Plots are the backbone of any story they provide the “why” of what happens.
Narratives tell “how” what happened is being told.
In principle, plots deal with possibilities and narratives with realizations.
In fact plots remain unknown until being narrated; in other words fictions are like Schrödinger's cat: there is no way to set possibilities and realizations apart.
There is strong relationship between two approaches that can't exist without the other.
They are complementary properties of an artifact in time.
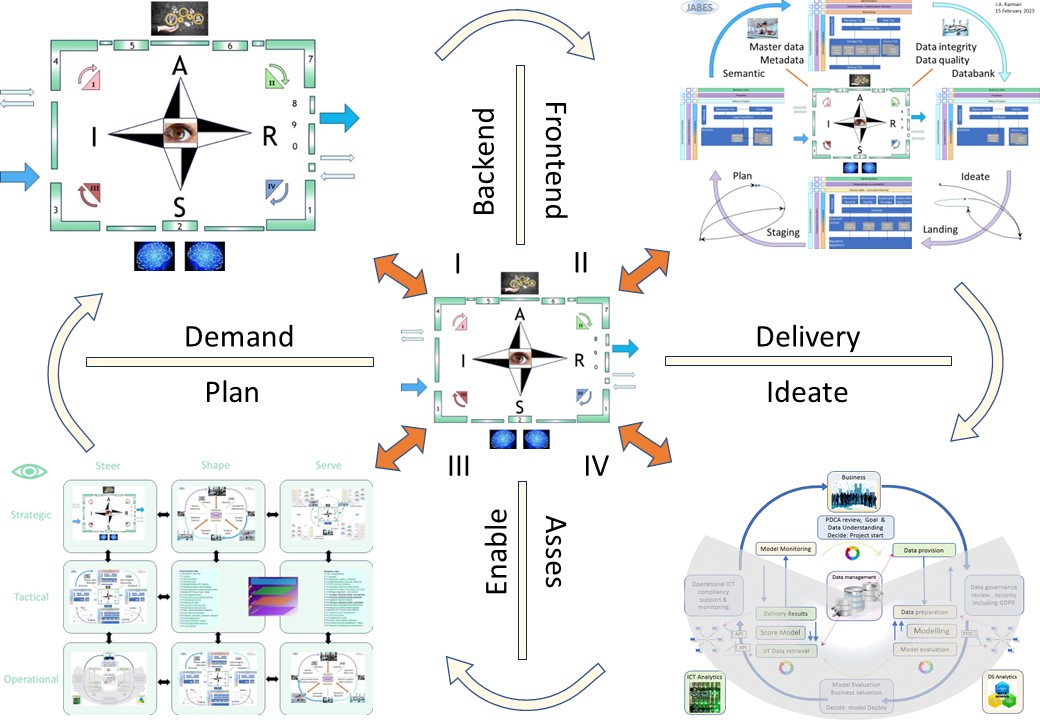
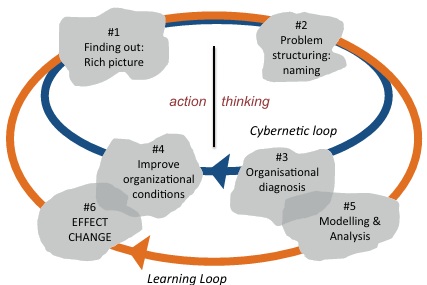
How to visualise this ying-yang relationship? There is an information flow for business processes.
Information classification is the process of organizing information into categories that make it easy to retrieve, sort and store for future use.
A well-planned information classification system makes essential data easy to find and retrieve.
This can be of particular importance for risk management, legal discovery and regulatory compliance.
From the process block of the flow chart only having I (input) and O (output Result) an change improvement.
Adding the Control and measurement (analyse or asses) lines.
This in line with Data-Mesh, that is adding the BI analytics management information in an analytical plan and experience area.
The SIAR model (see figure) is highly abstracted generalized.
I started it because the many models that are used seperately are missing to align the concepts and ideas as a whole.
There are many other contexts aside information processing in a similar way.
Only the details for the activities and flows are different.
For example:
Financials, Governments are heavily relying on information processing.
Facilities, Industrials are having an important administration component and needing information processing for optimizing.
| Classification | Description |
| The value stream | Premature negotiations (blue double arrows), main flow Left to Right |
| A cyclic process | Segregation in quadrants (2*2), and 3*3 partitions |
Control from strategy,
by tactical, to operational | From the eye in the middle to every compass direction.
Origin BI management information flow. |
| Information process duality | Interactions change intermediates in between every compass direction. |
Well known frameworks are embedded:
| What | Where in the SIAR figure |
| Pull | IV (R-S) Control a new Request for processing
III (S-I) Plan new Request, check for inventory and processing capacity. |
| Push | I (I-A) Assemble input to a new product
II (A-R) Verify quality of the new product and prepare for delivery result |
| PDCA | Follow: III Plan, I Do, II Check, IV Asses Act |
| DMAIC | Follow: II Define, I Measure, III Analyze, IV Ideate Improve |
| product | Follow flow: 0,1(request),2(split),3,4,5(assembly),6,7(validate),8(validate),9(result) |
❻ The PDCA DMAIC and OODA perspectives are included and as aid for using it in searching the direction.
❼ The change improvement, innovation itself is possible by several maturity stages.
| C&C Maturity | Wow Steer / Manage | WoW supply chain | WoW product - assembly | WoW demand / delivery |
| Reactive for what is going on in the now | Measurabele
processes | Practices
efficient | Instructions
Effective | Service
valuable |
| Pro-active for what is soon expected for the now | Control
processes | Practices
collect | Instrcutions
Execution | Services
evaluation |
| Pro-active for what is seen by a vision for the future | Control
governance | Ideation
collect | Operations
Execution | Validation
evaluation |
The PDCA and DMAIC are cycles starting at a different point in the cylce.
They are also found in the diagonal contexts.
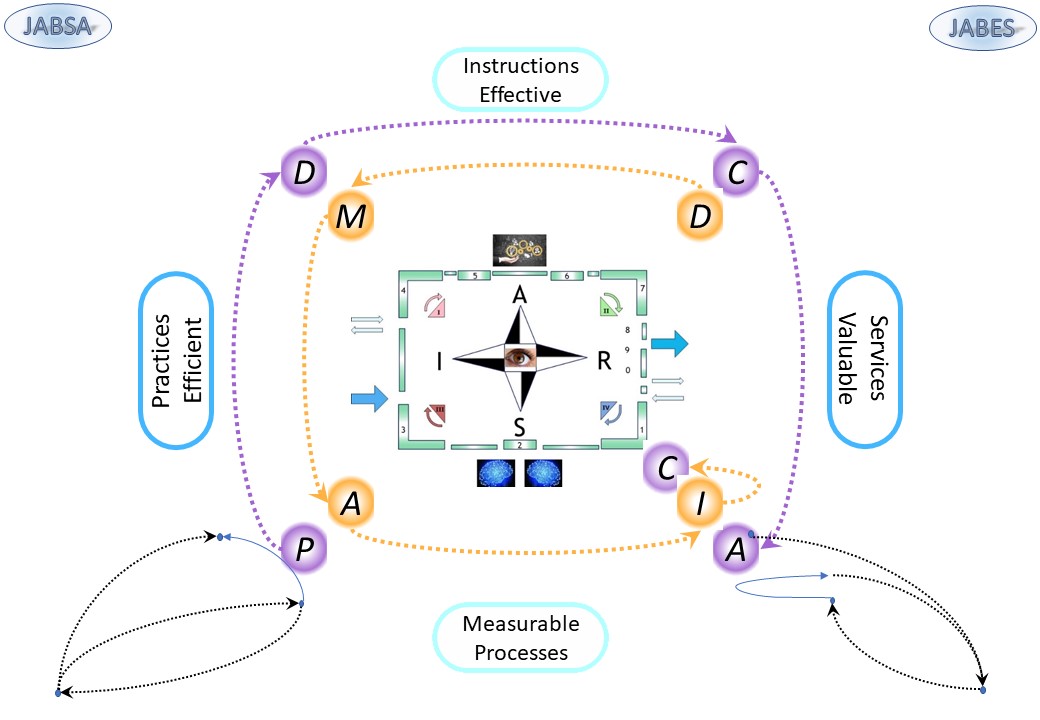
in a figure:
See right side.
⚖ E-2.1.2 Way of working: flow interactions
Foundation in methodologies
❽ Shu-Ha-Ri
It is a way of thinking about how to learn and master a technique. There are 3 stages to acquiring knowledge:
- Shu: learn the basics by following the teaching of one master. Imitating the work of great masters also falls in this stage.
- Ha: start experimenting, learn from masters, and integrate the learning into the practice.
- Ri: This stage focuses on innovation and adapting the learning to different situations.
“When the student is ready the teacher will appear. When the student is truly ready… The teacher will Disappear.” ― Tao Te Ching
PDCA, DMAIC, OODA informed actions changes
Processing information using ICT is assembling parts of information into new information products.
Aligning this approach to what has become lean processing at industry.
This will break a lot "doing what has always been done" with ICT approaches.
❾ Essential:
PDCA
Plan-Do-Check-Act is one of the key elements in lean manufacturing, or for that matter in any kind of improvement process.
Another: Dmaic a PDCA variant?
PDCA variants
This DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve Control) is a PDCA offshoot in the Six Sigma offshoot of lean manufacturing. While it has more words, the meaning is somewhat similar.
For this I don´t agree. Using PDCA in the flow of the production and DMAIC doing that backwards, determining what issues there are in the operational environment, makes more sense.
Problem solving
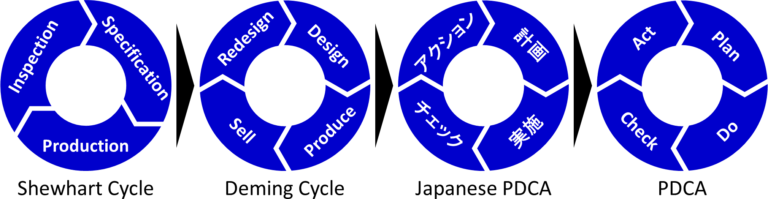
in a figure:
See right side.
Push Pull - Value Stream
The (True) Difference Between Push and Pull
But what exactly is the difference between push and pull? Also, what makes pull systems so superior to push systems?
❿ All About Pull Production.
The figure "Elements of the Kanban Formula" is counter clockwise. Flipping top and bottom will give a clockwise order.
Customer demand is a Request & Result.
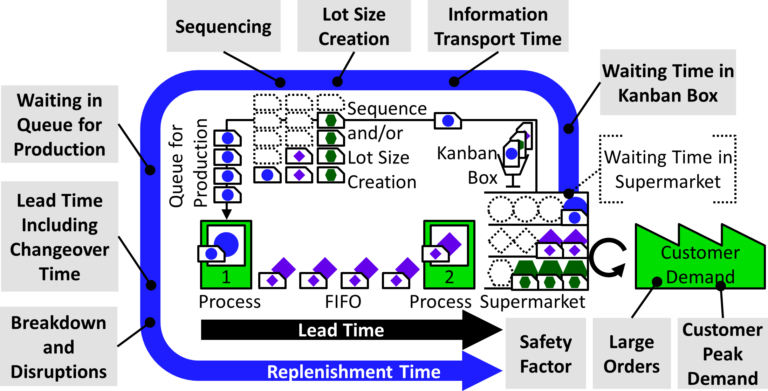
in a figure:
See right side.
The context of the audience: specialists vor value stream, lean.
⚖ E-2.1.3 Goals alignment: Architecting processes flows
Going from individuals to organisations
A person, individual is limited in what he can achieve.
By collaboration with other much more is possible.
Human society is based on groups of humans.
Their interactions are indispensable for alignment in intentions.
Organisations are using systems alignment
Alignment is realised by using methodologies.
Methodologies are parts of the culture and culture is hard to change.
Evolution in methodologies
Organisations are build with humans as components, we should understand their behaviour with limitations and opportunities when going for the whole.
Anthropology
Systems theory in anthropology is an interdisciplinary, non-representative, non-referential, and non-Cartesian approach that brings together natural and social sciences to understand society in its complexity.
The basic idea of a system theory in social science is to solve the classical problem of duality; mind-body, subject-object, form-content, signifier-signified, and structure-agency.
interactions can adapt to changing conditions but maintain a balance both between the various parts and as a whole; this balance is maintained through homeostasis.
Anthropologist Gregory Bateson is the most influential and earliest propagator of systems theory in social sciences.
⚖ E-2.1.4 Goals alignment: Architecting organisations
The anatommy of an organisation
The anatomy is a complicated challenge, it can be reduced into more simple ones.
The complexity of an organisation is by what it does and it does that, the goal of the organisation in efficiency end effectivity.
What the real goal of an organisation is, is not what it does.
The SIMF model to model the organisation
The anatomy of the organisation is for clear responsibilities accountabilities.
As a start: it should support the intended flow of a product (good, service) for the organisational and technology aspects.
Both lines of interest have 4 levels (system-5,4,3,1) that should work together in a system as a whole.
A logical layout for this would be by the following figure:
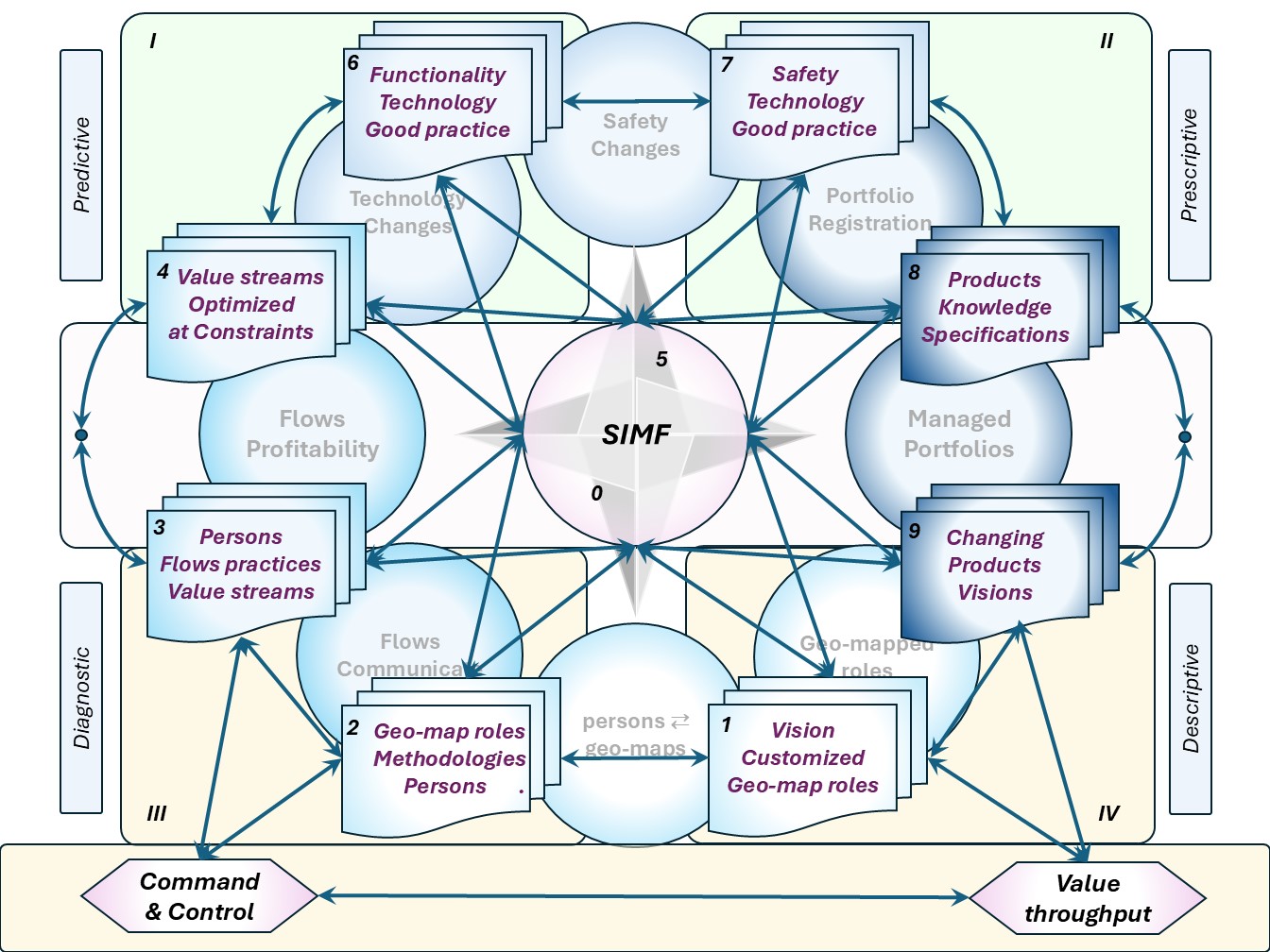
in a figure:
See right side.
The most valuable diagonal is from I to IV delivering value to the external customer.
There is a logical internal conflict at each side of the diagonal
The internal III to II line is the alignment: enabling, monitoring and giving the external service.
There is logic internal conflict over the diagonal.
Evolution in architecting organisations
There is a logical growth for responsibilities accountabilities :
- Integral The owners, founders, are also the leaders.
The assumption is all knowledge of "how to do" is at this single point.
This works in a small setting.
When complexity growths it fails by overloading overburdening the leaders.
- Functional segmentation in hierarchical levels.
This works when the delegated leaders are able to act for "how to do" for their functional part.
When complexity growths it fails and the responsibility accountability gets lost.
- Matrix is the segregation in the knowing "how to do" and the authority with accountability.
This works as long as the knowledge is explainable and usable for decision makers.
When complexity growths it fails with coordination for underpinned decisions for goals.
- Divisional segmentation for components reduces the complexity for components in the system.
When complexity growths it fails for alignment for the components for the system as a whole.
- Cluster segmentation for goals reduces the complexity for each system that is component of a system.
When complexity growths it fails for the goal for the system as a whole.

E-2.2 Knowledge Assurance: framework & tools
Objective definitions has to find its terms between the Charybdis of abstractions and the Scylla of specific processes.
The first to be avoided because they are by nature detached from reality, the latter because they would be too specific and restrictive.
🤔💡🎭 In-between objectives would be best defined through:
- Strategic objectives expressed using symbolic categories applied to environments, products, and resources.
- Modal time-frames identified in reference to events and qualified by assumptions with regard to symbolic categories.
- Functions to be optimized given a set of constraints.
⚒ E-2.2.1 Goals alignment: Engineering building platforms
Platform engineering, the beginning
We don't start to learn what is going on in a real changing environment.
We start learning in an isolated education environment that is assuming a fixed mindset in predefined fixed requirements, fixed methodologies.
Adapting change and what was learned is an after fact activity.
Increasing your Agility: An interview with Dave Thomas (2015)
People go through phases when they learn something.
When they first start out, they have no understanding of the context they find themselves in.
There aren't many decisions they can meaningfully make—all they can really do is follow rules.
But, as you gain experience, you start to understand the bigger picture.
And with this understanding comes a growing intuition about how things work.
❶
At this point, the rules you had originally hold you back.
You can see further and more clearly, and you can see how doing things differently might be better.
So you start to experiment, tweaking things here and there.
- If the result is better, you tweak some more.
- It it is worse, you roll back and try something new.
What we have here is that during the education time we have no other choice than to follow work what is being told.
After becoming more proficient thing change.
There is another choice, after learning the basics in those fixed methodologies:
- Become more proficient in that knowledge to be able to change the things, doing it different in different methodologies.
- Become more proficient in that knowledge to get more throughput in efficiency of being more effective in the results.
- Switch to a managerial role trying to lead in what is not known and not capable in, or set in serving managerial role in enabling those others.
These schisma's are a source four confusion and conflicts.
As the popularity of the manifesto grew, consultants and companies started to sense an opportunity.
We started seeing people using the tag "Agile" with their existing offerings in the same way detergent manufacturers add the word "Improved" to their product name.
Often they'd ignore the fact that "agile" is an adjective and instead use it as a noun: "learn Agile today!"
❷
Why do they do this?
Because it is easier to sell nouns (things) than adjectives (qualities of things).
You can't buy blue, but you can buy a ball.
If they wanted to sell "agile" they'd need to make it a thing.
The flow of engineering platforms
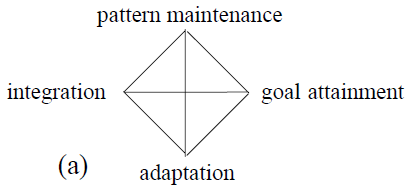
Development, engineering, a prefered methodology approach in several areas for a v-model and following Lean & AGIL (Adaption, Goal attainment, Integration, Latency).
❸ The four areas:
- Front-End: portfolio assets alignment and feedback to external stakeholders.
Setting a goal and identity for the internal organisation.
- Mission realisation: portfolio management by the organisation enabling the future.
Budgets generated form the operations in the now. (Portfolio-Plan)
- Technology realisation: The development of new and improved solutions with the goal serving the external customer. Aligned with operations in the now (Dev-OPS)
- Back-End: supply chain alignment and feedback to internal stakeholders.
Planning for what is realistic possible by available resources.
In a figure:
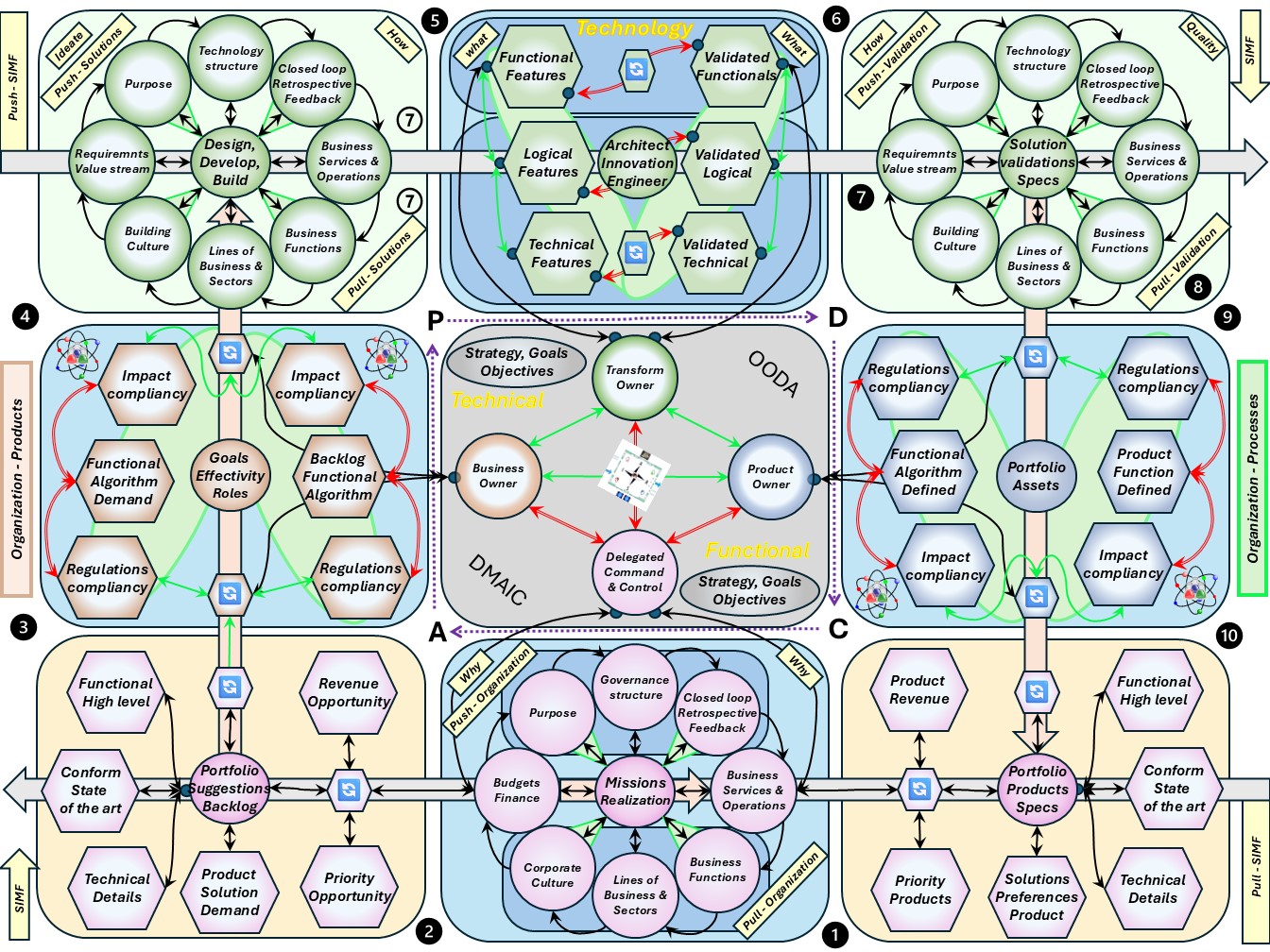 ❹
❹ There is a balancing force in another context:
- Portfolio suggestions backlog: the pipeline for the future.
- Technology knowledge: Ideas in improvements, innovations for design and products.
- Portfolio products specifications: The product knowledge in the now.
- Product validations: quality and quantity assurance & monitoring.
Platform engineering, the evolution
Increasing your Agility: An interview with Dave Thomas (2015)
I don't think we can fight this.
But I do think we can bypass it.
I think the original values are still valid, and we can use them to inform the way we work.
I like to express it like this.
❺
Every team that develops with agility follows these steps:
- Know where you are
- Take a small step towards where you want to be
- Evaluate what happened
- Repeat
This sounds easy—it isn't. It is hard because it applies to everything, at all levels. It applies to naming your variables, and it applies to defining your architecture.
And implicit in the steps is the often overlooked fact that we are never done.
We don't stop the process when we reach some goal. We stop it when the incremental value we deliver is less that the cost of delivering that value.
The way all of this similar attempts in history has gone wild is the real question to answer and think about.
My suggestion is, the real issue are:
- an easy financial business model is seen by setting mandatory methodologies for an idea.
- there is an social culture in not accepting the really impactful changes of the idea.
- the goal gets lost in mandatory methodologies, the methodologies are loosing their value.
- blaming the failures to something that is out of control, enabling to repeat the same.
⚒ E-2.2.2 Way of working: flow interactions communication
The Incose systems thinking (US based)
A change in the context of engineering going out of the box of technology.
The evolution of systems engineering as a transdiscipline (Michael Pennotti, Peter Brook, David Rousseau 2024)
❻
Systems engineering (SE) is a relatively young discipline, but evolving rapidly in the face of increasing recognition of the need for a systems approach to facilitate not only the successful engineering of complex systems but also the creative development of elegant solutions to complex problems.
The need for this systems approach arises inter alia via the:
- increasing evidence of the rapidly growing financial and performance risks associated with complex development projects of increasing scale and interdependence;
- increasing recognition of the systemic complexity of the urgent problems whose solutions matter most to human and ecological wellbeing.
- Widening recognition of the need for synergistic co-operation between multiple disciplines collaborating towards the solution of complex problems, especially those of global scale;
- explosion of opportunities for technical capability based on the exponential growthofscientific and technological insight;
- increasing recognition of the immaturity of the theoretical underpinnings of SE, especially as regards its ability to understand, and design/engineer for, what works or what matters across disciplinary interests (e.g., general systems theory).
❼
A clear sign of the struggle to cope with this increasing complexity in the light of so much change and risk is the burgeoning efforts to compile lists or catalogues of heuristics, principles, and other guiding assumptions and propositions that can assist SEs in learning from past experience while avoiding the risk of being locked into past views of “best practice” which might be inadequate in different futures.
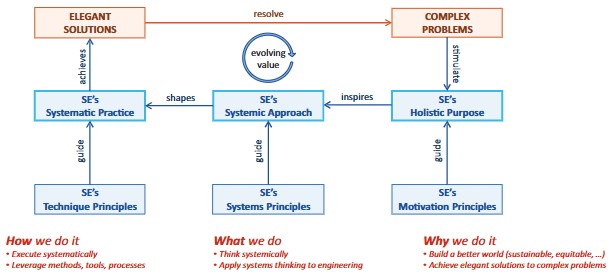
In a figure:
See left side
In the face of these concerns, some systems engineers began to develop prescriptive processes and standards in an attempt to make the practice more systematic.
In doing so, however, they weakened the link between the SE and the domain within which it was applied.
SE became more abstract and disconnected from the rest of the engineering required to bring systems to life. ...
❽
Griffin suggested four criteria for design elegance:
- Does the system work?
- Is it robust? If the context changes, does it degrade gracefully or fail cata strophically?
- Is it efficient? .. not only in terms of financial resources, but also human resources, energy resources, environmental resources, etc.
- Does it minimize unintended actions, side effects, and conse-quences?
... First, Iandoli et al. have shown that elegant designs remove unnecessary complexity and also render designs simpler to implement.
Second, Rousseau Billingham and Calvo-Amodiohave argued that the parameters of Griffin elegance amount to the fac-tors that contribute to assessing a system as “good,” and hence count as“systemic virtues” in the same sense as factors that make a person good (“personal virtues”) and a scientific theory good (“theoretical virtues”).
The SCIO and others systems thinking (UK based)
Holistic Flexibility for Systems Thinking and Practice (Researchgate: Rajneesh Chowdhury 2024)
Complexity theorists talk about underlying structures that govern behaviors of systems that are manifested in patterns and trends over time that we experience in our societies and organizations.
Order emerges out of such underlying structures and it need not be imposed by extraneous forces.
Several factors are inextricably intertwined resulting in complex dynamics in social, economic, regulatory, and technological spheres.
These dynamics are often characterized by local rules, nonlinearity, unpredictability, and volatility. ...
❾
The origins of complexity theory lay in mathematics, and traces its roots to Edward Lorenz’s chaos theory (Gleick 1987; Jackson 2000).
In the 1960s, involving 12 nonlinear differential equations, Lorenz decided to look for complex behaviors and he was led to the phenomenon of rolling fluid convection - this was part of his work on solving the problem of long- range weather forecasting using a simple computer simulation. ...
Organized complexity resides in the parts of a system that are non-random, clearly correlated, and display identifiable interactions between the parts.
Due to correlations, differentiated subsystems can be observed.
Interaction with other systems and subsystems are clear.
In the case of disorganized complexity, interactions within and between the subsystems or systems are random. ...
As Jackson (2019) notes, the primary concern in restricted complexity is with deterministic chaos, but this is not the world that practitioners encounter.
Rather, they confront general complexity, where the crux of complexity is in the human agents who form the bases of interactions in the systems and subsystems.
Human agents carry their own values and motivations and have their own power dynamics at the micro and macro levels.
❿
Therefore, any attempt to simplify disorganized complexity or general complexity using nonlinear dynamical programming is unlikely to offer deeper insights as the outcomes of such efforts rest at the level of computer simulations, rather than empirical observations (Jackson 2019). ...
Bogdanov (1902) developed a concept of “universal organization science”, an original systems theory that sought to find solutions to generalized scientific and philosophical questions for the unification of all biological, physical, and human sciences.
He advocated that this is only possible if sciences are approached as systems of relationships that are driven by fundamental principles of interrelationships and emergent behaviors. ...
⚖ E-2.2.3 The Jabes Framework knowledge cycle
What: Knowledge & Interactions in a cycle
A proposal is the framework for generic interaction and knowledge sharing.
Using this framework a clear structured definition of a portfolio becomes possible.
The technology, tools, context:

