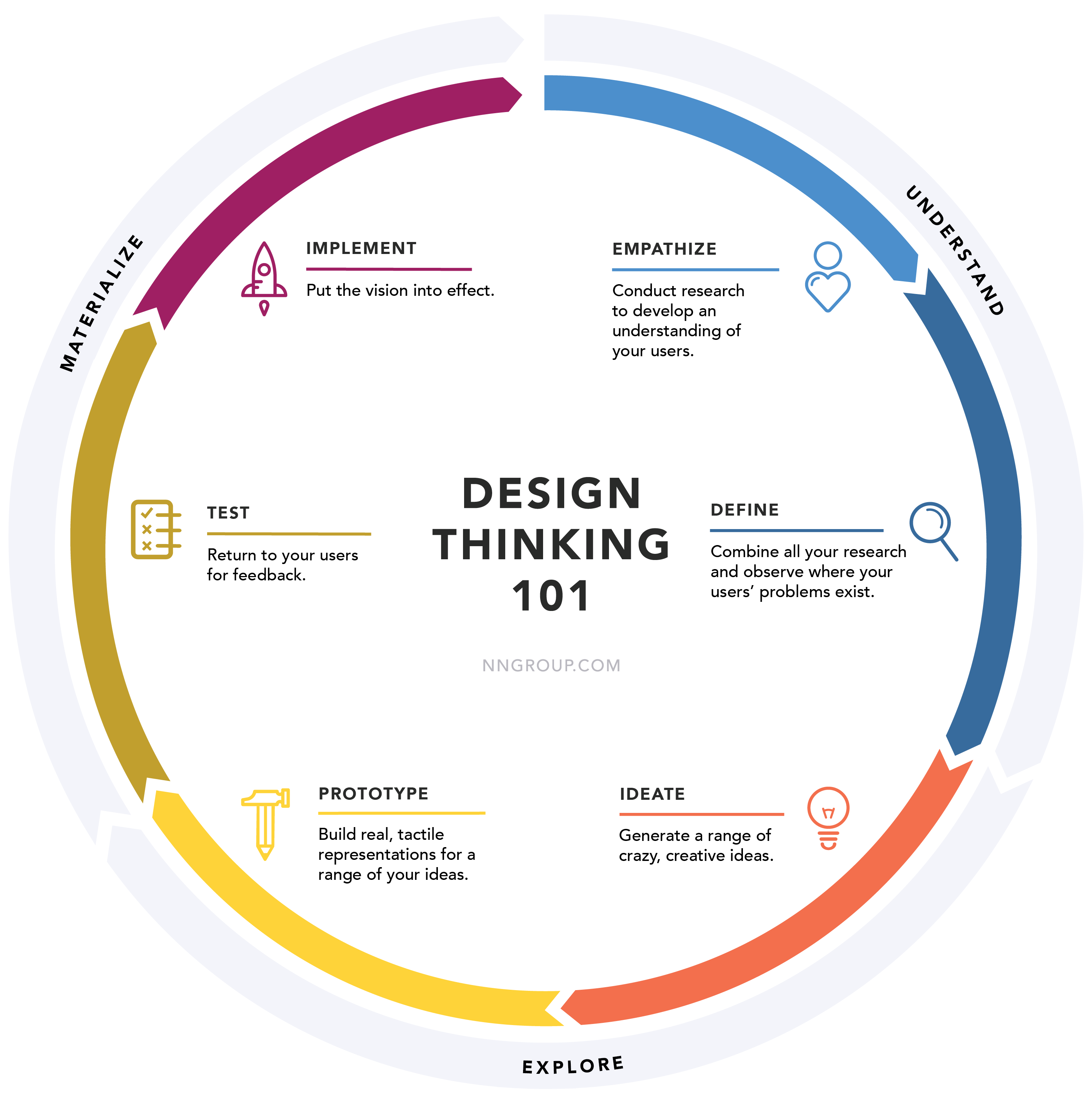
The design thinking ideology is following several steps.
Defintion: The design thinking ideology asserts that a hands-on, user-centric approach to problem solving can lead to innovation, and innovation can lead to differentiation and a competitive advantage.
This hands-on, user-centric approach is defined by the design thinking process and comprises 6 distinct phases, as defined and illustrated below.
See link at figure 👓.
Those six phases are in line with what the crisp-dm model states. Wat is missing when comparing this with the PDCA cycle is the Check- Verify of it works as expected after implementation.
💡 Logistics of the EDWH - Data Lake. EDWH 3.0
As the goal of BI Analytics was delivering reports to managers, securing informations and runtime performance was not relevant.
⚠ Securing information is too often an omission.
Transforming data should be avoided.
The data-consumer process should do the logic processing.
Offloading data, doing the logic in Cobol before loading, is an ancient one to be abandoned.
Processing objects, information goes along with responsibilities.
❗ A data warehouse is allowed to receive semi-finished product for the business process.
✅ A data warehouse is knowing who is responsible for the inventory being serviced.
❗ A data warehouse has processes in place for deleivering and receiving verified inventory.
In a picture:
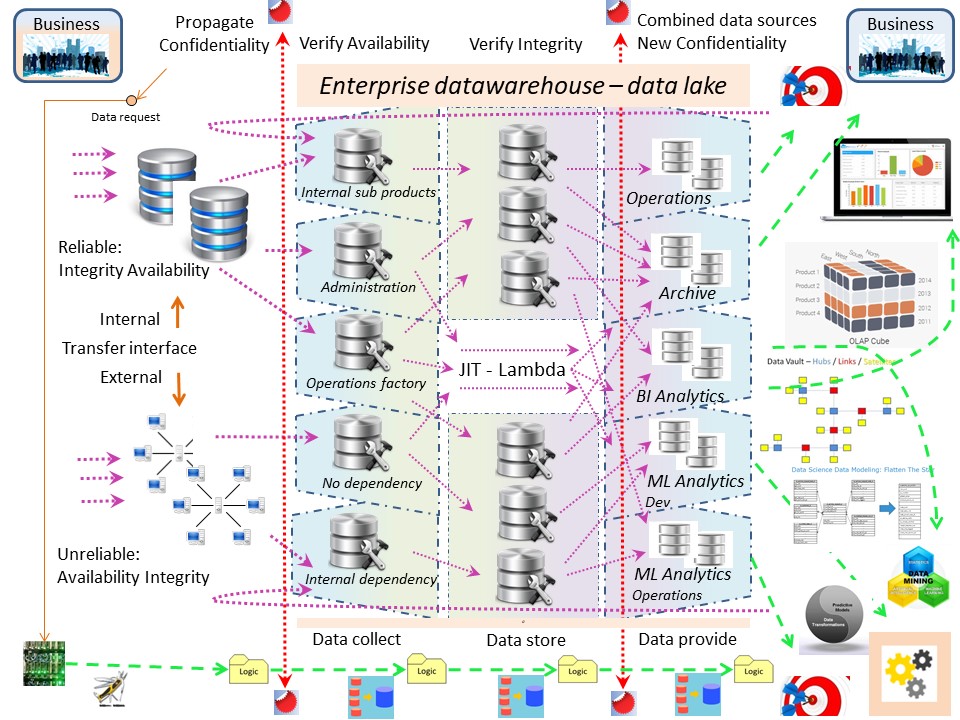
The two vertical lines are managing who´s has access to what kind of data, authorized by data owner, registered data consumers, monitored and controlled.
The confidentiality and integrity steps are not bypassed with JIT (lambda).