in a figure:
See left side.
Context of the audience:
Technology driven structural knowledge assurance.
With a very generic model of information systems there is a possible generic technology approach as product a tool for this.
The more detailed tools for more detailed situations are possible better fits in details but at a generic level it is adding sustainable value.
Recognizing Knowledge & Interactions unique ID
Using an uniform product identification enables trade and exchange while exporting and importing the database containing an information product conforming the Jabes metadata model.
Following a naming convention schema an identification could be like:
PPIC:ITC-00-000-001:ACT:ScoreNewCust-03
Licensing the identification, numbering, for uniqueness is a business model.
⚙ E-2.2.4 The Jabes Product knowledge assurance
Why: Knowledge & Interactions in a cycle
Product Pitching:
- Extending the framework with a product supporting the portfolio operational and transformational is unique & distinctive.
- There is nothing like this existing in the market.
There is a high demand to be more in control for information processing.
- The shown data model is for a transformation building up a platform supporting business administrative processes.
- A trial was done using only Word (moc). Real interfaces api's databases, to be done.
Licensing a product or running it as a services (SAAS) is a business model.
How: Knowledge & Interactions in a cycle
The metamodel covers all elemements in three layers, servicing the life cycle stages.
Innovation or solving known issues needs a defined "backlog".
The "backlog" items should be made clear enough and well understood to define requirements.

in a figure:
See left side.
Technology driven structural knowledge assurance.

E-2.3 Engineering collaboration by processes, services
Work units are to be understood in relation to their arrangement into processes and they should be defined accordingly.
🤔💡🎭 Linking processes to narratives, work units have three unities for Aristotles drama:
- Unity of action: one main objective, a single authority.
- Unity of place: executed at one space, all resources addressed & accessed independently, communications without mediation.
- Unity of time: set within fixed and continuous time-frames.
That is a necessity if controlled synchronization of tasks to be managed independently of context contingencies.
⚒ E-2.3.1 Goals alignment: Engineering processes flows
Value stream engineering
The Perilous Afterthought: Why Product Documentation Cannot Be an After-the-Fact Endeavour (Li Shumin Chen 2025)
In the fast-paced world of product development the allure of rapid iteration and quick deployment can be overwhelming.
However, this urgency often leads to a critical oversight: treating product documentation as an afterthought.
This practice, while seemingly efficient in the short term, is a recipe for disaster, a potential malpractice that can have far-reaching consequences.
❶
ASD-STE100, or Simplified Technical English, has a wide range of applications, extending beyond its origins in the aerospace industry:
- Manufacturing: Equipment manuals, maintenance procedures, and safety guidelines.
- Defence: Military equipment documentation, training materials, and operational procedures.
- Information Technology (IT): Software documentation, user guides, and troubleshooting manuals.
- Medical Devices: Operating instructions, safety information, and regulatory documents.
- Energy Sector: Plant maintenance, safety protocols, and operational procedures.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting requirements for clear and understandable documentation in regulated industries.
- Customer Support Materials: Creating easy to understand help files, and FAQ documentation.
❷
The solution lies in integrating documentation into the product development process from the very beginning.
By treating documentation as a core component of the product, companies can ensure accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
- Early Planning and Collaboration: Documentation should be planned and initiated during the early stages of product development, with close collaboration between developers, technical writers, and subject matter experts.
- Continuous Updates and Revisions: Documentation should be continuously updated and revised throughout the product lifecycle to reflect any changes or modifications.
- Utilising Modern Documentation Tools: Leveraging modern documentation tools and technologies can streamline the documentation process and improve efficiency.
By prioritising product documentation and integrating it into the development process, companies can mitigate risks, enhance safety, and build trust.
The operational flow of a value stream
Operating, executing, has a big similarity with engineering.
The preferred methodology approach is based on lean.
- Removing the limited constraint when doing improvements.
- For a stable system there should only one controlled constraint.
❸ The four areas:
- Alignment in products : the vision in what is the flow in demand and delivery.
Setting a goal and identity for the internal organisation.
- Prepare picking: The planning of what is going to be delivered.
Resources for materials aligned for the operations in the now.
- Demand at Customers: The product flow demand (sales) approach.
Aligned with operations, "prepare picking", in the now.
- Collecting packaging: quality and quantity assurance before delivering.
Planning for what is realistic possible by the properties in the deliveries.
In a figure:
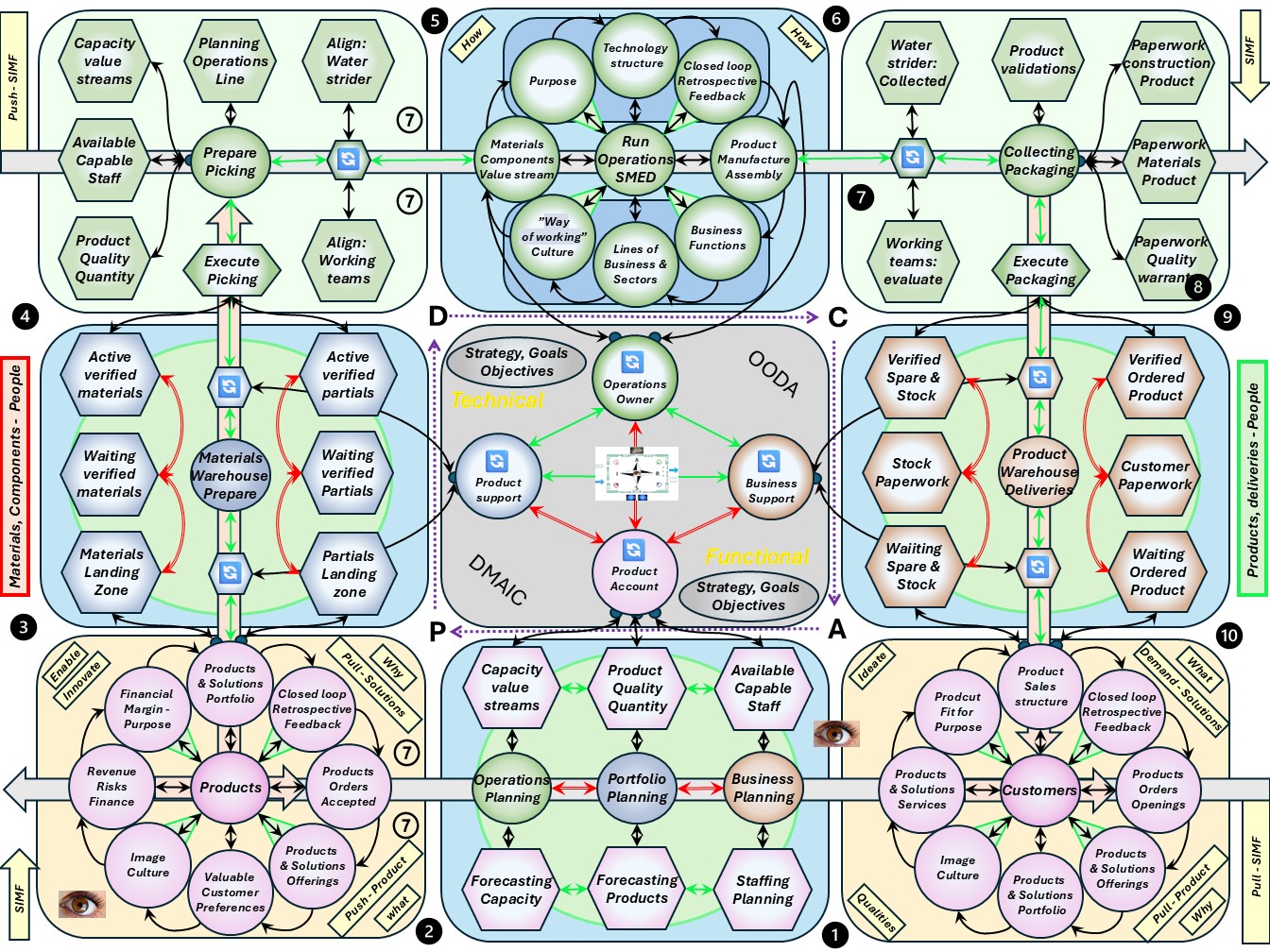 ❹
❹ There is a balancing force in another context:
- Delivery chain: continuity assurance in external dependencies.
- Alignment in resources : The vision in flow at demand and delivery. (Portfolio-Plan)
- Run Operations: Equipment SMED (Single Minute Exchange of Dies). (Dev-OPS)
- Supply chain: continuity assurance in external dependencies.
Value stream engineering, the evolution
The problem in the value stream is understanding of the product (good, service).
- When everything was data the meaning and context of data got lost.
- When all was about agile the meaning and context of agile got lost.
The agile hype is over, the sizzle into a new word:
Product.
Is your Product Owner actually a product OWNER? (W.J.Ageling 2025)
Most Product Owners I know are something else ...
❺
instead they are one of the following:
- Feature Owners They are accountable for maximizing the value of a product feature. They work on an element of the product that fulfils user needs but can’t function on its own.
A user may be happy with a product feature, but unhappy with how features work together and therefore unhappy with the product as a whole.
- Component Owners They are accountable for a distinguishable part of the product that often can’t function without other parts. Examples are the database, the front end, and reporting.
- Team Owners are accountable for the delivery of the product parts by their team.
They are working with a team backlog that is a subset of the program backlog.
Product Owners that are one of the above are Product Owners in name only.
They aren’t solely accountable for the value of the product.
More rigid is: the CPO (Chief Product Officer) is the one with authority and accountability for the product as a whole.
Is there no CPO than there is no lead, no C&C in place.
⚒ E-2.3.2 Goals alignment: Engineering tasks actvities
Evolution in methodologies at systems
A chief product officer (CPO), sometimes known as head of product or VP of product, is a corporate title referring to an executive responsible for various product-related activities in an organization.
The CPO is to the business's product what the CTO is to technology.
The role is a complex one of several area's. The social interaction is very important.
❻ Anthropology
The Macy Cybernetics Conferences (1946-1953):
The principal purpose of these series of conferences was to set the foundations for a general science of the workings of the human mind.
These were one of the first organized studies of interdisciplinarity, spawning breakthroughs in systems theory, cybernetics, and what later became known as cognitive science.
M Weber
Weber attempts an interpretive understanding of social action in order to arrive at a "causal explanation of its course and effects.
The social actions have subjective meanings that should be understood in its given context.
Weber's interpretive approach in understanding the meaning of an action in relation to its environment delineated a contextualized social framework for cultural relativism.
Evolution in methodologies at systems
T Parsons
work significantly impacted American sociology by integrating European classical theory, particularly the ideas of Max Weber and Émile Durkheim.
His theories sought to bridge the micro-level interactions of individuals with the macro-level structures of society, providing a holistic view of how societies function and maintain stability.
This integrative approach has made Parsons a central figure in sociological theory, despite the criticisms and debates his work has generated.
❼
A social system, according to Parsons, is a complex set of relationships among individuals and groups that interact within a structured environment.
Parsons defined a social system as a plurality of individual actors interacting with each other in a situation that has at least a physical or environmental aspect.
The interactions within the social system are guided by culturally shared symbols, which provide the normative guidelines for behavior.
These symbols include language, values, and norms that shape the expectations and actions of individuals.
The primary function of the social system is to maintain stability and order by regulating the behavior of its members.
This is achieved through the integration of individual actions into a cohesive whole, ensuring that the system operates harmoniously and efficiently.
The social system is thus seen as a dynamic and adaptive structure that responds to both internal and external challenges.
This system is characterized by the interdependence of its parts, the presence of shared norms and values, and the orientation of actors towards achieving collective goals.
❽
The integration of actors into social structures is crucial for the stability and functioning of the social system.
By internalizing shared norms and values, individuals align their behavior with the expectations of the system, contributing to social cohesion and order.
This process reduces the need for external control and enforcement, as individuals regulate their own behavior in accordance with the system’s norms.
His work on the AGIL schema, for example, provides a framework for analyzing the functional imperatives necessary for the survival of social systems.
In a figure:
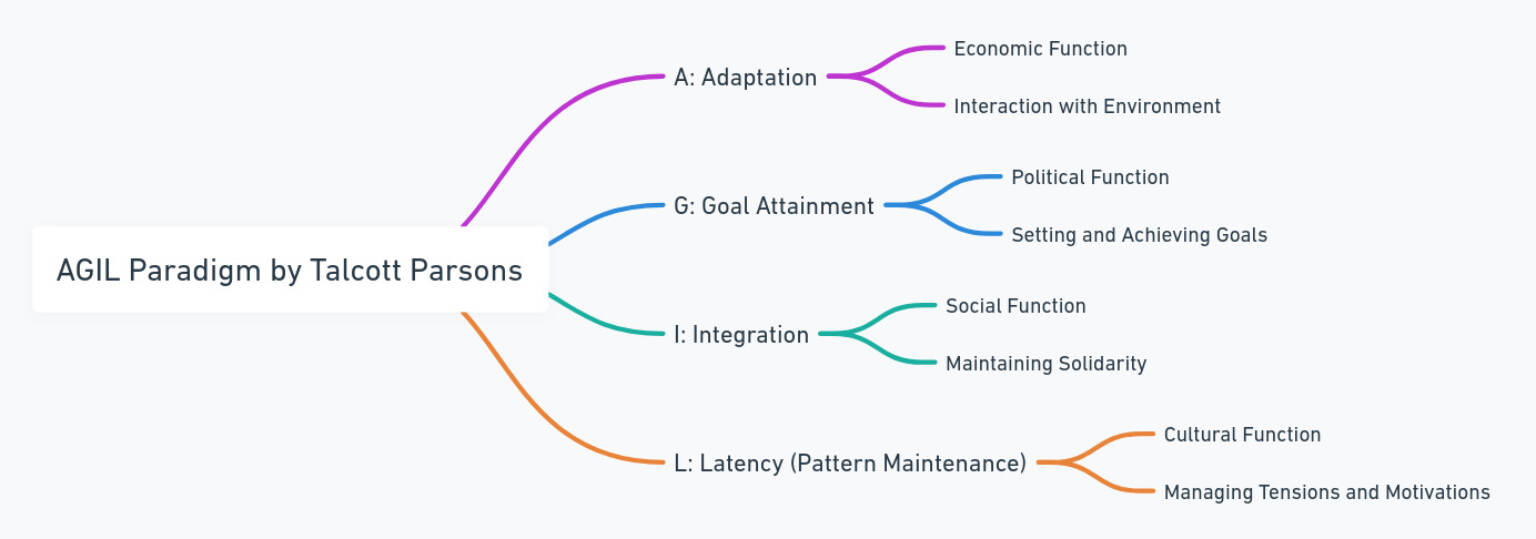
Evolution in methodologies
G Bateson
Bateson argues that there are "ecological systems, social systems, and the individual organism plus the environment with which it interacts is itself a system in this technical sense."
By adding environment with systems, Bateson closes the gap between the dualities such as subject and object.
"Playing upon the differences between formalization and process, or crystallization and randomness, Bateson sought to transcend other dualisms mind versus nature, organism versus environment, concept versus context, and subject versus object."
❾
In short, the behaviour of person X affects person Y, and the reaction of person Y to person X's behaviour will then affect person X's behaviour, which in turn will affect person Y, and so on.
He then discerned two models of schismogenesis: symmetrical and complementary.
- Symmetrical relationships are those in which the two parties are equals, competitors.
- Complementary relationships feature an unequal balance, such as dominance-submission (parent-child), or exhibitionism-spectatorship (performer-audience).
Schismogenesis is a term in anthropology that describes the formation of social divisions and differentiation.
❿
(schizophrenia) Full double bind requires several conditions to be met:
- contradictory injunctions or emotional messages on different levels of communication.
- No metacommunication is possible – for example, asking which of the two messages is valid or describing the communication as making no sense.
- The victim cannot leave the communication field.
- Failing to fulfill the contradictory injunctions is punished .
The strange behaviour and speech of schizophrenics were explained by Bateson et al. as an expression of this paradoxical situation, and were seen in fact as an adaptive response, which should be valued as a cathartic and transformative experience.
⚒ E-2.3.3 Way of working: Jabes flow administration
What: Knowledge & Interactions in a cycle
A proposal is the framework for generic interaction and knowledge sharing.
Using this framework a clear structured definition of a portfolio becomes possible.
Logical information context:

in a figure:
See left side.
Context of the audience:
Organisational structural knowledge assurance.
With a very generic model of information systems there is a possible generic technology approach as product a tool for this.
The more detailed tools for more detailed situations are possible better fits in details but at a generic level it is adding sustainable value.
Recognizing Knowledge & Interactions unique ID
Using an uniform product identification enables trade and exchange while exporting and importing the database containing an information product conforming the Jabes metadata model.
Following a naming convention schema an identification could be like:
PPIC:FLI-00-000-001:ACT:ScoreNewCust-03
Licensing the identification, numbering, for uniqueness is a business model.
⚒ E-2.3.4 Way of working: Jabes flow alignment
Why: Knowledge &mp interactions in a cycle
Product pitching:
- Using the framework with a product supporting the portfolio operational and transformational is unique & distinctive in the beginning.
- There is nothing like this existing in the market.
There is a high demand to be more in control for information processing.
- The shown data model is applicable for many business administrative processes but are not in place yet.
The first one will be the first in defining details.
- The first one will run and/or enable the approach by a bootstrap approach.
Creating the framework and products, running it as a services are business models.
How: Knowledge &mp interactions in a cycle
A generic fraemwork and a tool is a project to implement and maintain in life cycle stages.
Innovation or solving issues needs a defined "backlog".
The "backlog" impacts all the stakelhoders in the organisation and the organisation by requirements.
in a figure:
See left side.
Technology driven structural knowledge assurance.

E-2.4 Architecting collaboration in unpredictability
At the beginnings there were only objects as given by nature.
That changed by seeing them as artifacts that could be made on design.
🤔💡🎭 As communities set on making more complex products:
- they began to think about collaboration,
- subsequently about engineering processes,
- controlling & managing change as an afterthought,
- Unpredictability of contexts and execution making intermediate milestones necessary.
The first two narratives and action clearly depends on the idiosyncrasies in to ICT concerns, the other two in organization models.
⚒ E-2.4.1 Controlling and planning the now
The four types of variability
If flow is the paramount in system variability and system variability is blocking the flow, one should explore the nature of system variability encountered.
❶ Variability can be systematically minimized and managed but not eliminated.
- External types:
- Demand, Request variability characterized by fluctuations end deviation experienced in request patterns and plans.
- Supply, Input variability occurs in the supply network or deviations by dates (seasonally differences) for supply or promised in requests.
- Internal types:
- Execution, variability is normal random variability by the system in a steady state.
- Control, variability is associated with the human element making decision.

Consumable Solutions
Disciplined Agile
It isn't sufficient to simply produce something that is 'potentially shippable,' instead it must also be something that is:
- Usable. People should be able to easily understand and work with your solution.
- Desirable. Think of it like this, if you ship something that nobody wants to work with, do you consider that a success? Of course not.
- Functional. The solution must meet the needs of its stakeholders.
❷
The fundamental observation is we as IT professionals do far more than just develop software.
Yes, software is important, but in addressing the needs of our stakeholders we will:
- Develop high-quality software
- Provide new or upgraded hardware/platform
- Change the business/operational processes which stakeholders follow
- Change the organizational structure in which our stakeholders work
- Update supporting documentation
Minimally IT professionals should have the skills and desire to produce great software, but what they really need are the skills and desire to provide great solutions.
We need strong technical skills, but we also need strong "soft skills" such as user interface design and process design.
Operational support for the flow in the now
Operating, support executing, is in line with what has been engineered.
The preferred methodology approach is based on lean.
- Removing the limited constraint when doing improvements.
- For a stable system there should only one controlled constraint.
❸ The four internal areas :
- Alignment in visions, missions : the identity of an organisation.
Nurturing the goal and identity at the internal organisation.
- Executing capabilities: The standards in the ways of working. (Provision-Buyer)
Nurturing the standards of working in the operations for the now.
- Enabling capabilities: assignment processes. (Motive-Assets)
Allowing people, resources to use defined capabilities.
- Execution of operations: quality and quantity assurance before delivering.
Allowing the defined functional operations to happen.
In a figure:
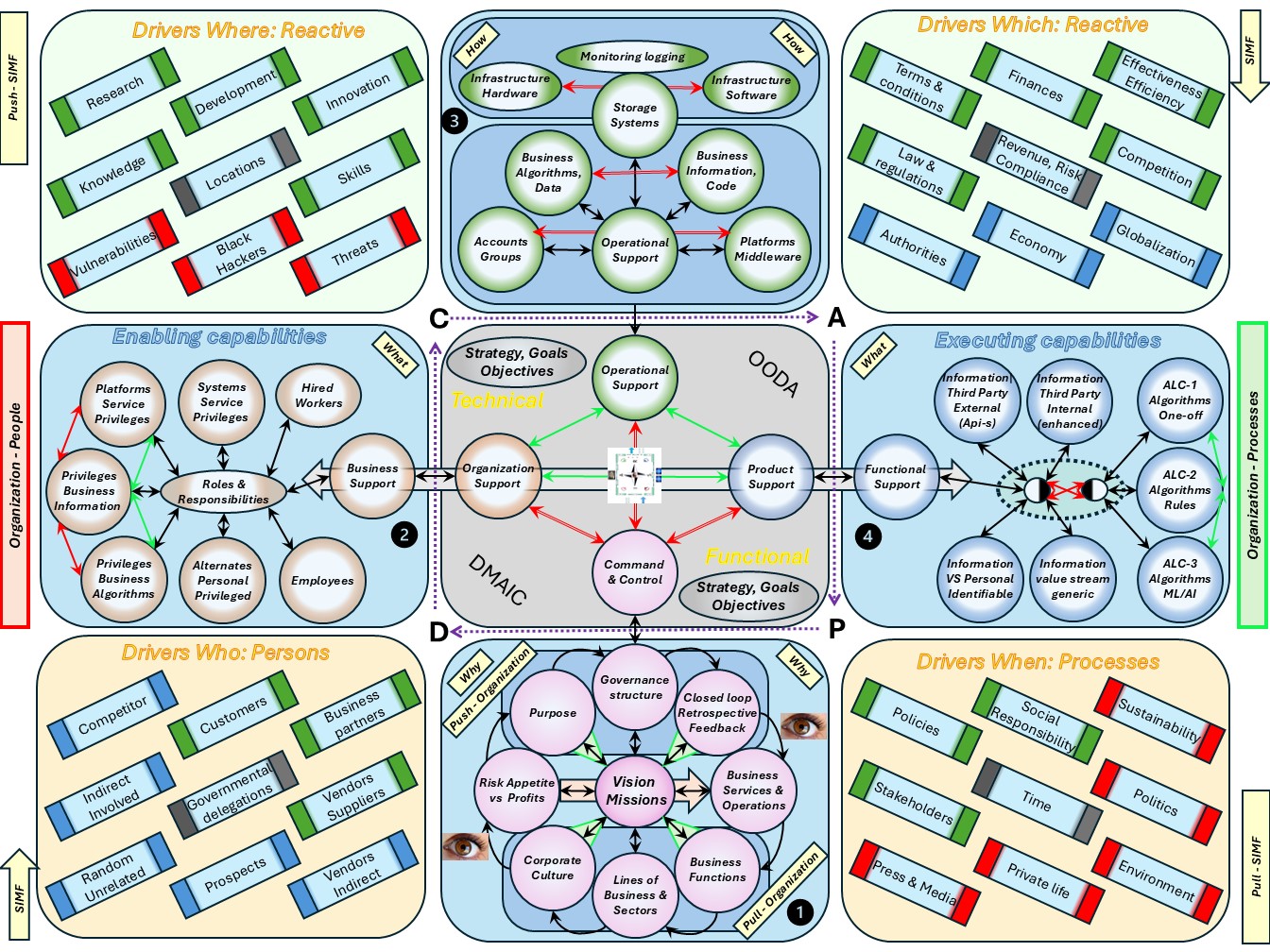 ❹
❹ There are external balancing forces in another context:
- Drivers which: reactive on what is happening for events to adapt.
- Drivers when: proactive and reactive adaption of policy processes.
- Drivers where: reactive and proactive mitigations of threat events.
- Drivers Who: Interacting at opportunities in communications.
A start to build for the needed extension in mindset
❺ External references in the context of ICT:
⚒ E-2.4.2 Realised activities: flow communication
good practice: ethical LCM challenges
Underpinning necessity distinct LCM approaches requires salving a misunderstanding.
❻ Doing LCM correctly for each distinct type of artifact seems to be positioned emotionally as only a technical problem.
There is no connection between reality of nature and decision makers.
Ethical scandals and LCM challenges
These are not technical problems, a list of organisational challenges:
❼ Information LCM, data flow, delivery and data quality.
| # | date | Event link newstopic |
| 1 | 1985 |
⚠ Event: Enron
was cited as the biggest audit failure.
Regulations SOX (Sarbanes_Oxley Act), Basel, Solvency were a result. |
| 2 | 2020 |
⚠ Event: Wirecard
a series of corrupt business practices and fraudulent financial reporting.
No guarantee to prevent recurrence. |
❽ LCM Infrastructure, LCM middleware, operational plane, risk management.
| # | date | Event link newstopic
| 1 | 2020 |
⚠ Event: Ransomware: Maersk
business interruption to Maersk, the world's largest container ship and supply vessel operator.
Getting attentions with cybersecurity cyberwarfare.
A lot not going well in organisations:
- Lack of technical segmentations
- Lack of functional segmentations
- lack of leadership involvement
|
| 2 | 2024 |
⚠ Event: Mistake: Crowdstrike
Cybersecurity company CrowdStrike distributed a faulty update to its Falcon Sensor security software that caused widespread problems.
The dogma of getting updates as soon as they are available being too rigid applied.
The used audit checklists did not foresee the alternative impact in failure in an update.
A lot not going well in organisations:
- Lack of technical segmentations
- Lack of functional segmentations
- lack of leadership involvement
|
❾ Analytics, operational research, risk management.
| # | date | Event link newstopic |
| 1 | 1986 |
⚠⚖ Event: Space Shuttle Challenger disaster
root cause design: .. The Challenger accident has been used as a case study for subjects such as engineering safety, the ethics of whistleblowing, communications and group decision-making, and the dangers of groupthink.
remarkable, 2003 Columbia disiaster, "the causes of the institutional failure responsible for Challenger have not been fixed."
|
| 2 | 2018 |
⚠⚖ Event: 737 max
root cause design: .. seems to be caused by neglecting safety in favor of profit and meeting deadlines.
- Failing culture
- Failing regulatory controls
remarkable the first reactions blaming the computer AI as the cause where the real root cause are the human leadership.
|
❿ Analytics, operational research, AI ML (artificial intelligence).
| # | date | Event link newstopic |
| 1 | 1960's |
👓⚙ Sizzle: Operations research (wikipedia)
was emerging for improving situations beyond assumptions.
It got other names: systems thinking, AI. AI went emotionally incomprehensible with non-linear situations but wheterforecast & smartphones got normal |
| 2 | 2020's |
⚠⚒ Non-Events: futurisme
feeding concerns with anxious and brittleness. Reality: nothing to be afraid of.
|
💣 Don´t expect when fundaments are not robust, what is build on those, will be robust.
⚒ E-2.4.3 Realised activities: flow administration
Information quality
Information security is not possible when there is no data governance.
Anti-Cyber Crimes (Vellore Institute of Technology University, M.K.Jayanthi Kannan 2017)
Data Governance Strategy Development is based on the model proposed by Enterprise Information Management Primer Developing a Roadmap for an Enterprise Information Management Program.
The Data Governance Strategy of an organization should focus on the following aspects ..
Inputs from the following list of stakeholders need to be considered and analyzed for the development of Information Security Strategic Plan. ...
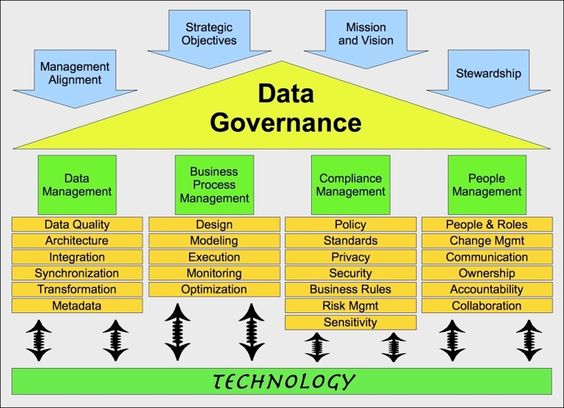
in a figure:
See left side.
There is an explanation for why to use the SABSA framework in this.
For the safety scope there are four pillars shown.
These are a variation of the generic four pillars.
Algorithms and models for interactions
ICT is a binary world the assumption is everything is true/false.
Reality is a complex and complicated one full of uncertainties without that binary assumption.
Should We Trust Algorithms? (David Spiegelhalter 2020)
There is increasing use of algorithms in the health care and criminal justice systems, and corresponding increased concern with their ethical use.
But perhaps a more basic issue is whether we should believe what we hear about them and what the algorithm tells us.
It is illuminating to distinguish between the trustworthiness of claims made about an algorithm, and those made by an algorithm,
which reveals the potential contribution of statistical science to both evaluation and "intelligent transparency."
In particular, a four-phase evaluation structure is proposed, parallel to that adopted for pharmaceuticals. ...
Finally, whenever I hear claims about any algorithm, my shortlist of questions:
- Is it any good when tried in new parts of the real world?
- Would something simpler, and more transparent and robust, be just as good?
- Could I explain how it works (in general) to anyone who is interested?
- Could I explain to an individual how it reached its conclusion in their particular case?
- Does it know when it is on shaky ground, and can it acknowledge uncertainty?
- Do people use it appropriately, with the right level of skepticism?
- Does it actually help in practice?
I feel that question 5 is particularly important.
⚒ E-2.4.4 Realised activities: flow alignment
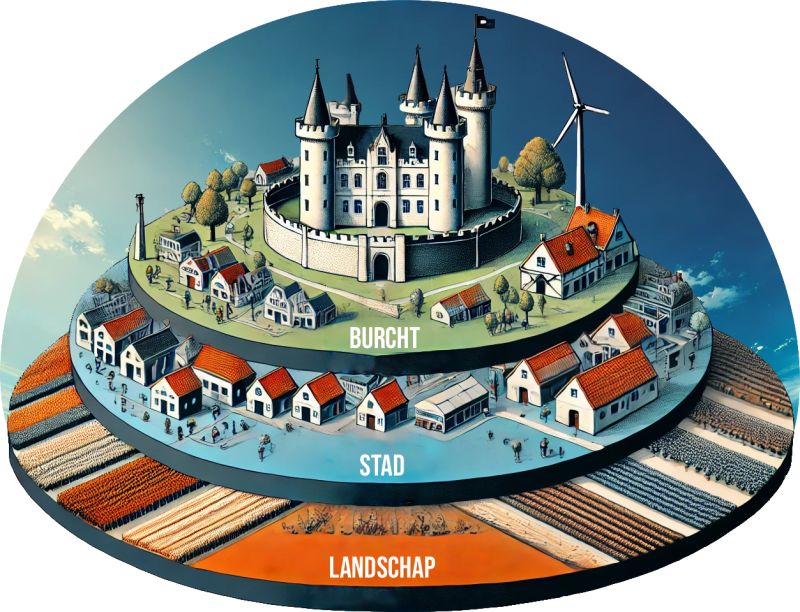
The metaphor model, ICT state of art
The common used model for information processes is a medieval settlement.
It is an outdated approach in many aspect in the age of the 21e century but explains a lot of the human behaviour.
- The ivory tower for the ones with authority.
- Cultural segmentation by what is seen of value.
- Segmentation in tribes and guilds for actvities.
- System viability ambiguity: no external connections, limited new energy, self sustaining goal.
Operational research (OR) is the overarching whole of what is divided into other phase spaces, living worlds.
From the Tightness Stereotypes (SB "Decision and Control" 1966, chapter 4) OR has to deal with:
- Scientists: the education gives him a bias. ➡ Use an interdisciplinary team.
- Problems: are declared with a bias. ➡ research the problem as a whole.
- Science: bias in cope for chance questions. ➡ nature is probabilistic.
- Solutions: biased by chosen phase space. ➡ research for a shared phase space.
- Pay-off: determined by management bias ➡ what it demands and can assimilate.
- Success: condition fulfilments are hard. ➡ ambiguities confusion by half measures.
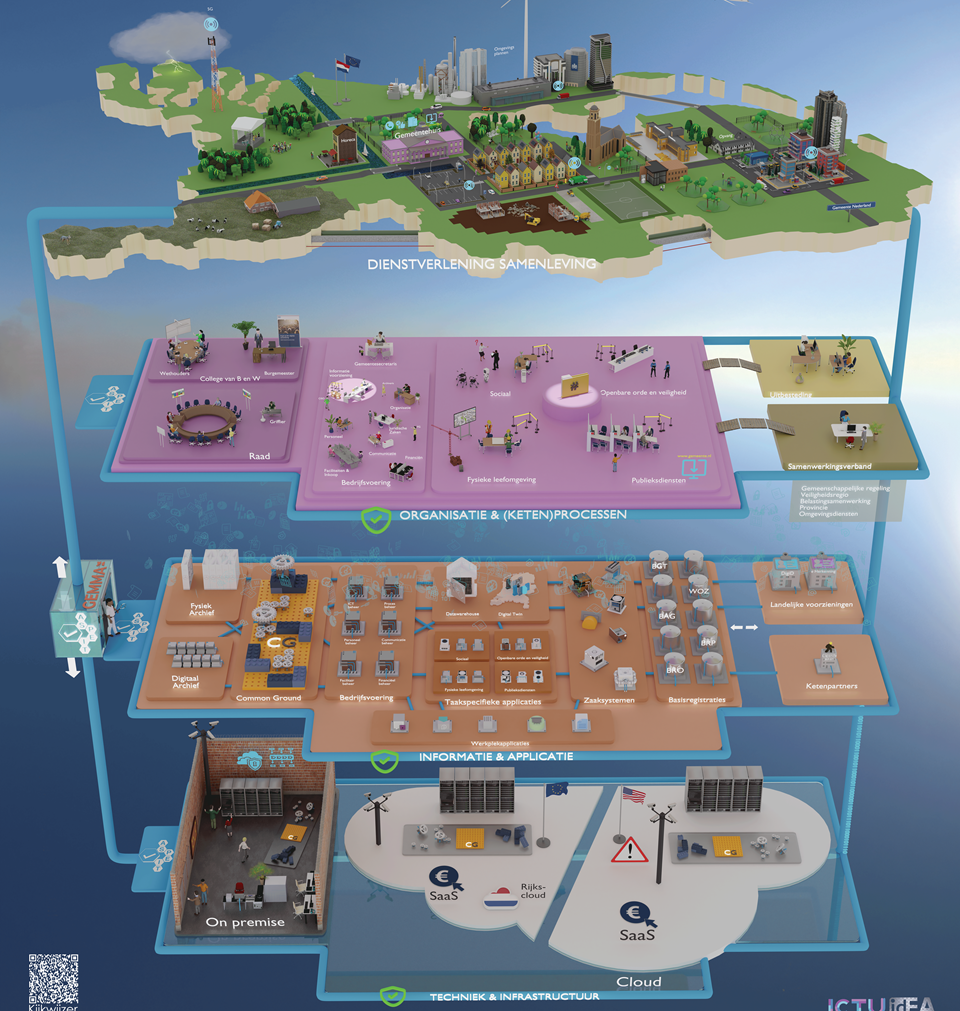
The metaphor model, ICT adapting change
A change leaving the old metaphor as hard, attempts are made.
The medieval settlement is getting transferred into adapting changes, see figure.
- The social society the settlement is part of is placed at the top, VSM system-5.
Missing:
- the way of the overarching government control.
- Executing operating technology components at the bottom, VSM system-1.
Missing:
- Administrative enabling support in the now
- Way of working executing capabilities in the now
- Alignment in shared mission, culture and identity
There should be many more system-1 tasks.
- An Information & application plane for managing the operations, VSM system-3.
Misplaced are:
- The operational execution of the organisation: ICT, functional, communications, structure
- common ground, dwh, digital twin, archives
- The future cloud be "organisation & chained processes" VSM system-4.
Misplaced are:
- The operational management for execution of the system (organisation)
- social services, safety, living environment
System-2 is not there in using regulators and algadonic channels.
There is work in progress to move to a viable system but without awareness of doing that.
E-2.5 Knowledge Assurance: measure, maturity
Measurements are not facts but observations obtained through conceptual & physical apparatus on purpose.
🤔💡🎭 For software architecting, engineering there are four purposes:
- Organisational and customer value of applications.
- Functionalities of supporting information systems.
- Size and complexity of the software systems.
- Architecting, engineering, building, verifying costs.
The first two metrics clearly depends on the idiosyncrasies in organization models, the other two to ICT concerns.
📚 E-2.5.1 Controlling and planning the future
Understanding risks for change
Learning from Mistakes is Overrated (LI G.Alleman 2025)
These questions and others need to be asked and answered before we can assess whether learning from our mistakes is a good idea.
The alternative to learning from our mistakes is to do the job right the first time.
- Why didn't we know this would be a mistake before we started?
- Or could we have known this before we discovered it failed?
- Or even better, was the failure we just experienced knowable at all?
This knowability question is the key to all project planning processes.
If something is not knowable, we cannot have known, so we only discover our mistake after the fact.
If it was knowable and we chose not to address it then we'll overrun our plan for no good reason.
❶
A critical concept that must be addressed in any credible management process:
- Investigative work - discovery is always needed on any development project. To think otherwise means we have a production process.
- Learning what we need to learn requires a budget. This is the basis of the increasing maturity of the Integrated Master Plan paradigm.
Someone has to pay for us to learn what we don't currently know and we need to make the cost of this learning visible as soon as possible.
Hiring smart people is pointless if they aren't allowed to make mistakes.
We must address who, what, when, where, why, and how this discovery process will be paid for FIRST.
Then, we can start failing on purpose to make the follow-on work better.
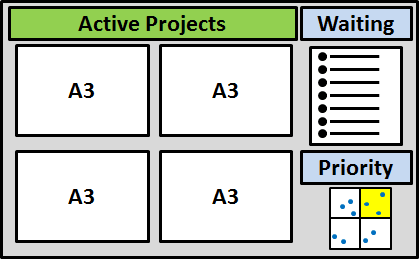
Variety in change
How to Manage Your Lean Projects – Number of Active Projects
Let's face it – you have more things to do than you can reasonably do in the available time.
A constant stream of tasks or problems are waiting for a lean solution. ...
❷
So how many projects should you have active simultaneously?
It depends. A single person works best with around two to three active projects (including daily chores).
A simple way to limit the number of projects that are active simultaneously is a project management board.
Operational support for the flow in the future
Operating, executing, has a big similarity with engineering.
The preferred methodology approach is based on lean.
- Enable the workfoce in seeing: Muri, Mudi, Muda, first are people
- Removing the limited constraint when doing improvements.
- For a stable system there should only one controlled constraint.
❸ The four areas:
- Information knowledge qualities: the understanding what it is all about.
Advisories in goals and identity for the internal organisation.
- Innovation, organisation: legal obligations liabilities and visibility for service demand.
Resources for materials aligned for the operations in the future.
- Safety - Continuity: all kind of technology related aspects that should get mitigate threats in risk evaluation.
One of the hyping words is cybersecurity.
- Organisational stability: Risk management on impact by decisions, mandatory legal obligations.
Doing what is necessary in alls aspects for trustworthiness.
In a figure:
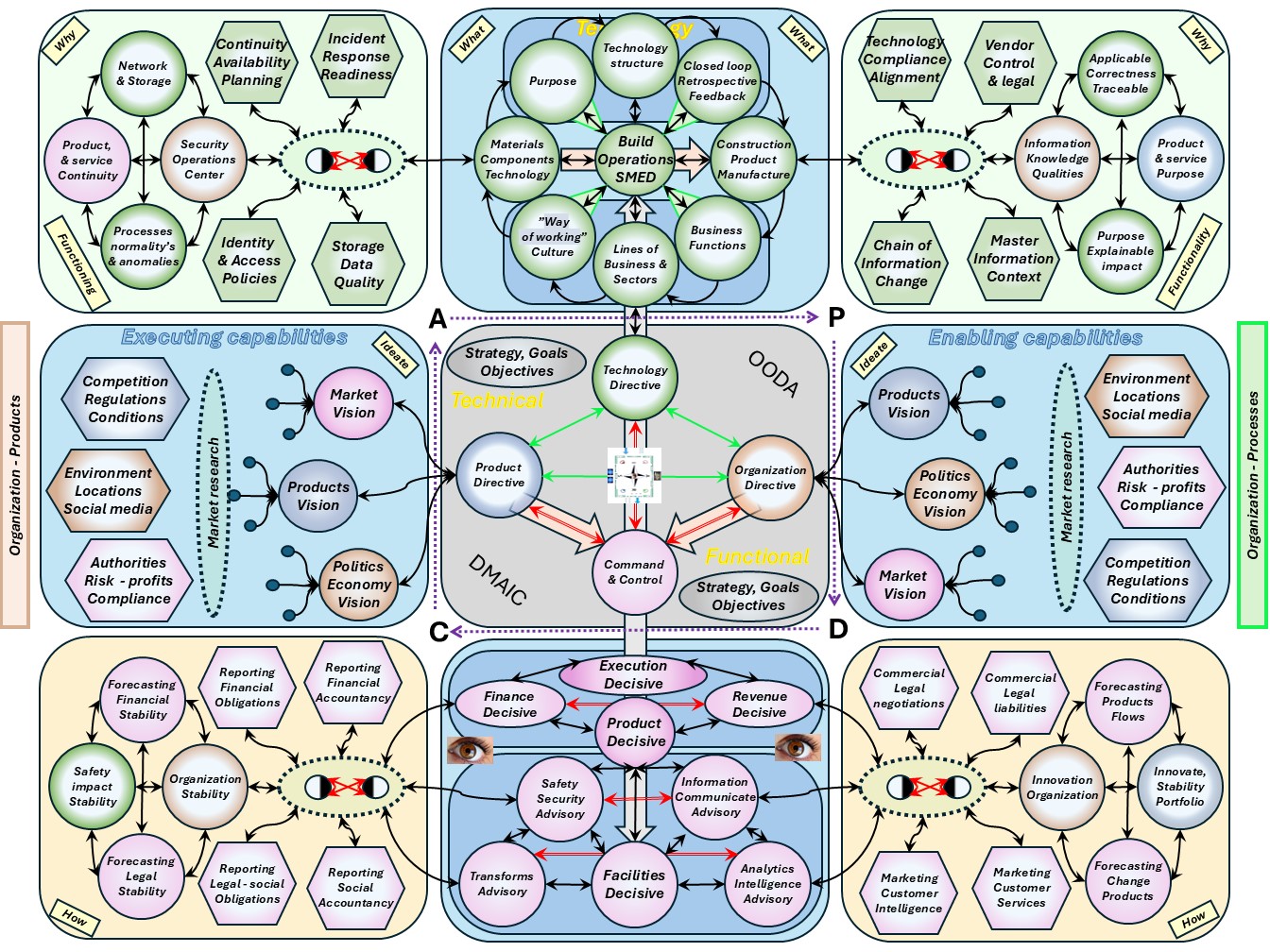 ❹
❹ There is a balancing force in another context:
- Authorities in decisions : The accountabilities to align with vision.
- Enabling capabilities: future continuity, planning adaptive changes.(Provision-Buyer)
- Execution capabilities: continuity assurance by set policies(Motive-Assets)
- Viable Operations: Equipment avoiding the issue in technical debt.
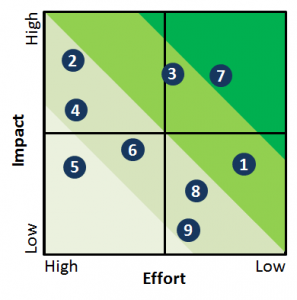
Variety in change
How to Manage Your Lean Projects – Prioritize
The question is now, among the many different projects waiting, which one do we start?
For my everyday practical decisions, I prefer a much cheaper and faster version of the cost benefit analysis: an impact–effort matrix.
There are different versions of this matrix found on the web, often with slightly different names.
In essence, however, one axis shows the effort/cost/difficulty/time that has to be put into a project and the other shows the impact/value/benefit/profit that the project will yield.
What is lean is difficult to define.
There is a long list of similar ones all practices, known patterns to improve effectiveness improve efficiency.
Operations research (OR) is not well understood.
❺❗
Operations research
attempts to provide those who manage organized systems with an objective and quantitative basis for decision; it is normally carried out by teams of scientists and engineers drawn from a variety of disciplines.
Thus, operations research is not a science itself but rather the application of science to the solution of managerial and administrative problems, and it focuses on the performance of organized systems taken as a whole rather than on their parts taken separately.
- OR as an science and application of science is an higher abstraction level in science.
- Cybernetics is a word for OR in the area of information processing
- Seeing all those as scoped biased suffering from tightness in OR is enlightening.
📚 E-2.5.2 Viable systems variety and maturity
Story telling getting it more practical
With OR Markov chains, closing the system using closed loops, System dynamics for chaotic systems modelling there are a lot of scopes.
These are all very abstracted approaches for systems.
❻ Complexity Theory & Political Change: Talcott Parsons Occupies Wall Street (researchgate: Martin Zwick 2012)
This paper revisits an early cybernetic and systems-theoretic model - today it might be called a complex systems model - proposed by the sociologist Talcott Parsons (1966, 1971), and argues that this model can help us understand some of the underlying causes of the major recession afflicting the US economy today.
 Indeed, this model was once characterized as being inherently conservative, because it allegedly assumed the stability and functionality of societal structures.
Indeed, this model was once characterized as being inherently conservative, because it allegedly assumed the stability and functionality of societal structures.
This characterization is incorrect, since Parsons' structural functionalism can actually be used to explain either stability or instability and either functionality or conflict.
Parsons conceived of the AGIL system as having fractal self-similarity, so each component can itself be decomposed into A, G, I, and L parts.
❼
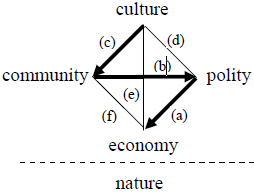 Using ideas from cybernetics and systems theory, Parsons orders the four components of the system hierarchically, indicated by the zigzag sequence of directed links shown in bold in the figure.
Using ideas from cybernetics and systems theory, Parsons orders the four components of the system hierarchically, indicated by the zigzag sequence of directed links shown in bold in the figure.
The top component (culture) is information-like; the bottom component (economy) is matter-energy-like.
Structural analysis goes beyond considering possible links between components.
Each component has sub-components and thus also an inner structure.
Community, for example, which is the I component of the societal system, has four sub-components; its polity-like subcomponent, i.e., the G in I, is “citizenship,” with its opportunities and obligations.
Parsons' model is not introduced here to discover societal problems or possible solutions to these problems that are now unrecognized.
It is introduced as a framework within which known problems and their possible solutions can be discussed coherently.
Abstract models may be more effective than concrete models for identifying the essence or deep structure of societal problems, for seeing the forest rather than the many trees.
The postion of persons in managing affairs
The problem in systems thinking, operational research having another abstraction level is a recent one.
It started at the beginning of the 20th century. (SB "Decision and Control" 1966, introduction)
❽
In the sixty odd years of the present century, there has been a colossal intellectual revolution in the basic thinking of science.
Basically, certainly chronologically, it began with the overthrow of classical physics.
The universe of space, time and gravitation became a different universe for the scientist after the theory of relativity became known.
The particles with measurable position and momentum which populated that universe took on a different meaning for the scientist after the discoveries of quantum mechanics.
The intellectual revolution of twentieth-century science has been accepted by the scientist, for it is proper to his work to uncover the essential characteristics of things.
From that revolution has stemmed a series of new discoveries, and indeed new sciences.
Atomic physics, astrophysics, a new chemistry, a new genetics, biochemistry and biophysics are all children of a revolutionary regime.
❾
For the man of affairs, however, the position is quite different.
His job is not to seek the truth, but to be the Prince.
He manages companies and industries, civil and military services, parties and policies, administrations and governments.
He manipulates large systems of men, materials, machinery and money.
The intellectual revolution of science has largely passed him by; it does not exist for him.
For the man of affairs to know much about science at all is rather unfashionable.
We have heard company directors boast of their ignorance of science, as if this automatically conferred a certificate of preoccupation with the higher things of life.
❿
The whole idea of using hard science as an intrinsic part of the managerial process is alien to many.
It is a proposal often countered by such remarks as 'management cannot be reduced to a science', or even 'management is an art'.
But neither of these replies is at all relevant to the issue.
The processes of management are complicated. They are complicated for the individual manager for whom insight, value judgment, flair, acumen, maturity and experience count.
They are even more complicated for the social entity that is a management group.
Don't wonder why there is that little progress for going into the age of information processing.
It is not the technology that is the problem it is human nature in decision and control to adapt the change.
📚 E-2.5.3 Jabes Measuring maturity: each dimension out of 3
Technology Scope: Tools, Infrastructure
❌ I - processes & information ✅ T - Tools, Infrastructure ❌ C - Organization optimization
Physical and operating system components:
| Maturity id | What | Context |
| CMM-4IT-1 | Network | Communications, zone isolations. Virtualisations impact |
| CMM-4IT-2 | Machines | Hardware: CPU, Storage, Memory. Virtualisations impact |
| CMM-4IT-3 | operating system | Functions to hardware & network. Virtualisations impact |
Tools, decision support and primary value stream system components:
| Maturity id | What | Context |
| CMM-4IT-4 | Tools Middelware | LCM without❗ organizational information |
| CMM-4IT-5 | Operational plane | Classsic well known LCM as always has been done |
| CMM-4IT-6 | Analytical plane | LCM always with organizational production ❗ information |
Maintenance, service, management and compliancy system components:
| Maturity id | What | Context |
| CMM-4IT-7 | Up to date | Maintenance production planning, act on gaps |
| CMM-4IT-8 | Cots vs "build" | Manage external purchased artifacts distinctly |
| CMM-4IT-9 | Regulations | Being prepared for conforming compliancy: BIA CIA |
Change Scope: Organisational Structure, Processes
✅ I - processes & information ✅ T - Tools, Infrastructure ❌ C - Organization optimization
Functional enablement support:
| Maturity id | What | Context |
| CMM-4AS-1 | Access Data | Provisioning information (data), limiting access |
| CMM-4AS-2 | Platforms usage | Enabling processing lines, operational value stream |
| CMM-4AS-3 | Monitoring | Enabling Monitoring , analytical plane what is happening |
Functional realisations support:
| Maturity id | What | Context |
| CMM-4AS-4 | Data preparation | Adjust information (data quality) using ELT / ETL |
| CMM-4AS-5 | Transformations | Chain management, operational value stream |
| CMM-4AS-6 | Data delivery | Value stream results (data), limiting access |
Functional architecture & compliancy:
| Maturity id | What | Context |
| CMM-4AS-7 | Corrective | Operational value stream, act on failures & mistakes |
| CMM-4AS-8 | Algorithms | Knowledge rules & instructions for transformations |
| CMM-4AS-9 | Regulations | Conforming regulations, directives with foreseen changes |
Purposes Scope: organisation, managing missions
✅ I - processes & information ✅ T - Tools, Infrastructure ✅ C - Organization optimization
Holistic Organisation - Enterprise alignment:
Running the organisation (execution) in the now:
| Maturity id | What | Context |
| CMM-4OO-1 | OR Enable Metrics | Operational research, lean enabling in the organisation |
| CMM-4OO-2 | Technology | Understanding technology processes value streams |
| CMM-4OO-3 | Operational DMAIC | Existing value streams improvements, minimal adjustments |
Running the organisation (execution) in the future:
| Maturity id | What | Context |
| CMM-4OO-4 | Employment | Income, Education, Equality, Morality, Assurance, Safety |
| CMM-4OO-5 | Local governments | Alignment to local environments social life circumstances |
| CMM-4OO-6 | Tactical PDCA | Any value streams improvements, advanced adjustments |
Running the organisation for a purpose:
| Maturity id | What | Context |
| CMM-4OO-7 | Plan structure | Decide or define. Make - refine - schedule/plan for execute |
| CMM-4OO-8 | Let it happen | Versatile: "to do", "to perform", also "add" (pull-push) |
| CMM-4OO-9 | Closed Loop | examine in order to determine its accuracy, quality, or condition |
📚 E-2.5.4 Jabes Measuring maturity: human culture each of 3
Vision - Number of CMM controls
For enablement a culture, vision is not only about technology it is about humans, famous: "Culture Eats Strategy For Breakfast".
ndma
A vision of the content of your work (your team's deliverables, e.g., a future technology vision, or a future business position) is dangerous.
In a volatile world, we need dynamic organizations -- not organizations locked into a response to yesterday's challenges and opportunities, yesterday's business strategies.
Agility is the key.
⚠ Note: a vision is not a business goal (like market share or revenue growth), or a strategy (like acquisitions or digital business).
❗ The vision is: How your organization will work.
How it will address any and all challenges and opportunities that arise in an agile, dynamic manner.