CIA Confidentiality Integrity Availability. Activities.
- Confidentiality check at collect.
- Integrity verified before stored.
- Availability - on stock, in store.
- Availability - "just in time".
- Confidentiality at delivery.
- Integrity at delivery.
CSD Collect, Store, Deliver. Actions on objects.
- Collecting, check confidentiality.
- Storing, verify Integrity before.
- Stored, mark Availability.
- Collect JIT, mark Availability.
- Deliver check Confidentiality.
- Deliver verify Integrity.
There is no good reason to do this also for the data warehouse when positioned as a generic business service. (EDWH 3.0)
Focus on the collect - receive side.
There are many different options how to receive information, data processing. Multiple sources of data - Multiple types of information.
- ⚒ Some parties are reliable predictable available.
With internal systems this is usual.
- Internal Sub products
- Administration (not possible as physical)
- Operational factory chain
- ⚒ Other parties are less reliable, predictable having less availability.
With external systems this is usual.
- No dependency
- Internal dependency, prescriptions outsourced subtask
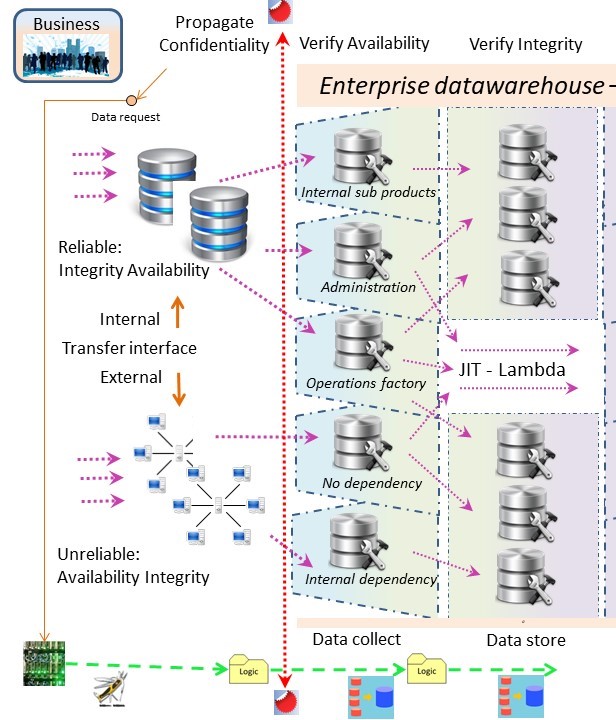
In a picture:
A data warehouse should be the decoupling point of incoming and outgoing information.
A data warehouse should validate verify the delivery on what is promised to be there.
Just the promise according to the registration by administration, not the quality of the content (different responsibility).
Focus on the ready - deliver side.
A classification by consumption type:
- ⚒ Operations For goals where standard systems are not appropriate or acting as an interface for not coupled systems. 💰 Results are input for other data consumers. Sensitive data allowed (PIA).
- ⚒ Archive of data - information not anymore available in operations, only for limited goals and associated with a retention period. ⚖
- ⚒ Business Intelligence (reporting). Developing and generating reports for decision makers. Possible as usage of analytical tools with DNF. ✅ Sensitive data is eliminated as much is possible.
- ⚒ Analytics Developing Machine Learning. ❗ This is: ALC type3. Sensitive data is eliminated as much is possible.
- ⚒ Analytics, Operations Machine Learning. ❗ This is: ALC type3. Sensitive data may be used controlled (PIA). Results are input for other data consumers.
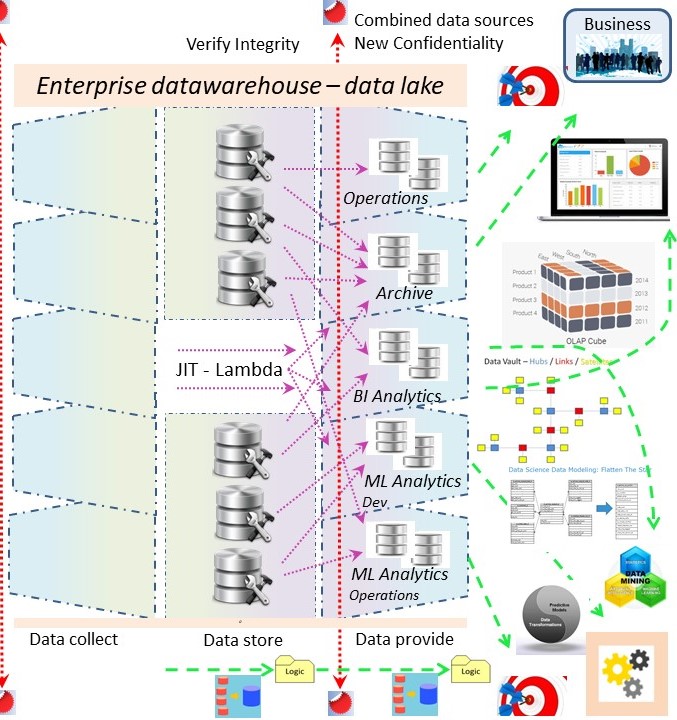
In a picture:
There are possible many data consumers.
It is all about "operational" production data" - production information.
Some business applications only are possible using the production information.
RHL-2.4 Understanding taxonomies - concepts - ontology
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
⟲ RH-2.4.1 Info
Administrative proposed standard pattern.
📚 The process split up in four stages of prepare request (IV, III) and the
delivery (I, II). The warehouse as starting point (inbound) and end point (outbound).
The request with all necessary preparations and validations going through IV and III.
The delivery with all necessary quality checks going through I and II.
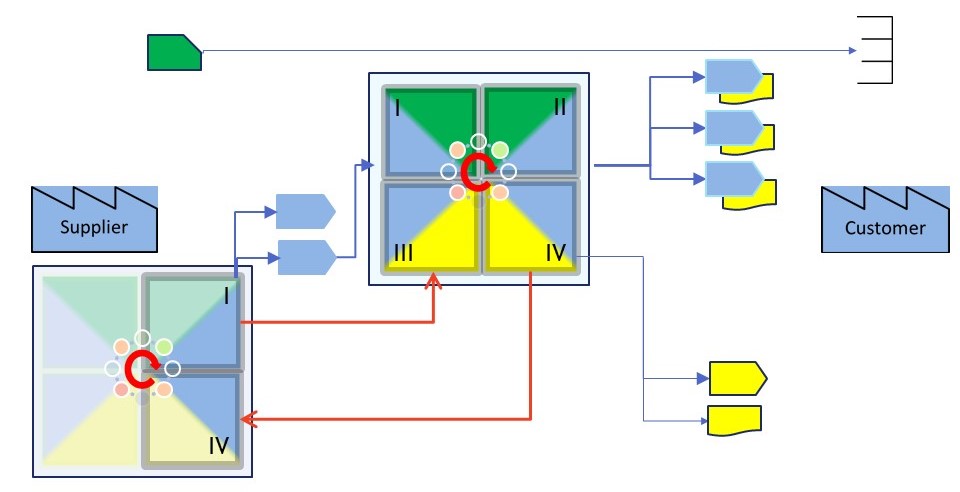
SDLC life cycle steps - logging , monitoring.
Going back to the sdlc product life, alc model type 3. This is a possible implementation of the manufacturing I, II phases.
💡 There are four lines of artefacts collections at releases what will become the different production versions.