Question: How to measure culture?
💡 There are no known positive objects.
Avoiding the three evils however, gives context in what should not be seen.
Split the important human aspects to three:
| | Serve IT Technology | Shape Data Driven | Steer Enterprise |
| Muda | CMM-4IT-0-Muda | CMM-4AS-0-Muda | CMM-4OO-0-Muda |
| Mura | CMM-4IT-0-Mura | CMM-4AS-0-Mura | CMM-4OO-0-Mura |
| Muri | CMM-4IT-0-Muri | CMM-4AS-0-Muri | CMM-4OO-0-Muri |
The result: there will be twelve metrics for each of the three levelled stages.
The totals is 36 having each a value of 0 - 5. A visualisation in circle for a 360 retrospective (polar/radar diagram).

E-2.6 Experiencing the understanding journey
Depending on purpose three main categories:
- Translation: source and target models for same contents with different languages.
- Rephrasing: initial descriptions improvements using the same language.
- Processing: source and target models describe successive steps along the development process.
The challenge in this: It are not the results being important, it is the journey of learning, understanding.
The knowledge of the journey to share
❗
📚 E-2.6.1 The why of learning organisations
The organisation in 6*6 approach
Once structuring my mind for information processing started for going into a 3*3 area's.
It did had a technical focus with the question for what is going on.
This clumsy tinkering draw up resulted in thinking in 6 columns for 3 rows where the contents in the rows went int0 a 2,2 setting.
The content went from technical to an abstracted non-technical level. The 2 dimensional model into a 3 dimensional one.
The figure:
Fractals in the organisation
Accepting recursiveness, fractals is breaking the classic knowledge hierarchy.
Only seeing this as an isolated component in a system doesn't help the system as a whole.
This is about human culture in many more aspects.
A promotion by
ndma BWB :
The business-within-a-business (BWB) paradigm is foundational to NDMA's work.
It provides guiding principles for the design of every aspect of an organization's operating model.
Engagement ndma A=A
Empowerment comes down to simply this: Authority and accountability match.
What is missing:
The accuracy of prediction is an observable measure of knowledge.
Prediction, which can take the form of a plan, strategy, a decision, or any statement about the future, requires a theory.
accuracy of prediction depends on the extent to which a theory is aligned with the world to which the prediction refers.
(Edward Martin Baker).
Fractals when applying changes
A mismatch in accountability authority at some level in the system as a whole is a pitfall in projects.
Prediction for outcomes is measuring for what is intended to achieve.
Although this is well known the mistake is made over and over again.
Why Projects Fail - The Real Reason (LI G.Alleman 2025)
The measures of project success MUST start with two other measures.
- Measure of Effectiveness (MOE)- The operational measures of success are closely related to the mission's achievements or objectives and are evaluated in the operational environment under a specific set of conditions.
- Are stated in units meaningful to the buyer,
- Focus on capabilities independent of any technical implementation,
- Are connected to the mission's success.
MoE's belong to the End User. They define the units of measure
- Measure of Performance (MOp)- Measures that characterize physical or functional attributes relating to the system operation, measured or estimated under specific conditions.
- Attributes that assure the system can perform,
- Assessment of the system to ensure it meets design requirements to satisfy the MoE.
MoPs belong to the Program.
The Systems Engineer develops them, measured by the Control Account Managers, and analyzed by program control staff.
📚 E-2.6.2 The what of learning organisations
Operational research (OR) and systems thinking
Whatever name is used it is the same abstracted goal (SB "Decision and Control" 1966, introduction)
The attack of modern science on complex problems arising in large systems of
- men, machines, materials and money
- in industry, business, government and defence.
Its distinctive approach is to develop a scientific model of the system, incorporating measurements of factors such as chance and risk, with which to predict and compare the outcomes of alternative decisions, strategies or controls.
The purpose is to help management determine its policy and actions scientifically.
The issue: another level of abstraction of science that is not common knowledge.
History of OR and systems thinking
With that lot of knowledge why it is failing to become common knowledge?
Fifty years of systems thinking for management (researchgate: MC Jackson University of Hull 2009)
Both operational research (OR) and applied systems thinking were born from the interdisciplinary ferment created during the Second World War when scientists from different disciplines found themselves working together on vital military problems.
Since that time the histories of OR and applied systems thinking have frequently come into contact and impacted upon one another.
For example, some of the early pioneers of OR (Ackoff, Churchman) later adopted the systems thinking label in preference to OR; soft systems thinking began life by defining itself in opposition to hard systems approaches such as OR (Ackoff, 1979; Checkland, 1978); and, more recently, both soft OR and soft systems thinkers have been involved in the development of problem structuring methods (see Rosenhead and Mingers, 2001).
🤔 The same origin is a natural similarity, but the thing as a whole falling apart.
To discover these points of interaction is not surprising because OR and applied systems thinking (AST - by which I mean, in this paper, systems thinking that has as its primary purpose the enhancement of management practice) have some crucial commonalities that draw them together and differentiate them from other approaches.
First, given the distinction forms of knowledge production, it is clear that both OR and AST are Mode 2.
- In Mode 1 research is defined by particular scientific interests by scholars.
- By contrast, Mode 2 research is produced to satisfy the demands of particular users.
It is (Gibbons et al, 1994) : Knowledge production carried out in the context of application and marked by its:
| ❶ transdisciplinarity; | ❷ heterogeneity; |
| ❸ organizational heterarchy and transience; | ❹ social accountability and reflexivity; |
| ❺ quality control which emphasises | ❻ context- and use-dependence. |
Tranfield and Starkey (1998) argue that management research generally should adopt a Mode 2 orientation, positioning itself in the social sciences as equivalent to engineering in the physical sciences and medicine in the biological sciences.
In fact, OR and AST have already occupied this space.
This explains their joint interest in 'clients', 'customers' and 'decision makers'.
Second, both OR and AST insist that rigour can be brought to Mode 2 research by building explicit models and using these during the course of an intervention and for later reflection.
🤔 The quest for management research is a reinventing the wheel.
This is going back for not commonly understanding of the additional abstraction level at OR AST.
Despite these crucial commonalities, that make OR and AST natural bed-fellows, advocates of the one often tend to know surprisingly little about the other.
They have their own textbooks, journals and conferences and relate to their own communities of practice.
- Applied systems thinkers often refer to the classical textbooks and write off all OR as a form of hard systems thinking.
- Operational researchers have been known to see systems thinkers as either unscientific, or impractical and too much in love with philosophizing.
This paper, by looking at the last 50 years of systems thinking in a manner that is relevant to OR, hopes to correct the distortion from at least the OR side.
Throughout, the importance of developments in AST for OR theory and practice is explained.
As a final point of introduction, however, it has to be said that any account of 'fifty years of systems thinking for management' will be partial.
I acknowledge the partiality of my account, particularly in respect of its bias to UK and US sources.
🤔 What is share is the problem of managing the complexity in systems.
A summary of Boulding's (1956) hierarchy of complexity, levels:
- structures and frameworks which exhibit static behaviour and are studied by verbal or pictorial description in any discipline; an example being crystal structures
- clockworks which exhibit predetermined motion and are studied by classical natural science; an example being the solar system
- are control mechanisms which exhibit closed-loop control and are studied by cybernetics; an example being a thermostat
- open systems which exhibit structural self-maintenance and are studied by theories of metabolism; an example being a biological cell
- lower organisms which have functional parts, exhibit blue-printed growth and reproduction, and are studied by botany; an example being a plant
- animals which have a brain to guide behaviour, are capable of learning, and are studied by zoology; an example being an elephant
- people who possess self-consciousness, know that they know, employ symbolic language, and are studied by biology and psychology; an example being any human being
- socio-cultural systems which are typified by the existence of roles, communications and the transmission of values, and are studied by history, sociology, anthropology and behavioural science; an example being a nation
- transcendental systems, the home of 'inescapable unknowables', and which no scientific discipline can capture; an example being the idea of God
🤔 Other interesting notes from the paper:
- Boulding uses the hierarchy to point out gaps in our knowledge, especially our lack of adequate systems models much above level-4.
That thermostat is in reality a level-2, when it is about temperature. A good regulator is an unsolved in classic science. Are there good understandable models at level-3?
- are the systems models produced really applicable at higher levels of Boulding's hierarchy?
- Structuralist explanations can, indeed, often seem 'reductionist' - pitched at the wrong level.
- Much of the really innovative work takes place outside universities.
'Whole Systems Working': the process of involving all stakeholders of a domain in discus- sion about service change - all parties are encouraged to think about the way the whole service delivery system works, rather than focusing only upon their own service.
Vision misssons in a PDCA cycle
BSI 9-steps (LI A.Constable 2025 )
The 9-Steps to Success™ methodology, is a proven framework for turning strategy into results.
Each step builds upon the last, ensuring strategy is clearly defined, communicated, and continually improved.
Guiding by nine essential steps:
- Assessment: Understand the current state.
- Strategy: Define the mission, vision, and goals.
- Strategic Objectives: Identify key focus areas.
- Strategy Map: Visualize how objectives connect.
- Performance Measures and Targets: Track progress with clear metrics.
- Strategic Initiatives: Launch projects to drive change.
- Performance Analysis: Monitor results and identify gaps.
- Alignment: Ensure organization-wide coordination.
- Evaluation: Refine the strategy based on insights.
🤔
The real strength of this approach lies in its ability to align mission, vision, and initiatives while promoting clarity and accountability.
It empowers better decision-making, fosters continuous improvement, and ensures strategies are practical and embraced throughout the organization.
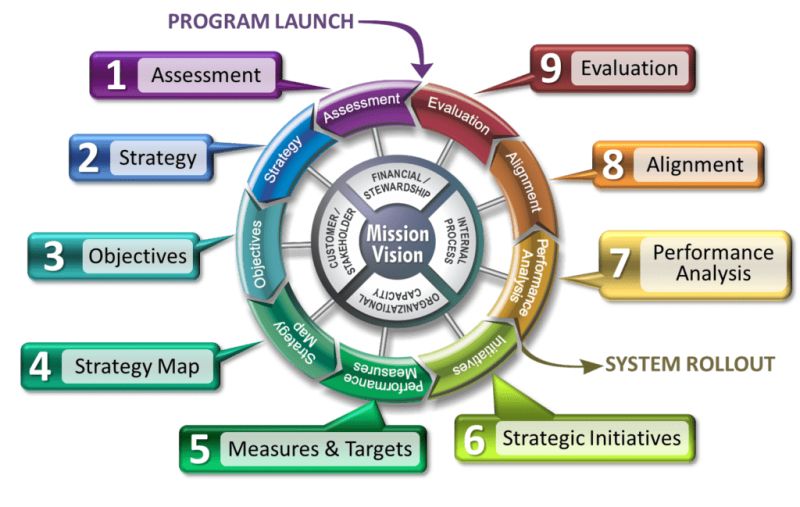
in a figure:
See left side.
Balanced Score Card (institute )
The experts at Balanced Scorecard Institute (BSI) specialize in providing consultation, training, and professional certification services to all types of organizations.
There is a lot of well sophisticated underpinned planning and little rush for doing.
The roll-out is a small step.
📚 E-2.6.3 The how of learning organisations, Jabes Jabsa
Jabes goal: 🤔💡🎭 avoiding failures, wrong results?
The everlasting issue to tame "GIGO: Garbage in, garbage out".
"The first rule of any technology used in a business is that automation applied to an efficient operation will magnify the efficiency.
The second is that automation applied to an inefficient operation will magnify the inefficiency". (‒ Bill Gates -)
Decreasing quality is an easy cost saving.
Effects by increasing failures - complaints, are not immediately measurable nor visible.
There are many constraints for a learning organisation.
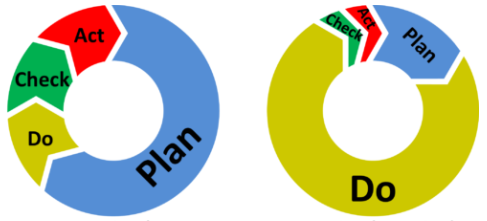
Jabes goal: 🤔💡🎭 Add all compliancy aspects to artefacts.
The Goal for Jabes started by an idea for improvement in information processing, the scope the platform design cycle.
Immediate realised that information processing itself could benefit from the same (extended scope).
🤔 got blocked at that (no Do), switched to understanding of the why.
| | Fixed setting: what | Wanted / Searched: how to | Jabes - why |
| Technology | We learn what is known | improve to innovate functionality | Manage knowledge |
| Processes | dictated by what is done | improve to innovate functioning | Share knowledge |
| People | dictated by hierarchy | autonomy in line with missions | Support in interactions |
| Structure | known ideologies as usual | changing environments to adapt | Support for decisions |
📚 E-2.6.4 Constraints in changing to learning organisations
Common fallacies, biases
In general, a bias is a distorted judgment that results from opinion, prejudice, and human cognitive limitations.
Biases rarely happen on purpose, and people are rarely aware of them. ...
And if people aren’t aware of them, wrong decisions are made.
🤔
Here are some examples of fallacies that play a crucial role in strategy:
- Planning : vastly underestimating time and money it costs to achieve goals.
- Sunk Cost: sticking to a strategy simply because you have already spent a lot on it.
- Overconfidence: bias being too confident, being right or about the future will unfold.
There are many more biases and many of them exist for a reason.
They are shortcuts that help us make decisions fast and that tend to be right most of the time in ordinary life.
Common bubbles
Bubbles are the specific groups people are part of and by which they distinguish themselves from other groups.
Their main effect is that people are more exposed to people that are similar to them, than to people that are different from them.
🤔
In strategic decision-making at least the following three bubbles come to mind:
- Company: employees of an organization tend to develop specific ways of thinking.
- Industry: each industry has its own “rules of the game” telling you how it works.
- Professional: each role in the organization has its own language, codes and habits.
Bubbles are great, because they bring likeminded people together and foster collaboration.
They are also misleading because, the stronger one identifies with a particular bubble, the more distorted one’s view on reality may become.
Common Blindspots
Blind spots are a category of cognitive limitations that distort people’s view on the world.
These are what people don’t get because of their particular viewpoint, position or perspective.
🤔
For strategic decision-making examples in not seeing new:
- Technology coming because one is so invested in an existing technology.
- Market: or customer type emerging because one is focused on another market.
- Organizational: developments going on inside being so much focused on what’s current.
Everyone has blind spots. Because, as soon as one focuses one’s attention on something, the attention moves away from something else.
In general this is a strength. To get things done, people need to be able to focus and ignore a lot of the “noise” out there.
In strategy, though, the “noise” that may not seem relevant today, may be crucial to know toward the future.
As such, these blind spots distort strategic decision-making more than other types of decision-making.
Managing the 3Bs of bad strategic decisions
The common knowledge everybody knows but hardly anyone is applying in real life. There is another nasty question:
Biases, Bubbles & Blind Spots in Strategy (LI J.Kraaijenbrink 2025)
The bad news is that there is no way to avoid biases, bubbles and blind spots. They are part of life and we even need them to survive.
But, there are a couple of steps that you can take to reduce their impact on strategic decision-making:
- Awareness, that you have them.
- Make them explicit. Identify which biases, bubbles and blind spots.
- Flip them. Deliberately generate alternative and opposing viewpoints.
- Involve others. Diversity is key here, different people and perspectives.
🤔
While perfect strategic decisions do not exist, applying these four steps can help to significantly improve their quality.
E-3 Alignment impact on organisational systems as a whole

E-3.1 The state of information processing
It'ss difficult to see much progress in the undertanding of information processing, namely analysis for goals purposes to engineering.
As such imbalance creates a bottleneck that significantly hampers the potential benefits for the whole.
- Strategic: these plannings ar going as long as risk-management schemes can cover for ill-fated turns of events.
- Deterministic: unambiguous events into information, knowledge.
- Stochastic: events in randomness whose range goes into information, knowledge.
The knowledge of the journey to share
❗
⚖ E-3.1.1 Executing information systems
The why of persistent managing problems
Many managers wonder why their team or their department always behaves so "strangely" - quite differently than expected.
The problem is, even if we think we have something to say as managers (and especially as consultants), in the end, they are self-organization systems.
If you don't know how these self-organizing systems "tick" then something different comes out than you think.
But if you ignore self-organization, you can be sure that it goes wrong.
 "Self-organization is a mechanism that enables almost sudden changes in the states of order in open systems consisting out of autonomous subsystems!” (Haken Schiepeck)
"Self-organization is a mechanism that enables almost sudden changes in the states of order in open systems consisting out of autonomous subsystems!” (Haken Schiepeck)
❶
Attention: most of the systems we are dealing with are also complex - that means that 100% certaintity that something will happen doesn´t exist.
When we think about our work, we often have to deal with teams/departments/areas - these are open systems.
- Something flows in - ideas/suggestions/concepts/inquiries/orders/projects and
- something flows out (hopefully) namely results.
Furthermore, they consist of autonomous subsystems -
- departments/teams and above all people.
❷
And, no matter what someone claims, people are autonomous.
No matter which instruction a person receives or which processes are defined - in the end, every person decides every day anew whether he sticks to the instruction or the process.
At the core, however, there are only two (three) things you "have to" do in order to achieve a change of order in a self-organized system:
- Set the control parameter correctly - so that the autonomous subsystems have room for maneuver and can orient themselves in new directions.
- To generate a signal and thus build a feedback loop that helps the autonomous systems to do what makes sense for each individual and serves the superordinate goal - i.e. to install an order parameter.
- Give the system an impulse to change.
Maturity in decisions and control
Age of TPS, Lean, Toyota way there is obvious no really progress in systems thinking.
Need to adapt rather than simply adopt?LI 2025)
If the Toyota Way works in the USA, why do so many people make pilgrimages to Japan every year to see it in action?
- TPS ? 80+ years old
- Lean ? 35+ years old
- Toyota Way ? Nearly 25 years old
Is it time to acknowledge that we need to adapt rather than simply adopt? (R.Kesterson).
 ❸
❸
An answer:
TPS wasn't designed as a universal toolkit, it evolved in a specific cultural and operational context.
After 80+ years, it's clear that simply adopting Toyota's methods doesn't guarantee success.
Lean has been around for decades, yet most Lean transformations fail outside Japan because the focus remains on tools instead of systems.
❹
What's missing?
The Theory of Constraints (TOC).
TOC provides a universal, culture-independent approach to managing constraints and maximizing throughput.
This shift requires critical thinkers who understand that copying Toyota isn't the goal-improving performance is.
At GM, the Throughput Improvement Process (TIP) used TOC to deliver $3 billion in documented results by adapting these principles to a North American environment, not copying Toyota's practices wholesale.
So yes, it's long past time to adapt.
Lean principles work, but only when integrated into our existing business culture using constraint-focused, profit-driven thinking. (K.Kohls)
Understanding what TOC (Theory of Constraints) can do is not that easy. There is an optimistic usage theory of constraints by examples.
Decreasing entropy is helping in the removal of a bottleneck.
Bottle Oiled Wheels Demonstration (Arrie van Niekerk).
Translating this as a model to another real practical situation is the hard part.
⚖ E-3.1.2 Engineering Information systems
On Fixing Belief
( SB "Decision and Control" 1966, chapter 2 )
The moral of all this is to suggest that so long as the social, economic and industrial environments change slowly, the method of tenacity that our brains employ works well. We adapt.
❺
Today, however, these environments are changing rapidly.
❻
Three modes of thinking will be found extremely relevant to the modern industrial situation Charles Peirce . "the father of pragmatism".
A fourth main method, that alone is the scientific one.
The method of tenacity produces too slow an adaptation to cope with the revolutions that the world is undergoing in every sphere.
Unless those responsible for policy-making abandon this method, and turn to other ways of exploiting their cerebral equipment, our society will not adapt sufficiently quickly, and we shall become economically extinct.
Manifestly, the nation is moving towards this fate.
Governments are selected by the method of tenacity (the class vote); they operate by this method too (the British way of life).
Industry is managed by the method of tenacity (it was good enough for my grandfather).
New thinking everywhere is blocked by the method of tenacity (this idea has not yet been tried out, let someone else make the mistakes).
Conversely, when new ideas about management and control have been discussed for a sufficiently long time, they too will be generally adopted, not by logic, but by the method of tenacity.
But this time, perhaps, it will be too late.
- The Method of Authority (2)
The second way of settling opinion without being scientific is by appeal to authority. In today's society, this mode of thinking is possibly the most important in fixing belief; it is the will of the institution.
On the face of it, this is a simple matter, with no subtle undertones; after all, people usually know when they are 'playing politics'.
- The The Method of Apriority (3)
The third and last category of non-science settling opinion. ...
An a priori argument in logic is one which begins from a set of axioms which are assumed to be true, rather than from experiences that have been undergone.
Some philosophers have argued that such axioms are innate in the mind, that they existed prior to experience (hence the name). ...
But whatever the philosophic issues, it is certainly the case that people do in real life produce all kinds of arguments which begin with unexpressed assumptions that they take to be selfevident.

- The Method of Science (4)
It is tempting, perhaps, to say that the method of science is rational, whereas irrationality characterizes most human thinking, and yet one can be rational without being scientific.
It is better to attend to a special feature of the method of science, which might be called rigour.
❼
Rigour is a precise formulation of method: something clear and definite, testable and repeatable.
If we want to use words carefully, in fact, the method of science is method.
It follows from this that we ought not to have called the three modes of thinking already described 'methods' at all.
They are habits of thinking, and the most flattering word we can use to describe them is 'procedures'.
(Some dangerous Precedents-1)
The challenge now being issued is of this form: 'You are a scientist (of some sort), which means that you have a mind trained to investigate natural phenomena, logically to take them apart with a whole set of highly sophisticated techniques, to reassemble them and to declare what makes them tick;
I have here an operation which is certainly a natural phenomenon; go ahead.' ...
❽
He is asking the scientist to research into operations and this, not surprisingly, is operational research.
... In short, if the whole team consists of the same sorts of people, a bias that has nothing to do with the work in hand will become evident.
So that is how and why operational research came traditionally, powerfully, and perhaps necessarily, to be interdisciplinary.
The strategic issue (Some dangerous Precedents-2)
There is a ready example to hand; one that affects every kind of activity today.
This is the breakthrough in automation and computation.
Given that these new facilities and capabilities exist, it is not an exaggeration to say that no enterprise is the same as it was ten years ago. ...
It is very widely said, and fairly widely accepted, that there has been a mysterious lag in the exploitation of these technological advances.
People mumble about the slow-but-sure ways of practical evolution; they hope this explains the lag, and excuses it too.
But the reason is different in kind from this.
❾
This organization is committed by its structure to an attempt to dress up the old system in modern clothes. ...
This is the recommended treatment for automation and computation today.
Instead of the technical breakthrough it is used precisely to automate men: the payroll application, the stock-control application, the costing application, the programmed lathe, and so forth.
All these developments are good enough in themselves, but the new, higher-order strategic plan that is now possible has been largely overlooked.
It is a job for operational research.

Stereotyped Scientists (Tightness issues -1)
This point is underlined because there is a strong tendency in industry today to accept for OR work only the kind of scientist that one would expect to meet within the industry anyway.
In metallurgical industries, management is accustomed by now to meeting engineers, physicists, chemists and metallurgists.
They are puzzled by the arrival in OR teams of biologists and sociologists, for example.
But these are the very people who will be of most use in solving managerial problems of tactics and strategy.
They are neither stereotyped nor committed in advance to a point of view.
Stereotyped Problems (Tightness issues -2)
If a committee of responsible people is formed, they can commission an OR study of the problem before them.
This will mean that a group of scientists, which is interdisciplinary, which has access to all the facts, which has permission to investigate difficulties wherever they may lie and to pursue ramifications of the problem wherever they may lead, is engaged full-time in objective scientific pursuit of the right answer.
While this is going on, the members of the committee can happily go about their business.
The OR report is then produced to the committee, and will have roughly the following form.
❿
The problem will be tentatively definedpossibly in terms rather different from those envisaged at the committee's first meetingand an attempt will have been made to describe the whole of the newly-discovered problem area in a systematic way.
- The facts bearing on the problem will have been collected and collated,
and fitted into this description.
- Various scientific activities will have been undertaken:
with a view to examining suitable courses of action.
- In the end, a number of possible answers will have been formulated which will be laid before the committee with an assessment of the probabilities, costs, risks and potential benefits of each.
In short, the precise problem requiring managerial decision will have been pinpointed, and the area of uncertainty that surrounds it narrowed as far as possible.
⚖ E-3.1.3 Egineering organisational systems
Run vs Change
There is that confusion on what it is about, is it about functionality or is it about the functioning.
You need always both of them but the practical question is setting the correct context for a situation.
It is a duality and dichotomy to recognize and act on.
Ying and Yang - you always have both.
As manager it’s absolute important to know when you have production and when you have projects to manage.
- If you use a project control to manage production – yes it will work, but
you pay for it with additional planning and monitoring effort.
- If you use a production control (and all agile methods are production controls) to manage projects, yes it will be much simpler to manage.
And yes, it will work, but you pay a dramatic high price: the lead time will be much longer than needed.
👁 The example is for functionality vs functioning to extended to any duality & dichotomy.
Buzzwords a root cause for anti-patterns
There should be a high demand in recognising in what is true and what not.
It is sometimes simple logical, not "science of logic" but
mathematical logic.
- The managerial or marketing human claim that: when 80% of the conditions have been met it would be successful, is complete bull-shit.
- It is even worse when the claim is: if any condition is met, than all other wouldn't matter.
DIB Guide: Detecting Agile BS
Agile is a buzzword of software development, and so all development projects are, almost by default, now declared to be “agile.”
The purpose of this document is to provide guidance to program executives and acquisition professionals on how to detect software projects that are really using agile development versus those that are not.
in a figure:
See right side.
➡ When all attributes must be met before it comes true then: when only one is failing the whole of all is failing.
👁 The example is for Agile buzz but can be extended to any buzz including Ai buzz.
Information processing suffering from Apriority methodology
ETL ELT recurring in new names by hypes, The purpose of the why what & how has been forgotten.
Data Products: A Case Against Medallion Architecture , And
The product difference
The Medallion Architecture was coined as a way to describe a structured approach to organising data lakes into layers of quality.
The name is cleverly metaphorical, drawing from the idea of medals to represent increasing levels of data refinement and quality: Bronze, Silver, and Gold.
While data management seemed more doable, with different tiers having progressively different quality expectations, each benefitting from the former, it was apparent progress without real progress.
The misdirected purpose of each layer led each tier to inherently host poor data, which compounded in the next tier.
While the three-tier architecture is aesthetically pleasing and does divide the work across teams, it goes against the natural state of data and, in fact, obstructs the natural consumption patterns of business data.
The why what and how of the lean meaning: "pull", "push" in a different conflicting context.
We don't waste much time before jumping into a case for the Data Product Ecosystem.
The lever we have used to build the case is a Push vs. Pull lens.
This lever enabled us to paint a very clear picture of the entire story through one end-to-end argument.
In contrast, a Data Product approach prioritises strong, self-contained foundations.
Instead of relying on a hierarchical transformation model, data products are designed to be reusable and self-sufficient from the start.
👁 The example is for what was started in supporting decision control but got off course.
⚖ E-3.1.4 Architecting organisational systems
Understanding an Enterprise as viable system
These perspectives are hinting to understandable processes by processes and roles.
😉 For functioning by functionality there is the well known "DevOps".
Added to that is "folioPlan".
There are more to define in the structure.
😉 For audits evaluations there are 6 shown in the video.
The on/off boarding of resources, staff is part of floor 0-1.
There are more to define in the structure.
Functioning perspectives from the sides in a video:
👁 The example is for Agile buzz but can be extended to any buzz including Ai buzz.
Decision & Control in AI buzz
AI only sees the data trail (information) not the human story.
Decision Intelligence ,
AI isn't just transforming technology (Cassie Kozyrkov Feb 2025)
A reminder that technology revolves around the human element, even in complex systems where it's hard to see the human behind the curtain:
- AI only sees the past, not the future.
- AI only sees the pattern, not the purpose.
- AI only sees the data trail, not the human story.
- AI only sees compliance, not commitment.
- AI only sees keyword matches, not understanding.
- AI only sees what you wrote, not what you thought.
- AI only sees message response times, not friendship.
- AI only sees your calendar events, not what they mean to you.
- AI only sees what was implemented, not what was considered.
- AI only sees the final decision, not bolts of inspiration.
- AI only sees what worked before, not what will work next.
- AI only sees what you did, not why you did it.
- AI only sees your digital shadow, not the real you.
In case you missed it! AI isn't just transforming technology—it's redefining leadership.
As a senior leader, the spotlight is now on you: your ability to adapt, connect, and translate AI's complexity into real business value.
Here's your quick guide to thriving in this brave new world of GenAI:
- Principle #1 - Get clarity on the who
- Principle #2 - Get clarity on the what
- Principle #3 - Be the author of meaning (how)
- Principle #4 - Think in terms of good enough (when)
- Principle #5 - Use human ratings as a proxy (where)
- Principle #6 - Try an experiment (which)
- Principle #7 - Tie it back to the business (why)
👁 The example is for AI buzz but shows it is basically needing to be reduced in that 6w1h.