- collecting input sources into a combined data model.
- modifying the combined data model into a new one suited for the application (model).
- running the application (model) on the adjusted suited data creating new information, results.
- Delivering verified results to an agreed destinationt in an agreed format.
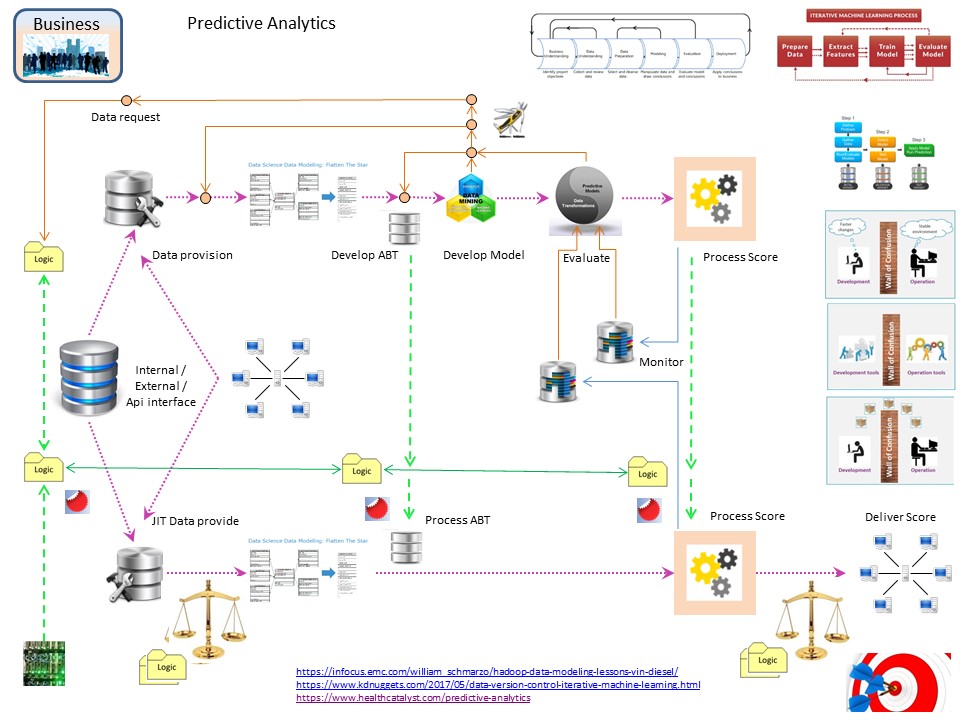
💡 There are two points that are validating the state en create additional logging. This is new information.
- After having collected the input sources, technical and logical verfication on what has is there is done.
- Before delviering the results technical and logical verfication on what is there is done.
This is logic having business rules. The goal is application logging and monitoring in business perspective.
When something is badly wrong, than halting the process flow is safety mitigation preventing more damage.
There is no way to solve this by technical logfiles generated by tools like a RDBMS.
💡 The results ar collected archived (business dedicated). This is new information.
- After having created the result, but before delivering.
- It usefull for auditing purpused (what has happended) and for predcitive modelling (ML) .
RH-2.5 Understanding temporal boundaries dependencies
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
⟲ RH-2.5.1 Info
butics
⟲ RH-2.5.2 Info
butics
⟲ RH-2.5.3 Info
butics
⟲ RH-2.5.4 Info
butics
RH-2.6 Understanding for what drives systems maturity
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
⟲ RH-2.6.1 Info
butics
⟲ RH-2.6.2 Info
butics
⟲ RH-2.6.3 Info
butics
⟲ RH-2.6.4 Info
butics
RH-3 Impacts consequences of technological details at realisations