E-3.2 The state of technology for systems
Given that disproving convictions is typically easier than establishing alternative ones, it may be necessary to deal first with some fallacies that all too often clog the path to a sound assessment of system analyses.
Facts are not given but observed, which necessarily entails some observer, set on task if not with vested interests, and some apparatus, natural or made on purpose.
If they are to be recorded, even “pure” facts observed through the naked eyes of the innocent will have to be translated into some symbolic representation.
The knowledge of the journey to share
❗
⚖ E-3.2.1 Ideating information processes
Making Enterprise Architecture Actionable
Bridging Strategy and Execution (LI Vijya Joshi 2025 )
Enterprise Architecture (EA) is often regarded as a strategic enabler that helps organizations align their technology landscape with their business objectives.
However, many organizations struggle to translate EA from theoretical frameworks into practical execution. ...
❶
What could be the underlying factors?
- Complex Frameworks: Many EA (Enterprise Architecture) models are often viewed as overly detailed, difficult, and challenging to implement.
- Lack of Business Alignment: If EA does not directly address business goals, stakeholders may perceive it as merely an academic exercise.
- Stakeholder Resistance: Teams may resist EA initiatives due to the belief that they introduce bureaucracy and slow down innovation.
- Perception of EA as Artifacts Management: EA should guide technology and business decisions, but it is often reduced to the understanding of artifacts and policies management rather than an evolving strategy.
Fallacies in Enterprise Architecture (EA)
It is hard to see any progress in software engineering in all those year that information processing is seen is the new era.
There is a an everlasting gap in what the logical functional perceptions are and how the technology is used.
the-book-of-fallacies
Given that disproving convictions is typically easier than establishing alternative ones, it may be necessary to deal first with some fallacies that all too often clog the path to a sound assessment of system requirements.
Imbalance creates a bottleneck that significantly hampers the potential benefits for the whole of engineering processes, our understanding of requirements should be reassessed in order to align external and internal systems descriptions;
in other words, to put under a single modeling roof business objects and processes on one hand, their system symbolic counterparts on the other hand.
❷ Failures in understanding model representation: logic, symbols and numbers.
- Facts are not given but observed.
Which necessarily entails some observer, set on task if not with vested interests, and some apparatus, natural or made on purpose.
And if they are to be recorded, even “pure” facts observed through the naked eyes of innocent will have to be translated into some symbolic representation.
- Truth (or Objectivity) is not to be found in Models
The mother of all fallacies is to think that models can describe some real-world truth.
Models necessarily reflect business and organizational concerns, expressed at a given time, and set within specific contexts.
- Requirements are not meant to be “Engineered”
This is overlooking the role of architectures between stakeholders and users expectations on one side, systems capabilities on the other side.
- Objects are not universal
Object Oriented approaches are meant to deal with the design of software components, not with business objects and organization.
While it may be useful to look at business contexts from an OO perspective, there is no reason to assume that business objects and processes can be analyzed using the semantics of software design: hope is no substitute for methodology.
❸ Failures in the homomorphic model technology translation understanding.
- “Natural” languages cannot be applied to every domain
Except for rivial solutions, significant business domains rely on specific and often very formal languages that will have to be used to express requirements.
That may be illustrated with examples from avionics to finance, not to mention law.
When necessary, modeling languages are to provide a bridge between specific (domains) of and generic (software) descriptions.
- Business concerns are not “Conceptual”
Whatever the meaning of the adjective “conceptual”, it doesn’t fit to business concerns.
Business concerns are very concrete indeed, rooted in the “here” and “now” of competitive environments, and so must be the requirements of supporting systems.
Abstract (aka conceptual) descriptions will be introduced at a later stage in order to define the symbolic representations and consolidate them as software components.
- A model is not Code
If models were substitutes for code, or vice versa, that would make software engineering (and engineers) redundant.
Surprisingly, the illusion that the information contained in models is the same as the one contained in programs (and vice versa) has sometimes wrongly taken from the Model Driven Engineering paradigm.
Despite a rationale going the opposite way, namely toward a layered perspective with models standing for abstractions of systems and programs.
- “Pie-in-the-sky” Meta-models
As any model, a meta-model is meant to map a concern with a context.
But while models are concerned with the representation of business contexts, the purpose of meta-models is the processing of other models.
Missing this distinction usually triggers a “flight for abstraction” and begets models void of any anchor to business relevancy.
That may happen, for example, when looking for a meta-model unifying prescriptive and descriptive models; having very different aims, they belong to different realms and can never be joined by abstraction, but only by design.
 ❹
❹ Failures in the homomorphic model understanding:
- logic, symbols and numbers. These are not necessary absolute. It can be likely, estimates in uncertainties or stochastic ones
- The used model might be to generic or not homomorphic. Loop-backs between the model and the reality should be in place.
- Problem & Solution Spaces must be aligned with architecture layers
System engineering cannot be reduced to a simplistic dichotomy of problem and solution as it must solve three very different kinds of problems:
- Business ones, e.g how to assess insurance premiums or compute missile trajectory.
- Functional ones, how the system under consideration should help solving business problems.
- Operational ones, i.e how the system may achieve targeted functionalities for different users, within distributed locations, under economic constraints on performances and resources.
As it happens, and not by chance, those layers are congruent with modeling ones on one hand, architectural ones on the other hand.
- Enterprise Architecture cannot be equaled to Systems
It is often confused with IT systems, which induces misguided understandings of business architecture.
The key confusion here is between architectures, supposedly stable and shared, and processes, which are meant to change and adapt to competitive environments.
But managing the dynamic alignment of assets (architecture capabilities) and supported business processes is at the core of enterprise architecture.
Functionality for organisations I
The question in this in going back tot the origins: what is architecting and what is engineering?
The difference in those words is one of class associated by a social hierarchy.
The art of systems architecting (sdincose.org: Mark W. Maier, Eberhardt Rechtin 2000 )
The continuing development of systems architecting Architecting, the planning and building of structures, is as old as human societies - and as modern as the exploration of the solar system. ...
Today's architecting must handle systems of types unknown until very recently; for example, systems that are very high quality, real-time, closed loop, reconfigurable, interactive, software-intensive, and, for all practical purposes, autonomous.
New domains like personal computers, intersatellite networks, health services, and joint service command and control are calling for new architectures - and for architects specializing in those domains.
Their needs and lessons learned are in turn leading to new architecting concepts and tools and to the acknowledgment of a new formalism, and evolving profession, called systems architecting; a combination of the principles and concepts of both systems and of architecting. ...
❺
The nature of classical architecting changes as the project moves from phase to phase.
- In the earliest stages of a project it is a structuring of an unstructured mix of dreams, hopes, needs, and technical possibilities when what is most needed has been called an inspired synthesizing of feasible technologies.
🚧 It is a time for the art of architecting.
- Later on, architecting becomes an integration of, and mediation among, competing subsystems and interests
🚧 a time for rational and normative methodology.
- And, finally, there comes certification to all that the system is suitable for use,
🎭 when it may take all the art and science to that point to declare the system as built is complete and ready for use.
⚖ E-3.2.2 Ideating information systems
About Models
(SB "Decision and Control" 1966, chapter 6 )
Let us call this mental representation of the world that is not direct perception of the world a model of the world.
The term is appropriate: models of things may be more or less accurate, and thereby better or worse able to predict the behaviour of what is modelled.
Just because they are predictive, models are open to experimentation as a means of evaluating the likely performance of the thing modelled. ...
❻
Can the model be equated with a scientific hypothesis?
Clearly not; the model does not postulate the causal mechanisms that underlie events, it simply represents the pattern of the events themselves in advance by extrapolation.
Is the model like a scientific theory then?
Again, it is not; it has no explanatory content.
A model is simply a reflection of whatever is the case, which is explicitly made available for experimentation.
The use of models
Talking about the business of science is now quite common among scientists themselves, in that the use of the term 'model' is familiar.
It seems doubtful, however, whether many scientists have thought very hard about the connotation of this term.
Many of them are prepared to say that the word has itself been imported as a neologism which really does mean either 'theory' or 'hypothesis'. ...
❼
In scientific circles, the noun 'model' is very frequently qualified by the adjective 'mathematical'.
According to the viewpoint offered here, a mathematical model is an algebraic statement of the representation already discussed.
It is not simply an equation purporting to relate one set of variables existing in the world situation with another set and this is the very much debased sense in which the term 'mathematical model' seems often to be used. ...
Since we are talking about the uses of science within enterprises, we might well ask the parallel question as to how the manager handles the model in a way appropriate to his profession.
❽
The scientist who tackles a management problem is in a totally different situation, for he declares hopefully that he comes upon the situation 'with a fresh mind'.
He believes this to be a good thing; but our explanation of his approach must begin with the alarming acknowledgment that he has by definition no historical models of the situation with which to set up correspondences to the present model, and that again by definition he cannot possibly know any of the rules for changing this model to make it fit tomorrow's reality. ...
Although the scientist has no historical models of the situation with which to compare his present model, he has other sorts of model which he can use.
It must be remembered that the managerial task is concerned with the control of large and complicated systems.
❾
The scientist, quite apart from any relationship he may have had with enterprises, has inevitably been trained to understand the structure and control of some large and complicated systems.
The model of any one system stands in some sort of correspondence with the model of any other system: the question is only whether the correspondence is great or small and therefore more useful or less useful.
If it is useful to a sufficient extent, and useful in the right way, the scientist will solve the manager's problem.

Improving models from models
The OR team as a whole is focusing spotlights from a number of different directions on the point at issue.
The understanding of each, and the value of the contribution that can be made by any, may be defective and partial.
But the insights supplement each other supposing only that the scientists have learnt to communicate among themselves and this is really the kernel of the problem of post-graduate training in operational research.
❿
It is all very well to say that the control system of an industrial company is 'like' the central nervous system in the human body: but what does this mean?
Everyone knows, in particular, that even when a comparison is basically sound, it is all too easy to employ it illegitimately: 'You are carrying the analogy too far' we customarily say.
It is fully agreed that if nothing better than this can be done, the developing methodology is futile.
⚖ E-3.2.3 Ideating organisational processes
Narratives for creativity
Autonomy, adaption is about change and innovation.
When there is no engagement the human options are blocked by an mind of top-down control, there is a search for something by the ones that are the cause.
AI hyped in being the solution for everything.
Addressings a big problem in the age of AI:
- how do we teach creativity
- develop a skill that cannot be replicated by AI
Narrative Creativity: An Introduction to How and Why (cambridge.org - Angus Fletcher and Michael Benveniste 2025)
Limits of teaching creativity as per this book:
- Over-Reliance on Ideation (Generating Ideas):
Ideas alone are not enough—narrative creativity emphasizes causality, strategy, and execution rather than just ideation.
- Logic and Computation Cannot Fully Capture Creativity:
Traditional creativity models treat creative thinking as a logical process similar to computation, relying on pattern recognition, analogy, and optimization.
- Randomness Alone Does Not Drive Innovation:
Narrative creativity provides structure and direction by connecting seemingly random ideas through causal storytelling.
- Creativity is More Than Pattern Recognition:
Simply recognizing a pattern does not guarantee originality or usefulness creativity requires a deeper understanding of how ideas work together dynamically.
- Standardized Testing and School Curriculums Reduce Creativity:
Students are trained to think in a convergent way (one correct answer) rather than exploring divergent and narrative driven solutions.
- AI Cannot Teach Narrative Creativity:
AI's output is based on statistical prediction, not true creativity.
- Creativity Cannot Be Reduced to a Formula:
Narrative creativity allows for more fluid, adaptive, and exploratory thinking, which cannot be captured in rigid frameworks.
- True Creativity Requires Failure and Iteration:
Many creativity programs do not emphasize failure, experimentation, and revision key aspects of real creative work.
We've been miseducated to see narrative as a product of creativity. In fact, narrative is an engine of creativity.
Narrative is what our brain uses to invent new plans, tools, and ways of doing.
👁 The narrative is for AI buzz but shows it is basically about asking what to ask.
Functionality for organisations II
Changing systems is needing coordination over all stages, what is does is engineering the engineering.
A question in this when that coordination is the role what it is really about, than what are all those other coordiantion roles about?
The art of systems architecting (sdincose.org - Mark W. Maier, Eberhardt Rechtin 2000 )
Not surprisingly, architecting is often individualistic, and the end results reflect it.
As Frederick P. Brooks put it in 1982 and Robert Spinrad stated in 1987, the greatest architectures are the product of a single mind - or of a very small, carefully structured team.
To which should be added, in all fairness: a responsible and patient client, a dedicated builder, and talented designers and engineers.
in a figure:
See right side.
The architect and the expanded waterfall. (Adapted from Rechtin 1991)
This waterfall is structural and impossible to avoid.
Only the scope is one of learning in iterations an option.
The dependencies are logical ones.
Doing it all monolithic or in smaller steps matters.
What could possible go wrong?
In architecting a new program, all the important mistakes are made in the first day. (Robert Spinrad, 1988).
Generally speaking, engineering deals almost entirely with measurables using analytic tools derived from mathematics and the hard sciences; that is, engineering is a deductive process.
🤔
Architecting deals largely with unmeasurables using nonquantitative tools and guidelines based on practical lessons learned; that is, architecting is an inductive process.
🤔
A systems approach is one that focuses on the system as a whole, particularly when making value judgments (what is required) and design decisions (what is feasible).
At the most fundamental level, systems are collections of different things which together produce results unachievable by the elements alone.
👁 The narrative is about levels in design, and coordination, a confused disordered context.
⚖ E-3.2.4 Ideating organisational systems
Processes, operations, serviced by platforms
what-is-platform-engineering
Platform engineering is the discipline of designing and building toolchains and workflows that enable self-service capabilities for software engineering organizations in the cloud-native era. Platform engineers provide an integrated product most often referred to as an “Internal Developer Platform” covering the operational necessities of the entire lifecycle of an application.
An Internal Developer Platform (IDP) encompasses a variety of technologies and tools, integrated in a manner that reduces cognitive load on developers while retaining essential context and underlying technologies. It helps operations structure their setup and enable developer self-service.
Platform engineering done right means providing golden paths and paved roads that match the preferred abstraction level of the individual developer, who interacts with the IDP.
This is about technology innovation, engineering, the surprise:
- s-1 goal alignment Promoting to avoid the misalignments.
- s-3 lean in its classic principles promotion and usage.
- s-4 Information quality Support for reliable data for informed decisions.
- s-5 Change Innovation Avoidance of giant steps, go for agility.
The problem of misalignment of organisations and technology is not at this level.
👁 The narrative for the technology components in a system, a confused disordered context.
The operational information flow
The operational value stream in a Pull and Push in all steps looks complex but is simple when understood.
The dichotomy of materialised information that is technical data and the transformations by processing is a continuously change in perspective.
Both are equal important in the flow.
Architecting flows inclusive for cybersecurity safety:
- Information safety is tailored to tasks/roles for a person.
- Transformation safety is tailored to the skills of a person.
- The different floorplan layouts that should be combined to each other
There are four knowledge area's each of them dedicated for the process stage in the value stream.
The anatomy and physiology details in a video:
👁 The narrative is an attempt in structuring escaping the confused and disordered contexts.

E-3.3 The state of organisations as systems
The mother of all fallacies is to think that models can describe some real-world truth.
Models necessarily reflect business and organizational concerns, expressed at a given time, and set within specific contexts.
If models were substitutes for code, or vice versa, that would make software engineering (and engineers) redundant.
Surprisingly, the illusion that the information contained in models is the same as the one contained in programs (and vice versa) has sometimes wrongly taken from the Model Driven Engineering paradigm.
The knowledge of the journey to share
❗
⚒ E-3.3.1 Describing organisations as ViSM in a narrative
Descriptive analysis vs Prescriptive analysis
- Why Descriptive analysis:
examines what happened in the past.
You're utilizing descriptive analytics when you examine past data sets for patterns and trends.
It functions by identifying what metrics you want to measure, collecting that data, and analyzing it.
It turns the stream of facts your business has collected into information you can act on, plan around, and measure.
- Why Prescriptive analysis:
Prescriptive analytics uses the data from a variety of sources, including statistics, machine learning, and data mining to identify possible future outcomes and show the best option.
Prescriptive analytics is the most advanced of the types because it provides actionable insights instead of raw data.
This methodology is how you determine what should happen, not just what could happen.
❶ Decisions goal: achieving prescriptive. Avoid happiness in seeing something descriptive.
Visions, missions, solutions
X-matrix: logical frameworks logframes Unlocking the Power of Logical Frameworks (LogFrames - Gavin Robers, Carla Owen 2025)
Logical Framework', or 'logframe', describes both a general approach to project or programme planning, monitoring and evaluation, and -in the form of a 'logframe matrix'- a discrete planning and monitoring tool for projects and programmes.
Logframe matrices are developed during project/programme design and appraisal stages, and are subsequently updated throughout implementation while remaining an essential resource for ex-post evaluation.
❷
As a methodology, the 'Logical Framework Approach' (LFA) is a systematic, visual approach to designing, executing and assessing projects which encourages users to consider the relationships between available resources, planned activities, and desired changes or results.
At its core is a theory of change management which presents the logical flow of causal outcomes between achievement of a project/programme's activity targets, and the delivery of intended results.
Logframes, to this end, enable planners to establish a hierarchy of objective or result statements -i.e. a development pathway -which articulate their best understanding of how change can be achieved.
Visions, missions, solutions
This is a monolithic idea.
A better one is using fractals in systems thinking.
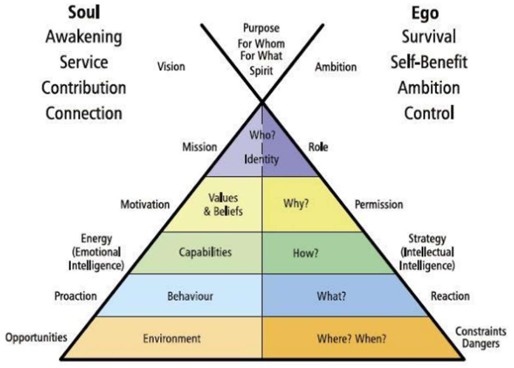 ❸
The Logical Framework Approach elegantly weaves together top-down and bottom-up approaches to project management. It brings together the classical, top-down for identifying the activities in a project, with a rigorous bottom-up checking process to make sure that these activity lists are comprehensive.
❸
The Logical Framework Approach elegantly weaves together top-down and bottom-up approaches to project management. It brings together the classical, top-down for identifying the activities in a project, with a rigorous bottom-up checking process to make sure that these activity lists are comprehensive.
- Goal - what results do we expect?
- Purpose - why are we doing this?
- Outputs - what are the deliverables?
- Activities - what will we do to deliver the outputs?
- Indicators of Achievement - how will we know we've been successful?
- Means of Verification - how will we check our reported results?
- Risks and Assumptions - what assumptions underlie the structure of our project and what is the risk they will not prevail?
The fractal propagation of Why How What
The "Why" or purpose, identity is associated with a "How" and "What" in activities.
❹
The next level in a logical frames is using that, but the context is changed.
- "How" ➡ becomes the new "why".
- "What" ➡ becomes the new "how".
- new "what" to be investigated for activities.
This can only work when at a level the activities are only detailed to what is needed at that level (autonomy).
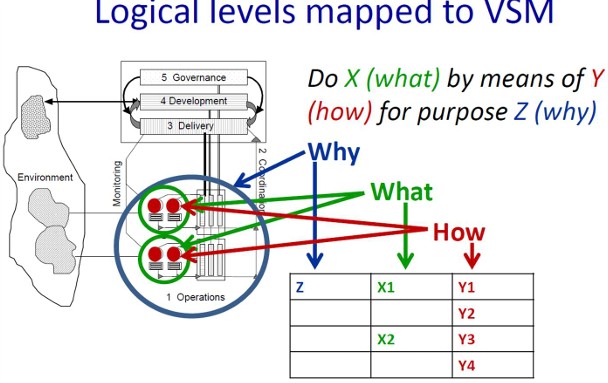 Micromanagement is excessive and unhealthy need of control, where a manager closely observes and monitors the work of their subordinates, often with a lack of delegation.
It involves constant surveillance and making decisions without consultation, leading to a direct impact on the autonomy and creativity of the team.
Micromanagement is excessive and unhealthy need of control, where a manager closely observes and monitors the work of their subordinates, often with a lack of delegation.
It involves constant surveillance and making decisions without consultation, leading to a direct impact on the autonomy and creativity of the team.
This kind of micromanagement: working on all details top-down , is not mentioned as a problematic pattern in VSM but it surely is.
⚒ E-3.3.2 Describing organisations as ViSM using a model
The Homomorphic Model
(SB "Decision and Control" 1966, chapter 6 )
The scientist must undertake this part of the task in the only languages he knows how to use with precision: the languages of mathematics, statistics and logic.
All three are highly developed scientific tools;
- basically, the first handles notions of quantity,
- the second notions of probability and
- the third notions of quality.
They are languages whose grammar and syntax is developed to a remarkable degree. The scientist therefore engages in a process of mapping each conceptual model into a neutral scientific language.
This is a process in which some of the conceptual richness must inevitably be lost, for some of that richness depends on nuance, and some on association, and some on mood none of which is transferable into rigorous terms.
But in return for this price, the scientist will obtain an account of the conceptual model that is precise and unambiguous.
❺
Returning once again to formal terms, the scientist now defines a set of transformations by which he can map contents of mind on to algebraic propositions.
The correspondences are many-one, this is what a loss of richness means.
And if the well-formulated result is to represent the antecedent set successfully, it should be homomorphic, too.
Having refined the conceptual models, the contents of mind, according to this procedure, the scientist produces two deeper-level homomorphic models and these may well be isomorphic with each other.
So he has achieved an identity between the managerial and the scientific situations which is shorn of mysticism and of poetry, and which is completely free of the bedevilling disputation that attends analogy.
A gap in mapping the model perception
It is worth noting that university teaching in operational research is devoted mainly to the study of particular mathematical techniques, and that the thinking on which this instruction seems to be based is that the modelling process is one of the direct algebraic formulation of relationships believed to exist within the managerial situation.
Where operational research has gone even further, by deliberately ignoring its roots in general science, and by trying to create mathematical models purely by abstraction from the system under study, the models have invariably been lacking in a reflection of the viability of the real-life system.
❻
It may seem that the concept of a model, even when stiffened by the substance of homomorphism, offers but a weak account of natural law.
None the less, the laws of nature with which we all grew up, are not the absolute truths most people think them.
They are essentially consequences of the conventions under which we formulate our thoughts about the world; they are deducible from the theorems which make formal languages consistent.
This is a complicated and philosophical point, and one which is therefore often missed by scientists themselves.
If the language, whether mathematical or metaphysical, is isomorphic with the world of fact, then its structure will reveal relationships which are true of the world itself.
❼
But how those relationships are expressed, where the emphasis lies, and hence in the long run whether those relationships are necessary or contingent, will depend on which language we use.
For in practice, the mapping will be homomorphicable to preserve some structure, but committed to losing some information.
Thus our account of nature is 'true', but defective, and our account of such characteristics of nature as causation and law will change with the linguistic mapping we choose.
Reflections on Models
The OR man has other concerns which do not preoccupy the academic scientist who normally regards himself as a specialist in a fairly narrow field.
He must operate across the various scientific disciplines, being sufficiently knowledgeable and mentally agile to identify the model he needs.
Although the whole field of scientific induction is difficult to penetrate, the inductions made by operational research are no more and no less difficult to understand and justify than those of any other kind of scientific activity; they simply make a more agile use of models than is customarily necessary in science.
Success in their application is a matter of practice, not on behalf of individuals but of a society.
❽
How the descriptive language is to be acceptably manipulated, how the set of rules is to be acceptably applied, and therefore what emerges that will count as a valid model: these things are social conventions.
Any society of scientists develops these conventions although what is acceptable in one branch of science, or even in one school of that branch, will not necessarily be acceptable in another.
As new facts accrue, they are fitted into the language in a way that makes them consonant with the model, which expresses their consequences in a way that reinforces the rules of induction and thence of behaviour itself.
❾
Facts, which are commonly supposed to be objective, turn out not to be unconditionally.
so: Now it is also seen that facts, which are popularly supposed to be neutral, turn out to be purposive, because of the way they are assimilated into a situation.
This state of affairs is dangerous to science, if it is not clearly recognized, for it can block new discoveries.
🤔
Progress in science might well be defined as the overthrow of a model, and its appurtenances, that has exhausted its usefulness.
A gap in the management goal
Science, in the form of operational research, serves managersof business, industry and government.
These operations too provide a social milieu for intellectual processesof decision and control.
❿
All that has been said about languages and their conventions, models and their limitations, rules of induction and their consequences, applies as well to such occupations as to scientific pursuits.
The dangers are the same; so are the opportunities.
- Management is not founded on observation and experiment, but on a drive towards a set of outcomes.
These aims are not altogether explicit; at one extreme they may amount to no more than an intention to preserve the status quo, at the other extreme they may embody an obsessional demand for power, profit or prestige.
- Management is not, even in intention, separable from its own intentions and desires.
- management is not normally aware of the conventional nature of its intellectual processes and control procedures.
It is accustomed to confuse its conventions for recording information with truths-about-the-business, its subjective institutional languages for discussing the business with an objective language of fact and its models of reality with reality itself.
Nothing emerges more clearly from this analysis than that management operates through a model of the business, a model in which:
- the organizational structure,
- the structure of costs and prices,
- the structure of labour relationships,
- the structure of production itself,
are all homomorphic mappings of the real thing.
⚒ E-3.3.3 Prescriptive organisational problem solving advice
mnemonics: CATWOE TASCOI for perspectives
CATWOE is used in business analysis and problem-solving, especially within the context of Soft Systems Methodology (SSM).
It stands for:
- Customers: Who are the beneficiaries or victims of the system? Who receives the output?
- Actors: Who are the people involved in carrying out the activities within the system?
- Transformation Process: What is the process that changes inputs into outputs?
- Worldview: What is the broader context or the bigger picture into which the situation fits?
How is the system perceived by the stakeholders?
- Owner: Who has the authority to control or make decisions about the system?
- Environmental Constraints: External constraints that impact the system's operation?
TASCOI is used in business analysis and problem-solving.
It stands for:
- Transformation: What is the process that changes inputs into outputs?
- Actors: Who are the people involved in carrying out the activities within the system?
- Suppliers: Who provides the necessary resources or inputs for the system?
- Customers: Who are the beneficiaries or victims of the system? Who receives the output?
- Owners: Who has the authority to control or make decisions about the system?
- Interveners: Who, people or entities, are of influence but are not directly involved in the system?
🤔 By analyzing these elements, TASCOI, CATWOE helps in understanding and ensures that all relevant factors are considered when defining and solving problems.
The focus is an analytical approach in systems thinking for stakeholder perspectives, emphasis on holistic problem exploration.
👁 The context is about opportunities in better understanding of problems.
Masterdata ViPlan PSM
Viability Planning
VIPLAN:
It is a methodology developed by Raul Espejo (1988 1992) to handle messy situations by using a set of heuristic activities that guide thinking and actions.
The VIPLAN methodology emphasizes the context in which these messy situations are handled, paying particular attention to the cybernetics of the situation through the Viable System Model (VSM).
This approach involves activities such as creating rich pictures, naming elements, and structuring problem situations, which helps to navigate complex problems more effectively.
It's used in various fields to address issues that are not clearly defined and involve multiple perspectives.
🤔 Problem Structuring Methods:
PSM
These are a family of approaches in operational research and systems thinking designed to tackle complex, "messy" problems that can't be clearly defined or easily solved.
These methods help to structure problems, facilitate understanding, and generate solutions by incorporating multiple perspectives and fostering participatory decision-making.
Some well-known PSMs include:
- Soft Systems Methodology (SSM): Developed by Peter Checkland, this method uses rich pictures and conceptual models to explore complex situations.
- Strategic Choice Approach (SCA): Developed by John Friend and Allen Hickling, this approach focuses on decision-making in uncertain and complex environments.
- Strategic Options Development and Analysis (SODA): Developed by Colin Eden and Fran Ackermann, this method uses cognitive mapping to support group decision-making processes.
🤔 PSMs are particularly useful in situations where there are conflicting interests, high levels of uncertainty, and complex interdependencies.
Use case ViPlan
A ViPlan narrative Introducing the VIPLAN Methodology -with VSM- for Handling Messy Situations – Nine Lessons (Researchgate: Stephen Harwood 2021)
Does an explanation using a narrative.
It is presented as a heuristic and comprises a set of six activities whichact as ‘pointers’to guide thinking and actions.
The methodology’s contribution rests uponits explicit focus upon the context within which messy situations are handled.
This drawsattention to the cybernetics of the situation (Cybernetic Loop), which can be made senseof using the Viable System Model. ...
It is to the Operational Research (OR) domain that our attention turns, as it has its own well-developed tradition for the pragmatic handling of problems, in particular, ill-structuredproblems.
In contrast to design thinking withits focus upon artefacts, the OR orientation is more orientated to issues of organisation andhow that can be improved (e.g. logistics, production, social problems).