RH-3.1 Data, gathering information on processes.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
⟲ RH-3.1.1 Info
butics

RH-3.2 Enterprise engineering, valuable processing flows.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
⟲ RH-3.2.1 Info
butics

RH-3.3 Information - data - avoiding process fluctuations.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .

⟲ RH-3.3.1 Info
butics

RH-3.4 Edwh 3.0 - Data: collect - store - deliver.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
⟲ RH-3.4.1 Info
butics

RH-3.5 Patterns by changing context, changing technology.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .

⟲ RH-3.5.1 Info
butics

RH-3.6 Change data - Transformations
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .

⟲ RH-3.6.1 Info
butics
© 2012,2020,2026J.A.Karman


 When the image link fails, 🔰 click here.
When the image link fails, 🔰 click here. 








 📚 Information questions.
📚 Information questions.  The demand side focus for some supply is a solution for the supposed mismatch business & ICT. The approach for that mismatch is an external supplier.
The demand side focus for some supply is a solution for the supposed mismatch business & ICT. The approach for that mismatch is an external supplier.

 💡 Solving gaps between silos supporting the values stream.
Those are the rectangular positioned containers connecting between the red/green layers. (total eight internal - intermediates)
💡 Solving gaps between silos supporting the values stream.
Those are the rectangular positioned containers connecting between the red/green layers. (total eight internal - intermediates) 
 The first containerships where these liberty ships. Fast and cheap to build. The high loss rate not an problem but solved by building many of those.
They were build as project shops but at many locations. The advantage of a known design to build over and over again.
The first containerships where these liberty ships. Fast and cheap to build. The high loss rate not an problem but solved by building many of those.
They were build as project shops but at many locations. The advantage of a known design to build over and over again.  project shop.
project shop.  🤔 A bigger organisations has several departments. Expectations are that their work has interactions and there are some central parts.
🤔 A bigger organisations has several departments. Expectations are that their work has interactions and there are some central parts. 
 Logistics using containers.
Logistics using containers.  💡 Transport of containers is requiring some time. The required time is however predictable.
Trusting that the delivery is in time, the quality is conform expectations, is more efficiënt than trying to do everything in real time.
💡 Transport of containers is requiring some time. The required time is however predictable.
Trusting that the delivery is in time, the quality is conform expectations, is more efficiënt than trying to do everything in real time.  Informations containers have arrived almost ready for delivery having a more predictable moment for deliveriy to the customer.
Informations containers have arrived almost ready for delivery having a more predictable moment for deliveriy to the customer. 