See figure.
🤔
The methodologycomprises six activities.
These are connected by two loops, the inner Cybernetic Loop and the Learning Loop.
These two loops denote, respectively, the operational and informational domains of the situation.
The operational domain is the realm of activity, interactions andgovernance, with emphasis upon the mechanisms of communications, where a mechanism is defined as an observed invariance in the dynamics of the operational domain (Harwood 2011).
| Action | Thinking |
| 1 Finding out: rich picture | 2 Problem structuring: naming |
| 4 Improve organisational conditions | 3 Organisational diagnosis |
| 6 Effect change | 5 Modelling & Analyses |
The text from the figure in a table:
There is constant evaluation in validity of the model to the world.
The informational domain is the realm of meaning, with emphasis upon the content of communications.
In practice they are intertwined.
Moreover:
- the left hand side pertains to realworld engagement (action),
- whilst the right side relates to the abstract world of conceptuali-sation (thinking),
-
though in practice, this is also intertwined.
👁 The context is about narrative understanding used models related to the real world.
⚒ E-3.3.4 Prescriptive technology problem solving advice
Technical debt, missing alignment!
Information processes, software engineering:
Don’t get caught in refactor hell
There are two types of development:
- Prototype Development: The goal of Prototype Development is to prove (or disprove) a hypothesis as quickly and cheaply as possible, such as “does this technology work?”.
- Sustainable/Scalable Development: If you already know what you want to build and roughly how to build it (and have the money to fund it), this is probably the way to go.
If your application must scale quickly or is mission or safety-critical, this is your only option.
Prototypes are generally not designed to scale or stick around for a long time.
Observability, testability, and expensive in-house engineers are optional.
For many, outsourcing is their only option.
This might be the quickest and cheapest way to build working software, but with some serious limitations - it must be relatively simple and not mission/safety-critical.
These codebases also have very short shelf lives - possibly only weeks, not months.
🤔
Sustainable development starts slow.
Whether you use Waterfall or Agile, upfront work is required.
You don't need to solve every problem right away, but sustainable software must be based on good assumptions and abstractions.
It must be designed to scale on some basic level regarding load, complexity, and team size.
Best practices and observability infrastructure must be there from the beginning, or you will never catch up.
❗ The team that builds and manages this application must also be experienced and have a particular set of skills and discipline.
This isn’t software development, it’s software engineering.
Once in a while, refactors will be required to maintain team efficiency and reliability. ...
The reason for some of these refactors might be that an assumption may not pan out, or a business requirement changed, but that's fine because your software was designed to handle this.
in a figure:
See right side.
What is the opposite of alignment?
If you answered yes to any of the following questions, then I would strongly consider sunsetting instead of refactoring.
- Does more than 50% of your code need to be modified to clear your debt?
- Is your software based on poor abstractions or incorrect data models?
- Is most of your software not written using best practices?
- Is your tech debt not limited to decoupled subsystems?
👁 The context is an engineering situation what is caused by management decisions.
The scientifical methodology
The formulation of a method typically involves creating a systematic approach to achieve specific goals or solve problems.
A robust method must incorporate the following characteristics:
- Clear: well-defined steps , easy to understand, leaving no room for ambiguity.
- Definite: precise objectives, leaving no doubt about what it aims to accomplish.
- Repeatable: yield consistent results when applied under the same conditions.
- Verifiable: Mechanisms to verify effectiveness by observation, experimentation, analysis.
These principles ensure that the method is reliable, rigorous, and practical for application.
The idea of scientific repeatability under conditions of chaos and uncertainty is a fascinating challenge.
🤔 Typically, scientific experiments aim to produce reliable, consistent results by controlling variables and maintaining stable conditions.
However, when studying chaotic systems like:
- weather patterns,
- financial markets , or
- even biological ecosystems,
The very nature of chaos resists predictability and exact repetition.
In these cases, scientists rely on statistical methods, probability, and patterns to identify trends or behaviors within the chaos.
For instance, the butterfly effect in chaos theory illustrates how small changes can lead to vastly different outcomes, making absolute repeatability challenging.
Still, identifying these underlying structures can lead to meaningful insights.
👁 The context on scientific approach including the uncertainties by patterns aside outcomes.

E-3.4 Processes at viable systems, internal
A knowledge perspective, systems usually distinguish between:
- organisational, business concerns: what's about,
- informations processing, software engineering: what's required,
- execution, operations: how to use it
With a shared goal using a shared goal: planned changes, comprehensive and seamless model-based engineering applied to shared business functions.
The functional view of information can be further detailed across enterprise architecture layers int he now and future.
The knowledge of the journey to share
❗
⚒ E-3.4.1 Changing the static state, processes
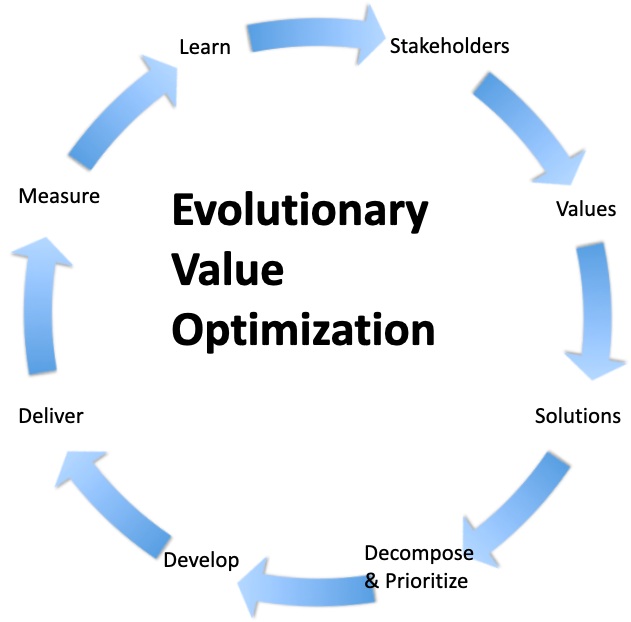
The cycle of evolutionary value optimisation
Changing an existing situation requires understanding in what to change, strategy and how to change, engineering.
In simple obvious situations that is an overkill.
For complicated situations planning is not ambiguous but when it is complex it is by the unknowns.
Conformation of this for example at:
The Evo cycle is similar to SIAR but extended to 8 processes in continuous improvements.
In this the focus is on changing processes (input/ouput).
Too simplificated if this would be all.
Lean, Agile, The cycle of evolutionary value optimisation (EVO)
An other link is giving the continuing evolvement,
Tom Gilb Resources (A.Shalloway)
A large cost strategy (it takes a month-to-years) can be decomposed in two ways:
-
Task Decomposition:
- This lists the tasks needed to do, before we can expect the strategy to deliver value.
- No task alone delivers much value, they do not deliver improvement on their own.
- Task are only components for a system. Functionality only seen in the system as a whole.
-
 Sub-strategy steps result into value:
Sub-strategy steps result into value:
- which can be implemented in any sequence,
- each of them will deliver value,
- can be implemented in parallel.
A strategy can potentially be decomposed into steps, not always.
Decomposing into sub-strategies under the mentioned conditions avoids unnecessary dependencies.
This well designed design for development is not the commodity mindset.
Properties shared with other approaches:
- There is decomposing strategy.
- The dichotomy: functionality - functioning.
- Seeing the system as a whole.
Lean, Agile, theory of constraints
There is a well known Theory of Constraints (TOC), in very simple terms: 'identify the factors, currently restricting your production flow, and ease them, or remove them, to improve productivity.'
❶
We, (Chris Dale, Al S, Steve T and I) decided that it might be useful to articulate these more-complex ideas, and see if we end up with something useful.
Properties shared with other approaches:
- Only partial requirements knowledge when starting.
- A level of autononmy for what is to be solved.
The 'Penta' Model insted of "iron triangles"
The classic Iron triangle is often used as a scapegoat.
❷
Problems with the Iron Triangle.
- Poor definitions: “Quality” is not defined at all. It is not referred to in the plural (qualities like Usability, Security, Reliability…. and many more).
- Insufficient Scope: Example: The Budget, Financial Resources, is always defined and assumed to be the financial cost until successful delivery.
It never hints the life-cycle maintenance costs of great variety and magnitude.
This is irresponsible narrow-mindedness of the most dangerous kind.
These later costs are often 10x or more, greater than initial costs.
- Lacking critical factors: This is partly for those costs, but the project management process is critical, and missing.
The notion of balancing multiple Stakeholder values, against all long-term and short-term resources is missing.
The notion of a prioritization policy is missing.
We 'all' know that if you do not engineer the system up front, to have low maintenance costs, you can ‘save' on initial costs, and get disastrous maintenance costs, and failure rates, as a direct result.
Not surprisingly, in PMBOK 4.0 the PMI came up with a suggestion of have six dimensions, with risk making it into the equation, with the “Project Management Star”.
❸ Of the six risks: Schedule (time), Budget (cost), Scope and Quality, Risk. Resources in PMbok the time element is not present in PENTA.
 Penta concept Co-invented by Al Shalloway and Tom Gilb, 2022 PENTA: Purposely Efficient Nodes for Top Attributes.
Penta concept Co-invented by Al Shalloway and Tom Gilb, 2022 PENTA: Purposely Efficient Nodes for Top Attributes.
The PENTA is a simplified model of 5 basic conflicting forces in any system, which can be adjusted to give a more optimum balance.
- Scope: is the specified set of stakeholder and system functions (what it must do) and constraints (what it must not do). Scope draws a border around a given system.
- Values: is the specified set of stakeholder values ('wants', 'needs', 'wishes', 'visions') and system qualities, including system performance attributes ('potential values' for stakeholders).
- Efficiency: is 'effectiveness-to-costs ratio'. Effectiveness includes all stakeholder-values actually delivered. The costs are life-cycle costs, not just ‘capital’ costs. This is a view outside the black box of Designs.
- Resources: are any critical and prioritized, set of limited resources for the system lifecycle, such as time, money, people, space.
- Designs: are any types of ‘implementable ideas’ (designs, strategies, architecture, solutions) which we use, in order to deliver a ‘best available’ balanced delivery of Values,Efficiency, Resources, and Scope, the other 4 Quints.
🚧 Imperfect: The Penta model is never complete, updated or fully detailed. It can be simplified and summarized.
It can view selected components, that are useful for consideration.
Obviously this model is just another model to help elaborate, evaluate and discuss all aspects of a project and it’s items.
A piece of a puzzle is how to practical manage change.

- Risk driven by focussing on 5 areas to solve
- The question of when it is delivered
- A 3d representation, dodecahedron: there are six areas top, botom, axis.
Having in the SIMF model for Jabes:
- Only an orientation for tasks and roles in flows,
- Two planes for the operations in the now and two for the future,
- a representation of an extended cube, six areas three axis where two are doubled (five),
❹ The approach of a dodecahedron model offers enough variety for changes to functionality and functioning.
Project management (PM) activities to model into that.
⚒ E-3.4.2 Enabling autonomous changes improvements
Risk-Based Thinking: RBT
Mastering Risk-Based Thinking in Quality Management (F.M.Boles 2004)
In today's dynamic business environment, the ability to anticipate and manage risks is critical to sustaining excellence and delivering quality products.
How to Use Risk-Based Thinking:
- Identify Risks: Analyze processes, stakeholders, and market trends.
- Evaluate Impact: Assess the likelihood and consequences of identified risks.
- Implement Mitigation Measures: Develop control plans to minimize risks.
- Monitor and Review: Continuously track risk indicators and improve strategies.
in a figure:
See right side.
Risk-based thinking (RBT) is a proactive approach embedded in modern quality systems, particularly ISO 9001:2015.
The Homomorphic Model
(SB "Decision and Control" 1966, chapter 8 )
In reaching the quantified answer to a particular problem, however, he has to substitute numbers for the letters that stand in the mathematical equations.
What are these numbers, and where do they come from ?
Certainly, each of them is a measurement of some kind.
❺
People behave for the most part as if a number, having been measured, must certainly be 'right'.
In fact, reflection will show that this claim cannot often be made, and that the circumstances in which it can be made are extremely difficult to define.
We can exemplify the possibility: to say that there are three people in the room is to utter what is probably an incontrovertible statement.
To enumerate the number of people milling about in a cocktail party, however, is not so easy; one would hardly take offence if told that one's count was in fact mistaken by one or two.
Many of the counts made in industry for managerial purposes, it must be conceded, are probably not exactly right.
Moreover, the measurements used by managers for taking decisions are not often straightforward enumerations; they are more likely to measure some kind of average.
Thirdly, they may not even pretend to be legitimate averagesonly estimates of averages.
So a particular measurement may turn out to be simply one of a number of estimates we might have obtained; a different answer would be 'right' had we taken a few more instances, or done the measuring on another day.
In fact, the comforting solidity of the digits neatly listed in front of the manager collapses under scrutiny.
❻
There are many kinds of uncertainty attached to each number, and there is no need for present purposes to identify them all.
It is sufficient to recognize that the real truth is something we never apprehend (which is why some people contend that 'real truth' is a chimerical concept altogether): it is always lurking elusively behind the measurements we are able to take.
All this adds up to one simple assertion: the quantifiers of real-life situations are variable.
Since the special circumstances which generate a number are never exactly repeated, never exhaustively enumerated, and never precisely measured, we are not entitled to regard that number as a sharp point on a scale.
❼
The theory of probability, which is central to this undertaking, is a full-scale subject in its own right.
All competent OR men know something about it; all competent OR groups contain mathematical statisticians.
But it is not an easy subject and there is no space here to go much further with the exposition.
For, despite the existence of a vast range of mathematical statistical techniques, dilemmas still exist at the level of philosophy of science.
No secret can be made of the fact that eminent statisticians disagree about the fundamental nature of probability and how to compute it.
None the less, science has a great deal to offer the decision-taker in considering the impact of chance and risk.
For the plain fact is that the man who has not studied these matters, but who works on an intuitive notion of what is likely, will often mislead himself quite wildly.
Teleology adaption and evolution
It seems that we must add to the theory of the homeostat, and its blind entropic process, a selforganizing capability which tends to reinforce survival-worthy patterns within the variety generator. ...
But it is unequivocally clear, despite the confused terminology, what this feedback loop does.
It interferes with the alleged randomness with which the variety generator poses solutions, as well as vetoing further attempts to pose the same unsatisfactory solution as before.
❽
Done by: the pain-pleasure (algedonic) loop, the reward function, teaching, bribing, the epigenetic landscape what the mechanism is most aptly called depends on the kind of organism being considered.
❾
A more complete understanding, as taught by nature, of what selforganization involves reveals why (to the observer imbued with teleological insights) these systems appear to be purposive.
The self-organizing system with the threefold responsive mutation device discussed here may be called a sentient ecosystem.
Laissez-faire and Direction
Beliefs in the central-state control or the free market expectation.
The laissez-faire economy was originally conceived as one in which all producers were allowed to make what they liked.
The term has been extended and is now generally used to refer to any theory of control which relies upon a natural system of checks and balances between the sub-systems of the whole.
The mandatory approach to control, on the other hand, declares that the laissez-faire mechanism is too slow, too arbitrary, and likely to involve local and short term disbalances.
These may be acceptable in some inanimate system or even in a population of cabbage aphides; but they are not acceptable in a human society where they may involve pockets of high unemployment, severe poverty and social injustice of other kinds. ...
There is some cybernetic justification for using either of these approaches; but there are two points to note.
❿
Firstly, whereas either of these systems may work in practice for a given epoch of time, each may easily turn into a self-defeating system.
- The laissez-faire economy may become so preoccupied with its own stability as to
- run down and die of high entropy; or it may
- become an ecological centrifuge which is so outward-looking in the search for nourishment (e.g. foreign markets) as to wreck its own interior, delicately balanced, economy.
- The mandatory system, on the contrary, may become so powerful that it overrules the self-organizing homeostats of the subsystems altogether, so that they become de-natured.
If this happens, the control will fail: because it cannot supply requisite variety without this aid.
The second point is this. Although both these approaches masquerade as theoretical solutions to the problems they seek to handle, they are not intellectually neutral approaches to the facts.
⚒ E-3.4.3 Plan, prepare the future of states & processes
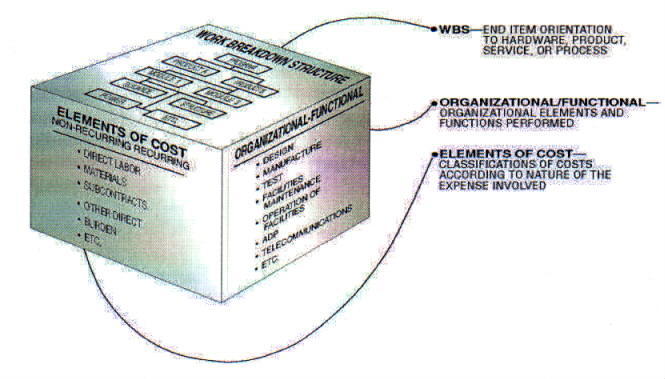
"no plan survives first contact with the enemy"
Rigor planning from the 1950ths went into frustrating micromanagement.
The program evaluation and review technique (PERT)
is a statistical tool used in project management, which was designed to analyze and represent the tasks involved in completing a given project. ...
PERT was developed primarily to simplify the planning and scheduling of large and complex projects.
During project execution a real-life project will never execute exactly as it was planned due to uncertainty.
This can be due to ambiguity resulting from subjective estimates that are prone to human errors or can be the result of variability arising from unexpected events or risks.
Planning in a WBS
A work-breakdown structure
(WBS) in project management and systems engineering is a breakdown of a project into smaller components.
It is a key project management element that organizes the team's work into manageable sections.
The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMI) defines the WBS as a "hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables.
A WBS provides the necessary framework for detailed cost estimation and control while providing guidance for schedule development and control.
PMI's Practice Standard identifies two major types of work breakdown structures:
- Deliverable-oriented WBS, also known as Product breakdown structure uses key deliverables to group each work in the project.
- Phase-oriented WBS groups the work under key phases or stages of project lifecycle.
👁 The content is a scientific approach for planning in a VUCA world.
mathematical technical cybernetics
The processing by models and numbers evoluated by the increasing options in technology.
Acta Cybernetica Vol_26_4
Cyber-physical systems (CPS) are systems in which software and physical parts interoperate deeply.
The physical part of these systems is often modeled by differential equations.
When properties have to be verifed on these systems, for instance the feasibility or the safety of a mission assigned to a robot, the solution of such differential equations is generally required.
Even if Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE) are mostly considered to model cyber-physical systems, obtaining an analytical solution to this class of equations is a complex issue and approximations obtained with numerical methods are sometimes suffcient to check a given property.
However, for some applications an approximation is not enough and an enclosure of the exact solution is required.
AI and the digital ecosystem
Analyzing chaotic systems requires statistical methods that embrace complexity and unpredictability.
Some of the most effective approaches include:
- Time Series Analysis: Techniques like Fourier Transforms or wavelet analysis help detect patterns, frequencies, or trends within chaotic data.
- Monte Carlo Simulations: These simulations use random sampling to model the probability of different outcomes in chaotic scenarios, especially in financial systems or weather forecasting.
- Fractal Analysis: Measures like the fractal dimension analyze patterns of self-similarity in chaotic systems, revealing hidden structures.
- Bayesian Inference: This method incorporates prior knowledge with current data to make probabilistic predictions, even when the system is uncertain.
- Nonlinear Regression and Dynamical Modeling: These tools fit mathematical models to chaotic systems, capturing nonlinear relationships and predicting future behavior.
- Entropy-Based Measures: Techniques like Shannon entropy or permutation entropy assess the degree of randomness or complexity within chaotic systems.
- Stochastic Processes: Methods like Markov chains or Brownian motion describe systems where randomness plays a key role, suitable for chaotic environments.
- Network Analysis: This identifies connections and relationships in complex systems, like ecosystems or social networks, where chaos is prevalent.
👁 The content is a scientific approach for prescriptions in a VUCA world.
⚒ E-3.4.4 Enabling planned top-down changes with insight
Information Channels
The good regulator paradigm is very ambiguous.
The mechanistic channels have got indicators but the algedonic just kept at: the dichotomy: pain vs pleasure.
🤔 Sentience is the ability to experience feelings and sensations.
Sentience is an important concept in ethics, as the ability to experience happiness or suffering often forms a basis for determining which entities deserve moral consideration, particularly in utilitarianism.
The sympathetic system is part of the autonomic acting on stress that governs involuntary physiological responses.
The parasympathetic system, is responsible for distress and recovery.
🤔 In the liberaphobia there are three negative stress reactions: Authoritarianism, Destructiveness, Conformity.
These are associated with the "fight or flight" response.
The proposal for two channels (a dichotomy) for six attributes:
| x | | Mechanistic | | Sentienstic |
| Extern | 1 | Intervention Regulation | 1 | Libertarianism, minimal intervention vs Authoritarianism |
| 2 | Resource Allocations - finance | 2 | Nurturing, growth and development vs Destructiveness |
| 3 | Environment Interrelationships | 3 | Creativity vs Conformity, Individualism |
| Intern | 4 | Operational Interrelationships | 4 | Democracy, collective decision-making vs Authoritarianism |
| 5 | Coordination (Sympathetic) | 5 | Autonomic Constructiveness vs Destructiveness |
| 6 | Monitoring (Parasympathetic) | 6 | Autonomic Preservation vs Conformity, Individualism |
👁 The content on scientific approach fir the cybernetic good regulator in a VUCA world.
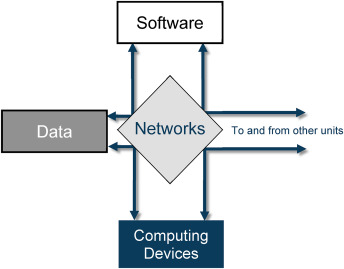
AI and the digital ecosystem
It's just distributed computing:
Rethinking AI governance (Milton L. Mueller 2025)
The digital ecosystem is a distributed cybernetic system for the production and distribution of communication, information and control capabilities.
It is composed of four basic technical components: computing devices, networks, data and software. ...
The breakdown of the digital ecosystem into these four components is analytically useful.
Standpoints, perspectives, from:
- economic: distinguish between markets for devices, data, software and networking services.
- technical: to see how specific manifestations of computing, such as platforms or machine learning applications, can be broken down into combinations of these components.
- political or policy: to see how public control of each component requires different regulatory or governance tools.
... The most important rationale for an ecosystem approach is that it highlights processes of evolution, co-evolution, and selection that lead to survival or extinction, growth or decline, of the socio-technical systems built around digital technologies, providing a framework for addressing the dynamics of distributed control, evolving capabilities and decentralized decision-making.
🤔
What we now call "AI" is actually a large, diverse set of machine learning applications.
Machine learning applications use feedback loops from digital data (and humans) to train complex software models (an algorithm or some derivative of a neural network) to recognize inputs and produce or predict desired outputs; they are configurations of innovative software architectures, powerful processors, high-speed networks and abundant sources of digitized data.
The only thing all machine learning applications have in common is their dependence on the four elements of the digital ecosystem.
👁 The content on scientific approach for applying information systems for systems in a VUCA world.

E-3.5 Services at viable systems, external
Given that services are by nature shared and symbolic, they can only be defined between systems.
The seamless integration of enterprise systems into digital organisational, business environments calls for a resetting of:
- value chains in regard to enterprise architectures,
- more specifically supporting assets.
Planning: the core of a systems survival.
Viable systems learning capabilities: planning should be defined by knowledge from the content in algedonic events.
The knowledge of the journey to share
❗
🎭 E-3.5.1 Promises for known products (goods, services)
DevOps double cycle- PortfolioPlan
The DevOps double cycle model "DevOps" is well known but just the half of what is going on.
❶ The need for planning products, operations with a budget.
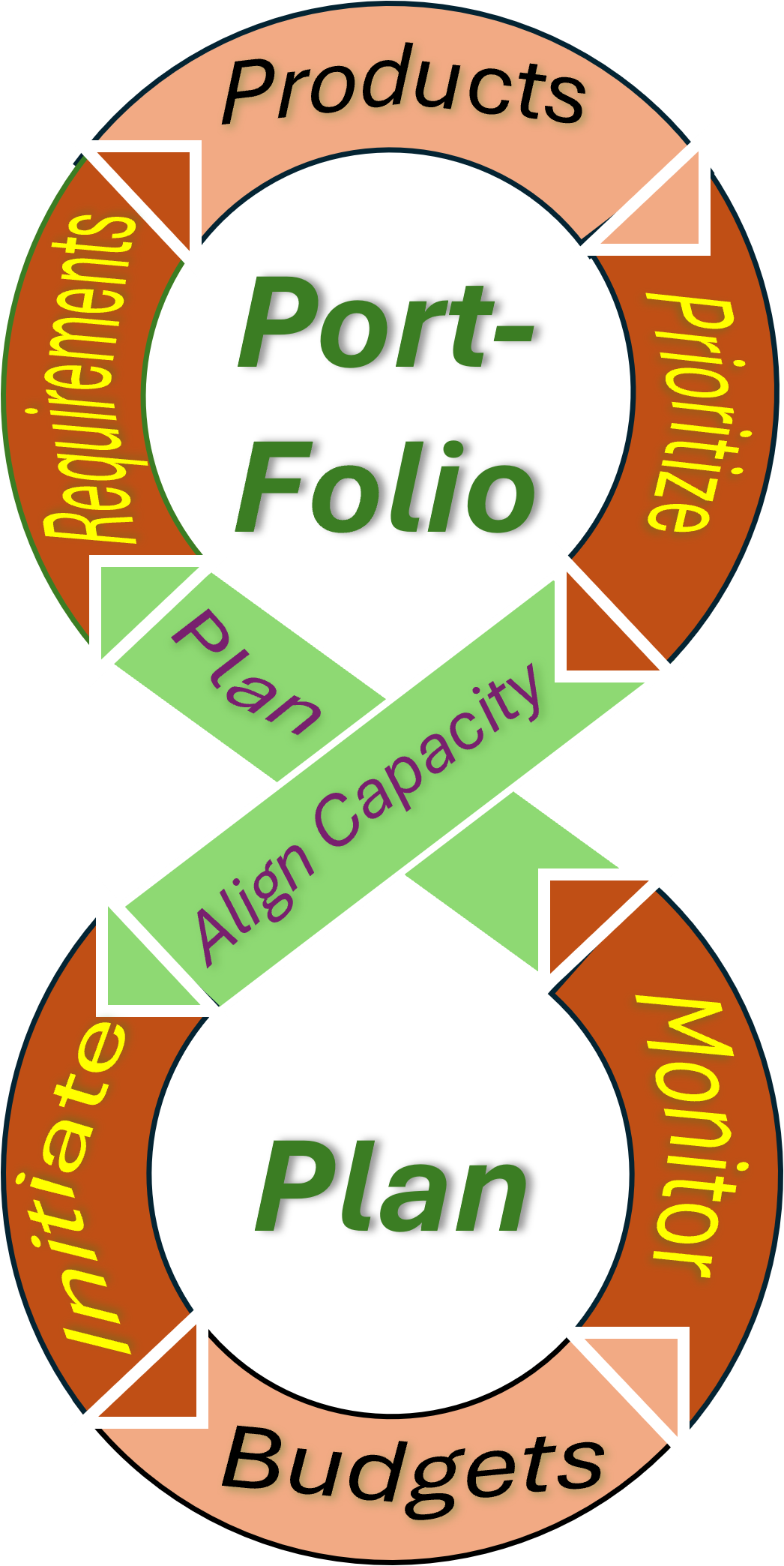
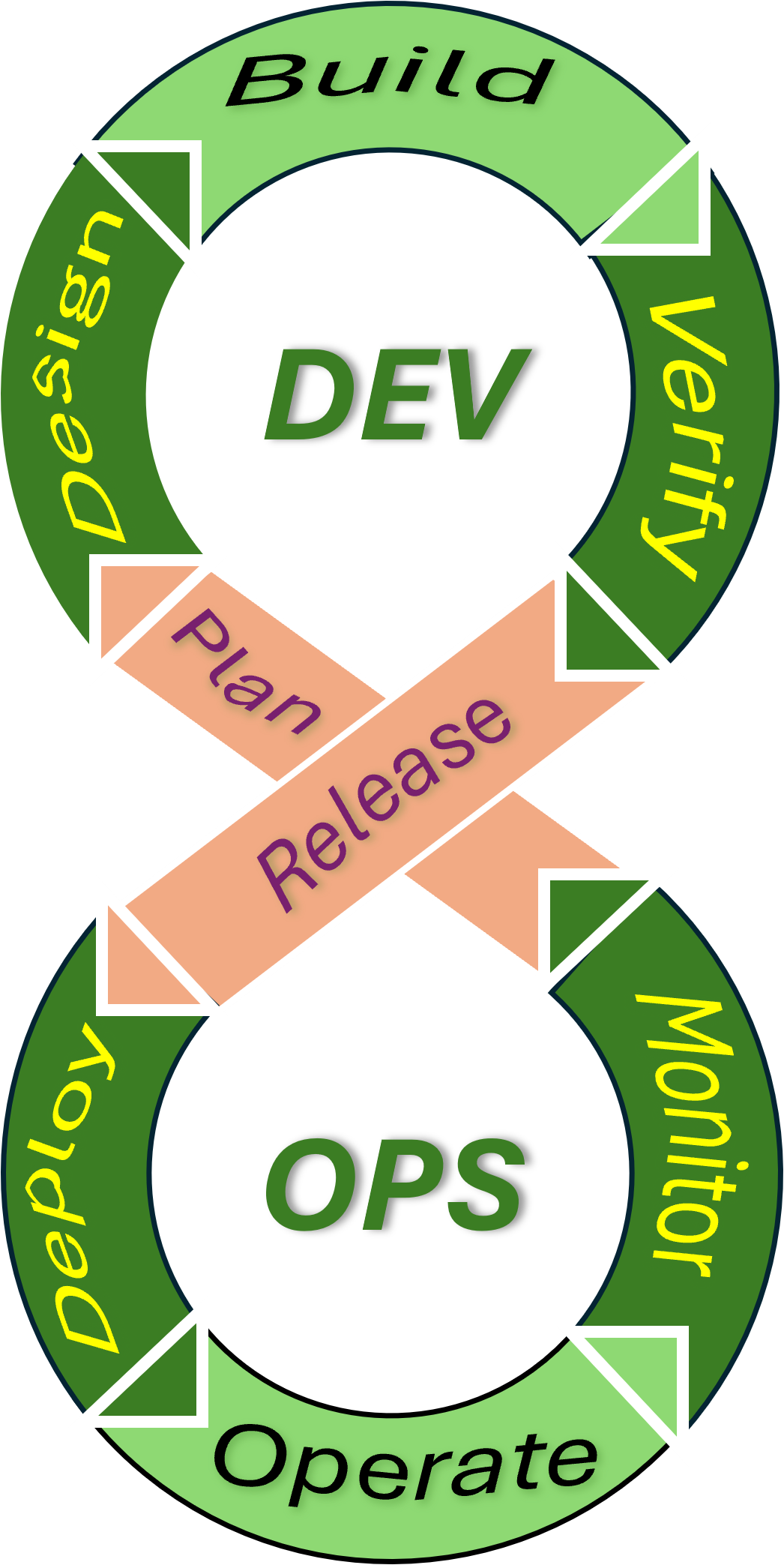 🚧
🚧 The "DevOps" model:
- Development is not about coding but: architecting engineering creating products, flows.
- Operations is executing the flow mainly in autonomy and initiating proactive improvements.
🚧The "PortfolioPlan" model (gap):
- 🕳 Product management
the accountability for decisions what to engineer and build.
- 🕳 Financial budgets
the financial enablement to do work for product flows in the now and than.
Frontend, backend double cycles
Marketing, customer intelligence, Services by governments are well known and seen as important activities.
There is no double cycle model name for it "Pro-visionBuyer" is used here for that.
❷ The need for interactions for the buyers of the purpose.
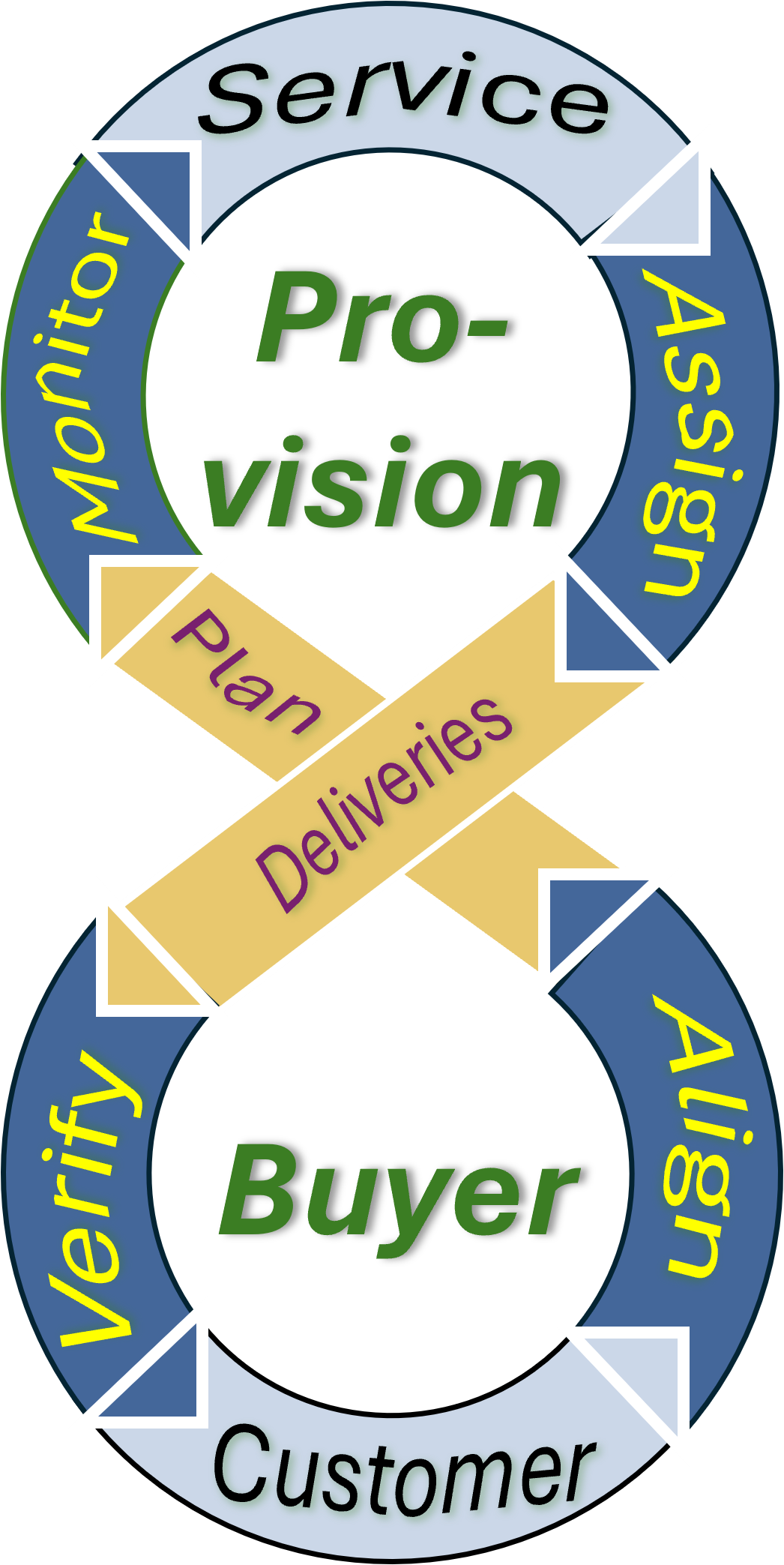
 🚧
🚧 The "Pro-visionBuyer" model:
- Vision, Provision is about having a vision into provision for a purpose. It is not about that any possible idea should be serviced.
- Buyer is about the who in the purpose that has the benefits of it.
🚧The "MotiveAssets" model (gap):
- 🕳 Supply chain management
the accountability for decisions how engineered components are kept being deliverde or kept functioning.
- 🕳 Assets, Financial - operational
the enablement in functioning of the operational flows.
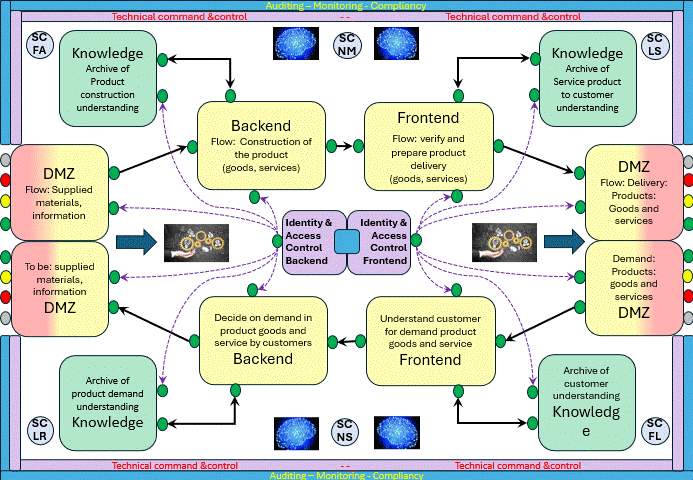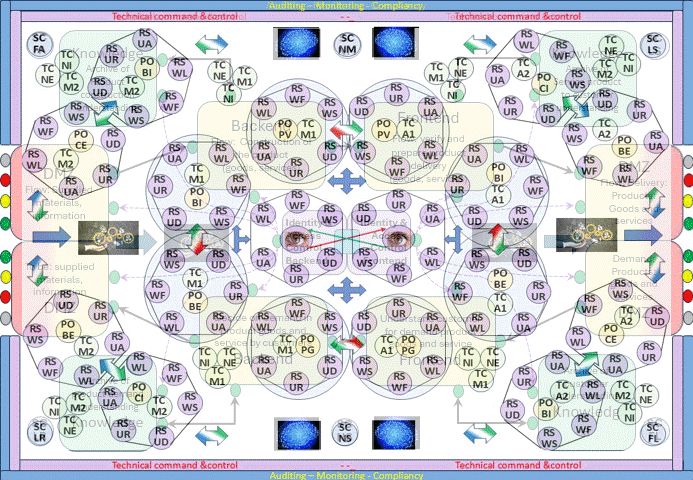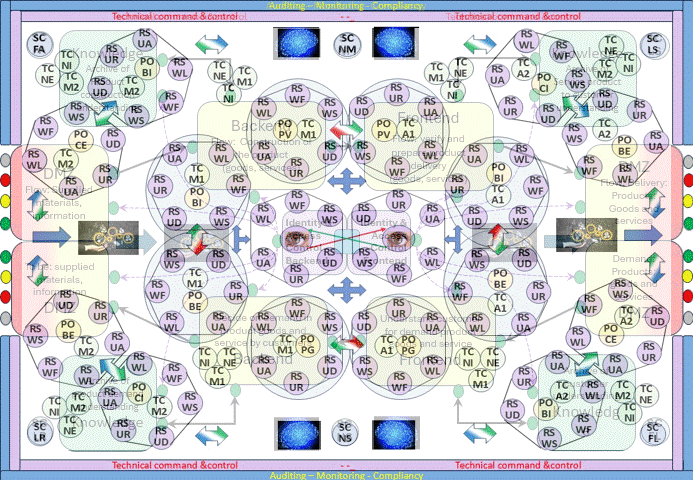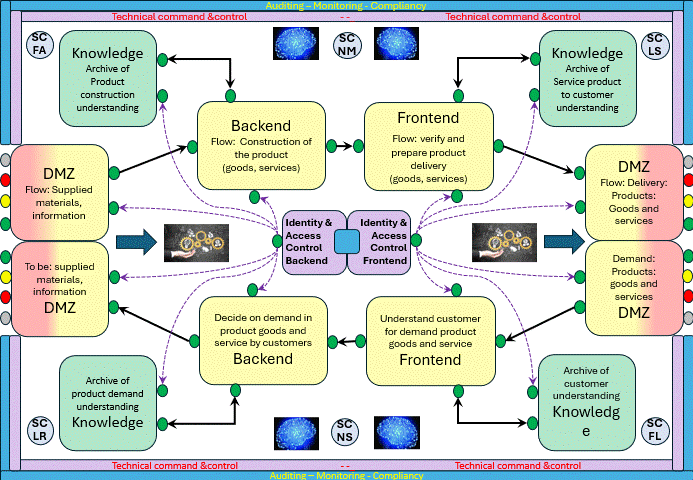
systems by micro-level
Analysing systems is usually done by looking at a complex macro-level situation and trying to understand that by simplifying.
There is that continuous duality change for information vs process.
❸ Starting at a micro level, anatomical:
- segmented areas, materialised information.
- Processing units to do logical transformations.
- Primary and secundory areas - processes.
The two components in the processing units have each a full classification in six attributes for safe usage.
All of the double cycles have a role somewhere in the whole.
The double cycles a fractal on their owner
The "DevOps" model got very much attenrion in the idea that solving something in technology woudl solve the system as a whole.
This is a failure from the bias in tha idea.
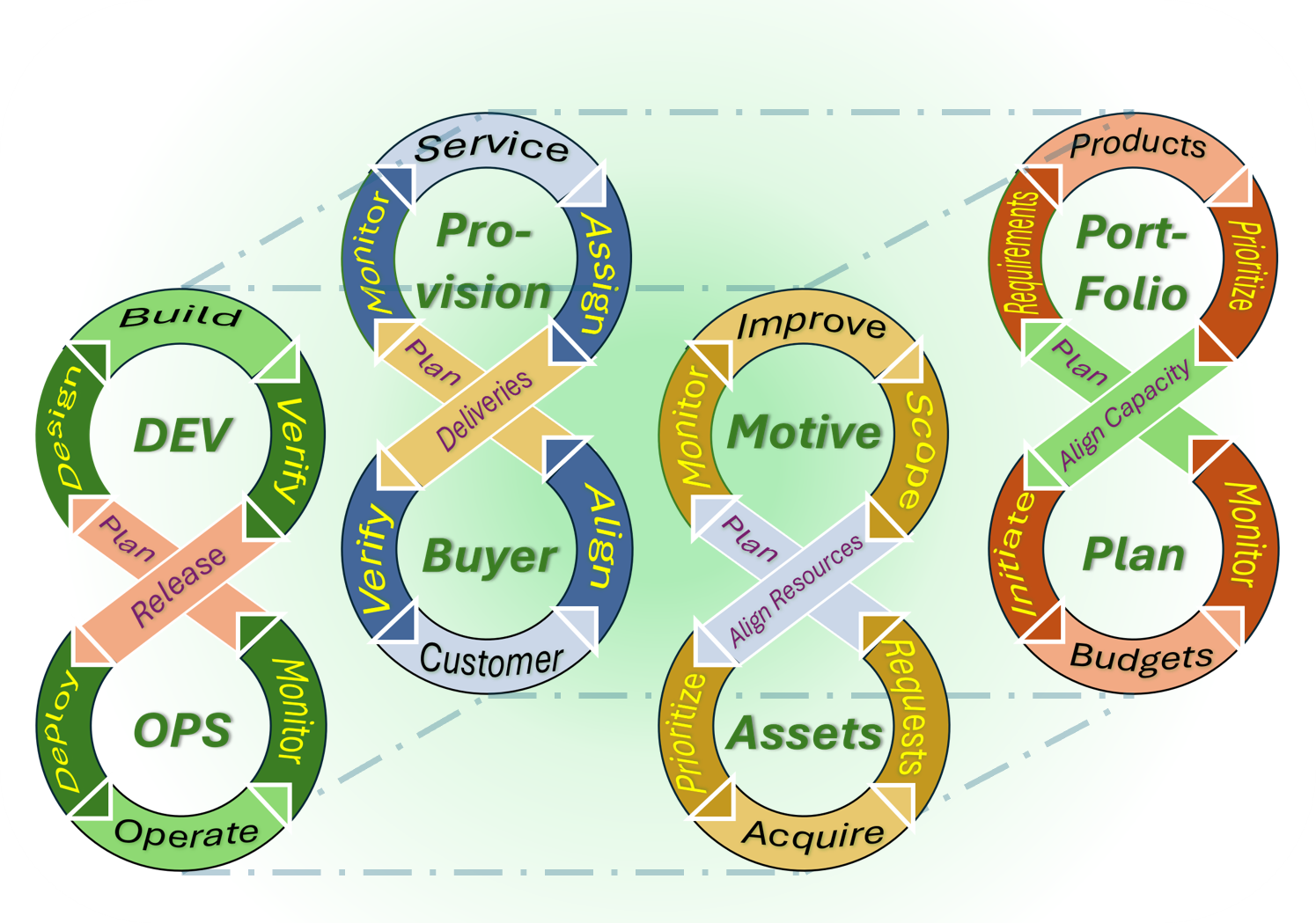
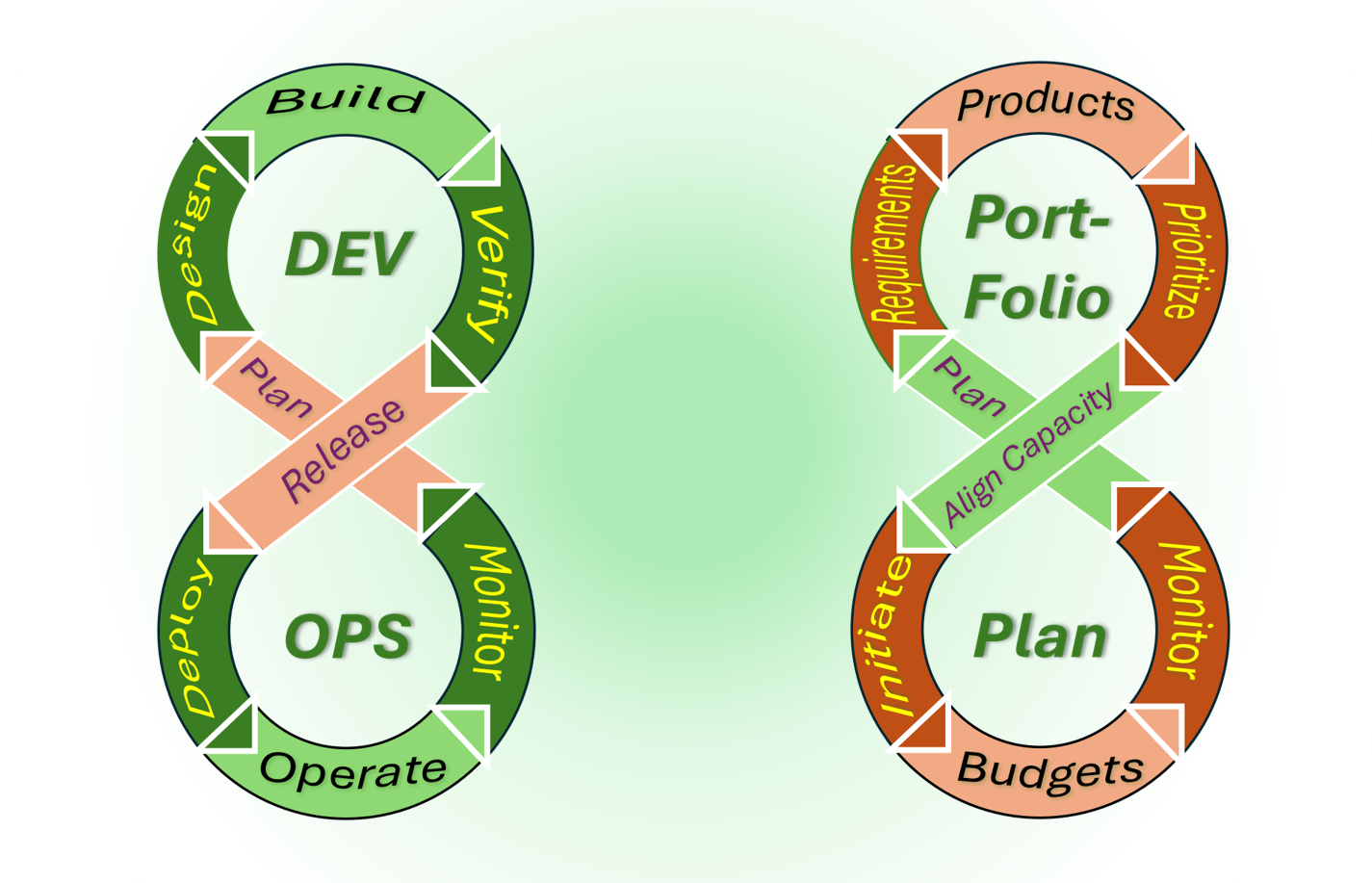 Just using the technology mindset is missing the purpose provision and the enablement in supply.
There are only two dichotomous where the system (SIMF SIAR) using flow has four.
Just using the technology mindset is missing the purpose provision and the enablement in supply.
There are only two dichotomous where the system (SIMF SIAR) using flow has four.
❹ All four double cycles to position in a quadrant enabling a system with flow.
🎭 E-3.5.2 Deliveries of known products (goods, services)
Managing social communities
the_Austrian_School_Ludwig_von_Mises_and_FA_Hayek (Researchgate: Christopher Westley, William L. Anderson, Scott A. Kjar 2011)
To understand the thoughts of Ludwig von Mises and Friedrich von Hayek it is necessary to understand their fundamental views on economics.
Like their Austrian School predecessors—Carl Menger, Eugen von Böhm-Bawerk, and Friedrich von Wieser—von Mises and von Hayek believed that a free economy was the natural outgrowth of a free society.
Free men voluntarily transact with each other in free markets, and society itself is an outgrowth of these voluntary transactions.
Further, free markets serve as a method of allocating society’s scarce resources: In particular, prices serve to highlight consumer desires, and entrepreneurs are guided to business decisions that support consumer preferences.
Mises roundly criticizes war socialism—defined as increased state control of the economy during wartime—in Germany and Austria, claiming that it hastened their final collapse.
In both countries, socialists and democrats rushed to fill the void left by the destruction of the monarchy, but neither group held to the classic liberalism that had dominated European political thought for a century.
❺
The key to Mises’s views on war and socialist calculation are found in his criticism of central allocation of goods and government control of methods of production.
In “Economic Calculation in the Socialist Commonwealth,” Mises made an important point about the role prices play in resource allocation, and especially in allocating factors of production.
For him, prices of final goods are determined by the interplay of suppliers and demanders in the market, and, following Menger, the prices of these final goods in turn are imputed to their higher-order factors of production.
The value of the factors of production used for any class of goods, such as war goods, is compared with the value of those same factors used in the production of other goods.
This allows resource owners to better select how to allocate scarce resources among competing products, and allows entrepreneurs to select production methods among alternate allocations of capital, labor, natural resources, and time.
❻
In 1949, Mises published his most important work, "Human Action".
This includes a chapter titled “The Economics of War.”
In it he again stresses that free markets are based on peaceful cooperation and how this cooperation falls apart when “citizens turn into warriors” (p. 821).
One virtue of the combined idea of limited war and free markets was the recognition that free trade was a necessary prerequisite for peace because it makes little sense for a country to wage war against its trading partners.
In the absence of free trade, conflicts over territory, religion, ideology, culture, and a host of other issues fester with no countervailing reason for calmness or rationality among the belligerents.
❼
In his most famous work, The Road to Serfdom (1944), Hayek writes that planning is “the deliberate organization of the labors of society for a definite social goal” (p. 56).
However, in democracy no single social goal exists.
“And we all think that our personal order of values is not merely personal but that in a free discussion among rational people we would convince the others that ours is the right one:
- The lover of the countryside who wants above all that its traditional appearance should be preserved and that the blots already made by industry on its fair face should be removed,
- no less than the health enthusiast who wants all the picturesque but unsanitary old cottages cleared away, or
- the motorist who wishes the country cut up by big motor roads,
- the efficiency fanatic who desires the maximum of specialization and mechanization,
- no less than the idealist who for the development of personality wants to preserve as many independent craftsmen as possible.
They all know that their aim can be fully achieved only by planning—and they all want planning for that reason.”
The key Hayekian objection is that because no central planner can possess all of the disparate pieces of knowledge found in society, no central planner can allocate resources as efficiently as can the decentralized market.
⟲ ⏳
By questioning the state as a force of social good, the writings of Mises and Hayek on economics and war went against the intellectual tide of their day.
Free markets, and especially free trade, were not the causes of war; indeed, these served as bulwarks for peaceful international relations.
Mises especially saw socialism and statism as evils that set people against one another, and he believed that “national purpose,” emphasized by collectivist states, led to conflict and war.
Hayek believed that planning led to serious economic resource misallocation, both in the present and in the future, leading people down a road to serfdom.
Liberaphobia
The balance quest for local autonomy vs central authority.
Escape from Freedom (The Fear of Freedom).
Fromm's writings were notable as much for their social and political commentary as for their philosophical and psychological underpinnings.
He distinguishes between "freedom from" (negative freedom) and "freedom to" (positive freedom).
❽
On its own. "freedom from", it can be a destructive force unless accompanied by a creative element "freedom to" the use of freedom to employ the total integrated personality in creative acts.
This, he argues, necessarily implies a true connectedness with others that goes beyond the superficial bonds of conventional social intercourse: "...in the spontaneous realization of the self, man unites himself anew with the world..."
In the process of becoming freed from authority, Fromm says we are often left with feelings of hopelessness that will not abate until we use our "freedom to" and develop some form of replacement of the old order.
However, a common substitute for exercising "freedom to" or authenticity is to submit to an authoritarian system that replaces the old order with another of different external appearance but identical function for the individual: to eliminate uncertainty by prescribing what to think and how to act.
❾
As 'freedom from' is not an experience we enjoy in itself, Fromm suggests that many people, rather than using it successfully, attempt to minimise its negative effects by developing thoughts and behaviours that provide some form of security.
These are as follows (Escaping freedom):
- Authoritarianism: Fromm characterises the authoritarian personality as containing both sadistic and masochistic elements. The authoritarian wishes to gain control over other people in a bid to impose some kind of order on the world, but also wishes to submit to the control of some superior force which may come in the guise of a person or an abstract idea.
- Destructiveness: Although this bears a similarity to sadism, Fromm argues that the sadist wishes to gain control over something. A destructive personality wishes to destroy something it cannot bring under its control.
- Conformity: This process is seen when people unconsciously incorporate the normative beliefs and thought processes of their society and experience them as their own. This allows them to avoid genuine free thinking, which is likely to provoke anxiety.
Fromm examines democracy and freedom. Modern democracy and the industrialised nation are models he praises but it is stressed that the kind of external freedom provided by this kind of society can never be utilised to the full without an equivalent inner freedom.
❿
Fromm suggests that though we are free from the totalitarian influence of any sort in this kind of society, we are still dominated by the advice of experts and the influence of advertising.
The way to become free as an individual is to be spontaneous in our self-expression and in the way we behave.
This is crystallised in his existential statement "There is only one meaning of life: the act of living it".
🎭 E-3.5.3 Promises for unknown products (goods, services)
Is Agile a fit in the 3d model?
Although Agile is now to in end in the sizzle, the question is woudl it fit in this?
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools ➡ culture, latency
- Working software over comprehensive documentation ➡ community, integration
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation ➡ polity, goal attainment
- Responding to change over following a plan ➡ economy, adaption
TLDR Answer: yes it fits.
The AGIL reference could accidental or intentional, it doesn't really matter.
Increasing your Agility: An interview with Dave Thomas (2015)
How attempts for getting more efficient have developed in time, it is logical.
The intent behind the Snowbird meeting was simply to explore what commonalities we could find between the different ways the 17 participants created software.
We discovered that, although the day-to-day executions were very different, we all shared a set of values-things that were important to us.
Managing Sentienstic Interactions
In the quest for control & decision there is no logical reason in a choice in the balance quest for local autonomy vs central authority.
However there not only an abstract technology argument but there also the Sentience one.
These are for more difficult to represent in some abstract symbolic representation because there is no technology that is able to measure those.
Only rough estimators as indication for some assumption are known practices.
👁 Sentienstic solution approaches including the uncertainties by patterns aside outcomes.
Managing Mechanistic Interactions
State space methods are a powerful approach to time series analysis, offering flexibility and adaptability in modeling complex dynamic systems.
Here are the key pros and cons of using state space methods, Pros:
- Flexibility: State space models can represent a wide range of time series processes, including ARIMA, seasonal models, structural models, and nonlinear systems.
- Handling Missing Data: Kalman filtering and smoothing allow for efficient estimation even with missing observations.
- Dynamic Adaptation: These models can incorporate time-varying parameters, making them ideal for nonstationary data and regime-switching models.
- Multivariate Modeling: They easily extend to multiple time series (vector state space models), enabling joint modeling of interconnected variables.
- Inference and Forecasting: Kalman filtering provides optimal state estimation and forecasting under Gaussian assumptions.
- Bayesian Extensions: They integrate well with Bayesian methods for probabilistic inference using Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) or Variational Inference.
- Structural Interpretation: Unlike purely statistical models (e.g., ARIMA), state space models often provide meaningful, interpretable components such as trends, seasonality, and irregular effects.
 Cons:
Cons:
- Computational Complexity: State space estimation (e.g., using Expectation-Maximization, Kalman smoothing, or particle filters) can be computationally intensive, especially for large datasets or nonlinear models.
- Model Specification Sensitivity: Choosing the right state space representation and transition dynamics requires domain knowledge and can be challenging.
- Numerical Stability Issues: Kalman filtering can suffer from numerical instability, particularly when dealing with ill-conditioned covariance matrices.
- Learning Curve: Implementing state space models requires an understanding of matrix algebra, probability theory, and filtering techniques, making them less accessible than simpler methods.
- Parameter Estimation Challenges: Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) or Bayesian inference may converge slowly or require strong prior information for identification.
- Software Dependence: While there are powerful libraries (e.g., Statsmodels, TensorFlow Probability, KFAS in R), their implementation can be more cumbersome than traditional time series models.
👁 Mechanistic solution approaches including the uncertainties by patterns aside outcomes.
🎭 E-3.5.4 Deliveries of created products (goods, services)
The context interacton chain
Having the ViSM model aligned to Siar and all others there is that resulting 3d model with many fractals.
All four fractals seen should be a fractal on their own.
From an organisation into the social community as a whole.
A higher abstraction level is the purpose, activities, interactions of the community organisations are a component of.
Combining the several abstractions:
| x | | Economy Mechanistic | | Community Sentienstic |
| Adaption | 1 | Purpose alignment in an understood perspective.
Craftmanship | III | Understandable accessible knowledge information for all relevant purposes and the involved human skills.
The educational system part of community purpose. |
| Goal | 3 | Intended purpose functioning fulfilling (Customer). | IV | Fulfilling community goals purposes: in all ambiguities, internal conflicts by all stakeholder differences. |
| Integration | 4 | Design functionality in differnt flow perspectives. | I | Shared goal by motivated community people: with all compromises, give-and-takes in choices. |
| Latency | 5 | Perspective verifications to purpose achievement. | II | Purpose achievement Perspectives: with all exceptions approximations inaccuracies and uncertainties |
Adding the time dimension into the stretched cube.
The time dimension is thew first important one to be involved, the option in the model is using a long repeating strain.
In the four strains there are two repeating sequences in the orderings: 5,4,3,1 and 1,2,3,4,5.
There are two starting points from a state into the future:
- Adaption: from supporting the organisation by technology
- Integration: From technology innovation by organising
In the quantum world all possible options are assumed to exist, the choice: which is the one to become the perspective in your reality.
The ordered ViSM strains in time shifting fractals:
| Organisation | | Frontend | | Technology | | Backend |
| 4 | Plan (budgets) | 1 | community, integration | 3 | OPS | 5 | |
| 5 | | 3 | Buyer | 1 | economy, adaption | 4 | Assets |
| 1 | culture, latency | 4 | Pro-Vision | 5 | | 3 | Motive |
| 3 | Portfolio | 5 | | 4 | Dev | 1 | polity, goal attainment |
| 4 | Plan (budgets) | 1 | community, integration | 3 | OPS | 5 | |
| 5 | | 3 | Buyer | 1 | economy, adaption | 4 | Assets |
| 1 | culture, latency | 4 | Pro-Vision | 5 | | 3 | Motive |
| 3 | Portfolio | 5 | | 4 | Dev | 1 | polity, goal attainment |
The purpose (5) is left open is the generalisation for is what is to do in a specific case.
👁 Solution approaches: including uncertainties for purposes and fulfilments in the whole.
The mechanistic & Sentienstic interactions to model
There are two perspectives for the whole:
- Economy: Product management life cycle and control,
- Community: balancing autonomy vs central authority.
🤔 In a two dimension view the result is a stretched cube for both.
Combining those thinking in a sphere would be more appropriate.
The are four staged types of interest toe evaluate in many perspectives as dimensions:
- building an organisation / community.
- enabling to fulfil product (goods / services) deliveries.
- processes & processing categories.
- Management control, hierarchy authority accountability.
- Changing time horizons, time spans, from paste to future.
- Social interactions by the components as humans and their tools.
The number of dimensions and their interaction are far too many for easy understanding.
The operational information flow
There are four interest area's each of them dedicated for the functioning stage in some process.
It is not anymore on thinking in getting more profits but in removing constraints that are holding off the achieve better results.
The physiology and neurology details in a video:
👁 Solution approaches: for the now and than with choices understanding risks and uncertainties.