 Having a main value stream from left to right, the focus can be top down with the duality of processes - transformations and the product - information.
Having a main value stream from left to right, the focus can be top down with the duality of processes - transformations and the product - information. Having the same organisation, the focus can be bottom up with the layers in silos and separation of concerns.
Having the same organisation, the focus can be bottom up with the layers in silos and separation of concerns. The focus for achieving success changed in using the same tools with those successes.
The focus for achieving success changed in using the same tools with those successes.  Presenting data using figures as BI.
Presenting data using figures as BI.  💡 The biggest change for a DWH 3.0 approach is the shared location of data information being used for the whole organisation, not only for BI.
💡 The biggest change for a DWH 3.0 approach is the shared location of data information being used for the whole organisation, not only for BI. 
 Having the four basic organisational lines that are assumed to cooperate as a single enterprise in the operational product value stream circle, there are gaps between those pyramids.
Having the four basic organisational lines that are assumed to cooperate as a single enterprise in the operational product value stream circle, there are gaps between those pyramids. 

 SAM Maturity (J.Luftman 2011)
SAM Maturity (J.Luftman 2011)
 Classic is the processing order:
Classic is the processing order:  All kind of data (technical) should get support for all types of information (logical) at all kinds of speed.
Speed, streaming, is bypassing (duplications allowed) the store - batch for involved objects. Fast delivery (JIT Just In Time).
All kind of data (technical) should get support for all types of information (logical) at all kinds of speed.
Speed, streaming, is bypassing (duplications allowed) the store - batch for involved objects. Fast delivery (JIT Just In Time).  Optimization Transactional Data.
An warehouse does not content structuring it must be able to locate the wanted content structured. Delivering the labelled containers efficient >
Optimization Transactional Data.
An warehouse does not content structuring it must be able to locate the wanted content structured. Delivering the labelled containers efficient > 
 ESB enterprise service bus
The technical connection for business applications is preferable done by a an enterprise service bus.
The goal is normalized systems.
ESB enterprise service bus
The technical connection for business applications is preferable done by a an enterprise service bus.
The goal is normalized systems. 
 Data modelling using the relational or network concepts is based on basic elements (artefacts).
Data modelling using the relational or network concepts is based on basic elements (artefacts). 
 Retrieve multiple well defined resources.
Retrieve multiple well defined resources.  Retrieve a data model around a subject.
Retrieve a data model around a subject.  Retrieve multiple unstructured resources.
Retrieve multiple unstructured resources.  Retrieve a data model around a subject.
Retrieve a data model around a subject.  Retrieve denormalised data for subject.
Retrieve denormalised data for subject.  Retrieve historical results (business) what has been previous scored. Execute business logic generating some result.
Retrieve historical results (business) what has been previous scored. Execute business logic generating some result.  Retrieve a data model around a subject. Apply businsess rules for assumed validity.
Retrieve a data model around a subject. Apply businsess rules for assumed validity.  Retrieve a result from an executed business logic process. Apply businsess rules for assumed validity.
Retrieve a result from an executed business logic process. Apply businsess rules for assumed validity.  From a weel defined resource, propagate to, from this processing context, external one.
From a weel defined resource, propagate to, from this processing context, external one.  💡 Additional information container attributes supporting implementations defined retention policies.
Every information container must have for applicable retention references :
💡 Additional information container attributes supporting implementations defined retention policies.
Every information container must have for applicable retention references :

 Different responsible parties have their own opinion how conflict in retention policies should get solved.
Different responsible parties have their own opinion how conflict in retention policies should get solved.  The design thinking ideology is following several steps.
The design thinking ideology is following several steps.  The two vertical lines are managing who´s has access to what kind of data, authorized by data owner, registered data consumers, monitored and controlled.
The two vertical lines are managing who´s has access to what kind of data, authorized by data owner, registered data consumers, monitored and controlled.  In a picture:
In a picture: In a picture:
In a picture:
 💡 There are two points that are validating the state en create additional logging. This is new information.
💡 There are two points that are validating the state en create additional logging. This is new information.