E-3.6 Retroperspective of the KA journey
Knowledge Assurance (KA) is a framework or set of practices designed to ensure:
- accuracy,
- reliability and
- effectiveness
of knowledge within an organization.
It involves the systematic management of knowledge to maintain and enhance its quality.
The challenge in this: It are not the results being important, it is the journey of learning, understanding.
The knowledge of the journey to share
❗
🚧 E-3.6.1 The why of learning organisations
Information processsing - Problem space
There are some fundamental questions:
- system-1: Everything is about software or data. The result is a confused situation (cynefin).
Software has different challenges to tackle, Large or small security and safety critical systems.
Who is responsible for the data, how does the data flow?
ordering the disorder for the goal:
- platforms / tools / middelware
- the business applications (data/code, business rules)
- support in EiS (Executive information systems) for decisions.
- helping to fulfill in regulator compliancy.
- system-2: where do changes and enrichment of data take place in processes and systems?
different challenges required different types of processes!
- system-3: What is the comamnd & control?
Projects are an abstraction that has lost its relevance except in very specific types of endeavours.
What is the theory behind them and why they don't work.
- system-4:
Cost models, where delivery is considered largest cost, need to be dissected and changed.
What matters is the much larger cost % in maintenance.
- system-5:
technology is a significant factor in what process can/may work.
Technology decisions can have a 10x (order of magnitude) impact on software delivery.
Problem Solving - Knowledge Assurance KA
Key components of KA, Knowledge include:
- Creation: Developing new insights, ideas, solutions by research & innovation.
- Documentation: Accurately recording knowledge: structured & accessible manner.
- Validation: Verifying: accuracy, reliability through peer reviews, audits, validations.
- Dissemination: Sharing, distributing knowledge ensuring it reaches the right people.
- Maintenance: Updating & refining knowledge keep it relevant and up-to-date.
- Utilization: Applying effectively for informed decisions & improved processes.
By implementing Knowledge Assurance, organizations can ensure that their knowledge assets are trustworthy, up-to-date, and valuable for achieving their goals.
Autopoiesis, rise - survival of the organisation
Luhmann’s theory of autopoietic social systems (David Seidl 2004)
The central concept around which the theory of social systems as developed by the later Niklas Luhmann is built is the concept of autopoiesis, originally developed by the two Chilean biologists Humberto Maturana and Francisco Varela.
Autopoiesis (< Greek: autos = self, poiein = to produce) means self-(re)production. Autopoietic systems thus are systems that reproduce themselves from within themselves, as for example a plant reproduces its own cells with its own cells.
Luhmann argued that the basic idea of autopoiesis applied not only to biological but also to a large number of non-biological systems. He thus appropriated the originally biological concept, modified it and applied it to the social domain.
In a similar way as biological systems social systems were thus conceptualised as systems that reproduced their own elements on the basis of it own elements.
- Living systems are cognitive systems, and living as a process is a process of cognition. (Maturana and Varela 1980: 13)
- On the level of its operations the autopoietic system does not receive any inputs from the environment but only perturbations (or irritations), which then might trigger internal operations in the system.
In other words, external events may trigger internal processes but they cannot determine those processes.
Luhmann (2000: 401) in this sense speaks of a “trigger-causality” [Auslösekausalität] instead of a “performance-causality” [Durchgriffskausalität].
In this sense the operations of an autopoietic system are defined as its cognitions; life and cognition are one and the same.
Hence, everything that has been said about life applies equally to cognition: cognition is a self-referential, autopoietic process.
This stance is generally known as Radical Constructivism (also: Operative Constructivism) expressing the idea that all cognitions (ideas) are constructs of the respective cognitive system and do not in any way reflect any kind of external reality. ...
According to Luhmann we can distinguish three types of social systems: society, face-to-face interaction and organisation.
All three systems are social systems insofar as they reproduce themselves on the basis of communications.
They are however different types of social systems insofar as they reproduce different types of communications.
Homeostasis - autostatic, organisational degrade - downfall
There are two different types in activity:
- autostatic, which relates to the concept of resisting change or maintaining stability automatically.
This term is often used in the context of systems or mechanisms that self-regulate to resist changes and maintain their current state.
- homeostasis, is any self-regulating process by which an organism tends to maintain stability while adjusting to conditions that are best for its survival.
🚧 E-3.6.2 The what of learning organisations
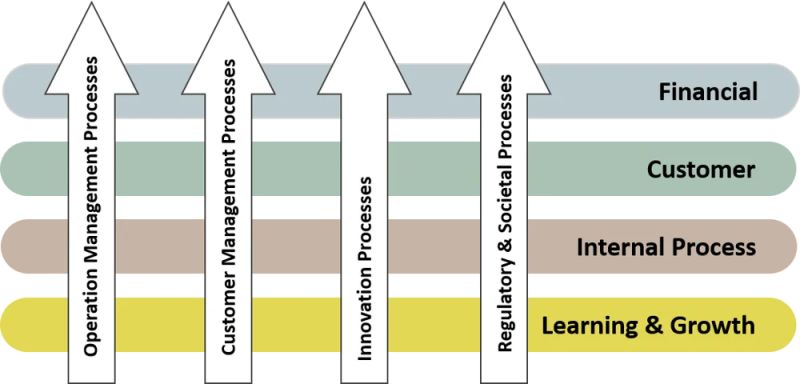
Strategic themes
There should be an alignment in the components of strategy (system-4) and execction (system-3, sytem-1) in the product (services goods) domain.
Why do strategic themes matter? (LI Andrew Constable)
Strategic themes are the backbone of an effective organisational strategy.
- Focus: They drive alignment across the organization, concentrating efforts on high-impact areas.
- Clarity: They simplify communication by organizing complex strategies into understandable areas.
- Accountability: Each theme has clear ownership, ensuring responsibility for execution.
- Alignment: Objectives and initiatives stay connected to overarching goals.
I recommend around three strategic themes. More than that can dilute focus, while fewer may not capture the full scope of the strategy.
When well-defined, strategic themes transform ambitious goals into actionable pathways, ensuring everyone in the organisation moves in the same direction.
Why strategy vs execution?
There should be an alignment in the components of strategy (system-4) and exaction (system-3, system-1) in the organisational domain.
Strategy vs. Execution: A Galactic Struggle, Episode #25 (LI Randy Kesterson)
If your strategy deployment and execution plan feels like a choose-your-own-adventure novel with no ending, it might be time for a LEAN reality check.
The Strategy Guy is lost in a sea of PowerPoint slides, and the Lean/CI Leader is left wondering what strategy actually is.
- Annual Strategic Planning:
Where we launch 50+ initiatives, finish none, and then proudly start over!
- Kaizen Mania:
We optimize the breakroom coffee machine, but forget to fix the production line.

in a figure:
See right side.
Strategy vs. Execution: Do they even know each other?
What is the opposite of alignment?

Technical debt, missing alignment!
There should be an alignment in the components of strategy (system-4) and exaction (system-3, system-1) in the operational domain.
Don’t get caught in refactor hell
I believe that most managers are aware of technical debt and that it is bad, but fail to understand its true impact.
This misunderstanding can lead to some very costly mistakes.
One of those mistakes is keeping a codebase around past its expiration date.
Yes, codebases have expiration dates.
Tech debt usually means that your code, abstractions, concepts, or data models no longer make the most logical sense.
If you have any outdated dependencies, areas of friction, or lack of testability - that also counts.
Was triggered by:
Underspending in fixing quality (LI Marc H Weiner 20235)
Tech debt isn’t an exceptional problem; it’s ordinary. Just like real infrastructure, it needs ongoing investment—not just an occasional “cleanup sprint” when things start breaking.
But when companies ignore it for too long, the system reaches what I call the Software Event Horizon: the point where the cost of making any change is so high that even the simplest features take forever, or result in bugs. And refactoring is impossible. There's no going back.
🚧 E-3.6.3 The how of learning organisations, Jabes Jabsa
the goal of ethical compliant processes
Several perspectives for compliant processes.
- Safe environment Risk reducing: lost service, data breaches.
- Information quality Avoiding: failures, wrong results.
- Impact on persons Explainable personal data usage is mandatory.
- Understandable algorithms Predictable results avoiding unwanted discrimination.
Some of the details for compliant processes are organizational missions, others are legal regulations.
Structuring ideas and able to explain new idea´s to other persons is difficult, is time consuming and possible a mission impossible.
It must have:
- all relevant information
- simple to understand
- left out what is not relevant
Silent killer of change
The Silent Killer of Continuous Improvement (LI A.Ozel 2025)
Why Does Your OpEx Program Fails?
In boardrooms across the globe, leaders are scratching their heads, wondering why their meticulously planned Continuous Improvement initiatives are failing to deliver the promised results. The truth? It's not about the tools or techniques.
The real culprit often lurks in the shadows of change management.
Let's dive deep into why Operational Excellence programs falter and how to breathe new life into them using John Kotter's renowned 8-step change model:
- Lack of Urgency:
Without a compelling reason for change, teams lose momentum. Create a sense of urgency by clearly communicating the need for improvement.
- Weak Guiding Coalition:
OpEX programs require strong leadership support. Build a diverse team of influencers to champion the change.
- Unclear Vision:
Without a clear direction, efforts become scattered. Develop and communicate a concise vision for your OpExprogram.
- Poor Communication:
Change can't stick if people don't understand it. Overcommunicate your vision through multiple channels.
- Failure to Remove Obstacles:
Identify and address barriers that hinder progress, whether they're processes, structures, or mindsets.
- Neglecting Short-Term Wins:
Celebrate small victories to maintain momentum. Recognize and reward early successes.
- Declaring Victory Too Soon:
OpEx is ongoing. Don't let up – keep pushing for deeper changes and broader adoption.
- Not Anchoring Changes in Culture:
Ensure new practices become "the way we do things around here" by integrating them into your organizational DNA.
Kotter 8 step change management model
Kotter's 8 Step Change Model
is a framework for implementing change in organisations or any people-centred change. Useful in Creating Change, Cultural Change.
“Creating a high enough sense of urgency among a large enough group of people is an issue I have come to believe is of overriding importance in a fast-moving, turbulent era.
When the urgency challenge is not handled well, even very capable people and resource-rich organizations can suffer greatly.
When the challenge is handled well, even those who face formidable obstacles can produce results we all want for our careers, employers and nations.
Put simply, a strong sense of urgency is moving from an essential element in big change programs to an essential asset in general.” (J.P.Kotter)
It also has some criticisms.
- One criticism is that the model is too linear and does not account for the complex and unpredictable nature of change.
Change is often messy and nonlinear, and the model may not apply to all change initiatives.
- Another criticism is that the model does not address the emotional aspects of change.
Change can be stressful and emotional and the model may not provide enough support for addressing these emotions.
🚧 E-3.6.4 Change constraints for learning organisations
System dynamics, Markov, Petri
What is system dynamics
Systems thinking is a way to describe and understand the causality and interrelations between variables within a system.
System Dynamics quantifies the impact of those interactions.
- Systems thinking is a causality-driven, holistic approach to describing the interactive relationships between components inside a system as well as influences from outside the system. Its background emerges from various fields including philosophy, sociology, organizational theory, and feedback thought.
- System Dynamics complements systems thinking by quantifying interactions and develops a time-dependent view of how the system behaves.
The approach focuses on building computer models that represent and simulate complex problems in which behavior changes.
These models bring to light less visible relationships, dynamic complexity, delays, and unintended consequences of interactions.
What is system dynamics
System dynamics (SD) is an approach to understanding the nonlinear behaviour of complex systems over time using stocks, flows, internal feedback loops, table functions and time delays.
Markov chains
In probability theory and statistics, a Markov chain or Markov process is a stochastic process describing a sequence of possible events in which the probability of each event depends only on the state attained in the previous event. Informally, this may be thought of as, "What happens next depends only on the state of affairs now." A countably infinite sequence, in which the chain moves state at discrete time steps, gives a discrete-time Markov chain (DTMC).
A continuous-time process is called a continuous-time Markov chain (CTMC).
Markov processes are named in honor of the Russian mathematician Andrey Markov.
dependability models based on petri nets and markov chains
FPGA-based (Field Programmable Gate Arrays) designs are sensitive to many effects that can change their programmed function.
These changes are most unwelcome when designs are used in safety-critical applications, where the material loss or mortality can be caused because of their failure.

learn from others how to manage it better
The Uniqueness Trap (Bent Flyvbjerg, Alexander Budzier, M.D. Christodoulou and M. Zottoli 20235)"
Your project isn't one of a kind, and that's a good thing because it means you can learn from others how to manage it better.
Managers are indeed highly prone to believing that their projects are one of a kind even though few, if any, actually are.
This causes them to think they have nothing to learn from other projects.
Most important, it leads them to underestimate risk and overestimate opportunity and thus make poor decisions.
Specifically, the more distinctive managers consider a project to be, the more likely it is to exceed its budget and the more likely the overrun is to be considerable.
That led us to the conclusion that improving project performance has less to do with managing the activities involved and more to do with addressing how project managers make decisions.
- The cure for uniqueness bias is to always assume that someone, somewhere has undertaken a project like yours, adopting what’s called an “outside view.”
- If you can’t find any direct analogues, break the project down into modules and subprocesses, which may then prove comparable across projects.
- Once you have found your analogues, be careful about how you process the information you glean from them.
Even when taking an outside perspective, project managers making forecasts and decisions can fall prey to other biases that cause them to discount the risks attached.
Technology a significant factor how to manage it better
🤔 The problem: Tools like Jira, Confluence, Togaf, SAFe, and sprint planning can be immensely valuable in the right contexts.
They provide structure, standardize workflows, and enable collaboration, especially in large-scale or distributed teams.
However, their effectiveness depends heavily on how they're implemented and used:
- When Used Properly: These tools can streamline processes, enhance transparency, and foster accountability.
For example, Jira enables task tracking, while Confluence centralizes documentation.
Frameworks like SAFe can align teams to work towards common objectives in complex environments.
- When Misused: The same tools can add unnecessary layers of oversight, create bottlenecks, and discourage adaptive thinking.
If teams rigidly adhere to frameworks or overuse tools for micromanagement, it often leads to "process for the sake of process" rather than meaningful productivity.

The key lies in balancing structure and flexibility.
Organizations need to remain agile enough to pivot when conditions change, while also leveraging technology and frameworks to provide a baseline of order.
This often requires:
- Cultural Alignment: Tools and methodologies should align with the organization's culture and goals, not impose alien processes.
- Regular Feedback: Constantly assessing whether tools are delivering value or becoming roadblocks is crucial.
- Simplification: If a tool or framework adds complexity without proportionate benefits, it may need to be re-evaluated or adapted.
In the end, tools are only as effective as the mindset and strategy driving them.
The answer of the problem why all these components don't result automagically in a good system development methodology is with hindsight quite logical.
| | 💡
📚
🎭 | A viable system development methodology (VSDM) is a functionality that is more and different than any and all the components it is build of. |
The success of Jabes depends on the in the level of integration:
- Emphasize customization for diversity needs by a centralised adjustable meta data structure.
- Collaboration over disperse locations, time & versions by unique, traceable identification.
- The tooling (to be build) should be intuitive encouraging adoption with minimized training.
- Jabes is possible for starting small and allows scaling up into large.
The key factor is defining the relationship in the defined systems by the identification and using those as components.
Interactions learn from others how to manage it better
The Bridge Between Anger and Kindness? That’s Uncertainty (LI Meenakshi (Meena) Das 20235)"
The weight of certainty, of being sure, of picking a lane and sticking with it…
❗ Certainty has a way of preserving the world as it is.
Those who are absolutely convinced of how the rightness of existing structures tend to defend them, even when those structures are flawed or harmful.
❗ Certainty reinforces tradition, protects institutions over humans, and safeguards rules, even when those rules no longer serve a just purpose.
Our anger in reaction to the world events of the moment is an act of defiance.
This is an anger of disruption for change.
- True kindness requires the courage to challenge systems that do not serve our communities and their humanity.
It requires seeing beyond what is socially acceptable to what is fundamentally just.
- Believe in the anger you feel when you see injustices.
Because there are doubts and uncertainties expanding your human-ness there.
And there is kindness waiting to shine through that pain.
- There is loneliness in not finding the best answers when you refuse to accept things as they are.
There is exhaustion in constantly questioning, resisting, and pushing against forces larger than oneself.
Besides, the world does not always feel kind to those who challenge its structures.
Compliance is rewarded way more than intentional critique.
- There is a bridge between your kindness and the anger we are experiencing now.
Kindness, at its core, is not an act of passive niceness but a radical openness to re-evaluating what we think we know when needed.
It is a willingness to live in the discomfort of uncertainty for the sake of our humanity.
I am not denying the burden this anger places on those who bear it.
This is not easy to carry, I agree.
We won’t realize then, that anger, while painful, is necessary. It sparks questioning that makes room for progress.


 Aside the global explanation of thoughts there is an index contents.
Aside the global explanation of thoughts there is an index contents. 

 The communication with stakeholders is often forgotten or ignored.
Working on questions what kind of information processing is a difficult one without needed insight without communication.
The communication with stakeholders is often forgotten or ignored.
Working on questions what kind of information processing is a difficult one without needed insight without communication. 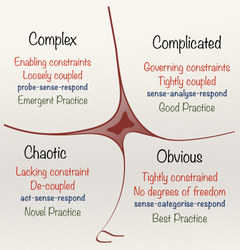
 Leaders need to avoid micromanaging and stay connected to what is happening in order to spot a change in context.
Leaders need to avoid micromanaging and stay connected to what is happening in order to spot a change in context. 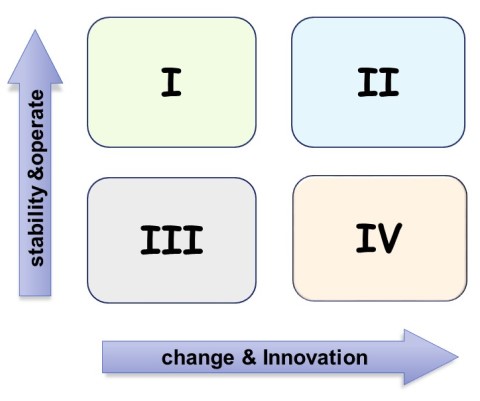 Conservative running as-is (vertical)
Conservative running as-is (vertical) 
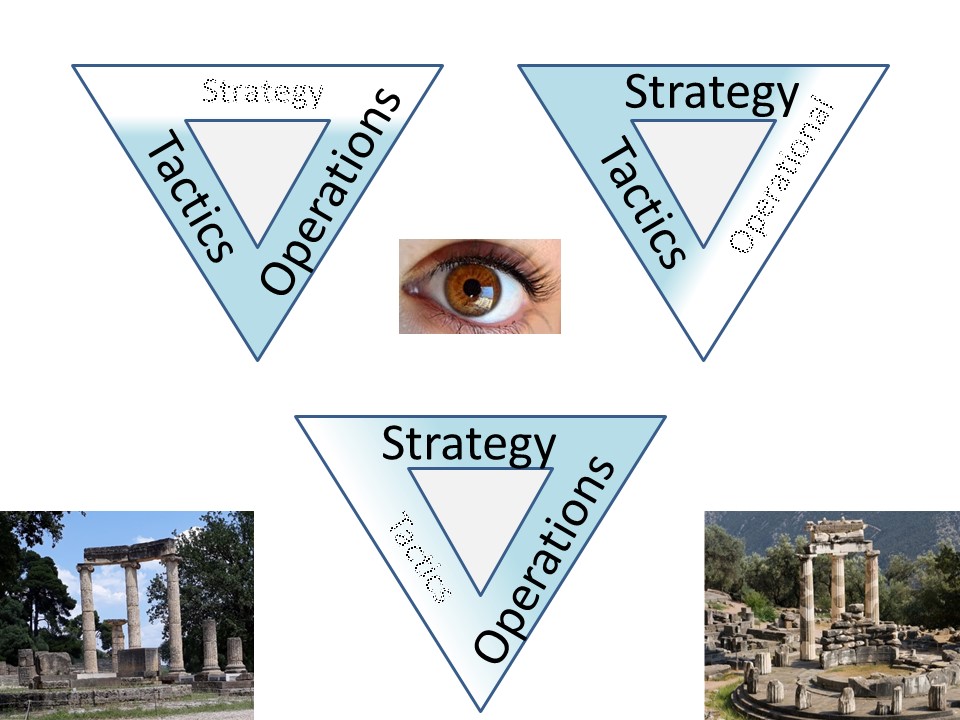


 bisl in three minutes
Guidance provided in Business Relationship Management Institute´s BRMBoK© with the ASL BiSL Foundation´s Business Information Services Library (BiSL©).
bisl in three minutes
Guidance provided in Business Relationship Management Institute´s BRMBoK© with the ASL BiSL Foundation´s Business Information Services Library (BiSL©). 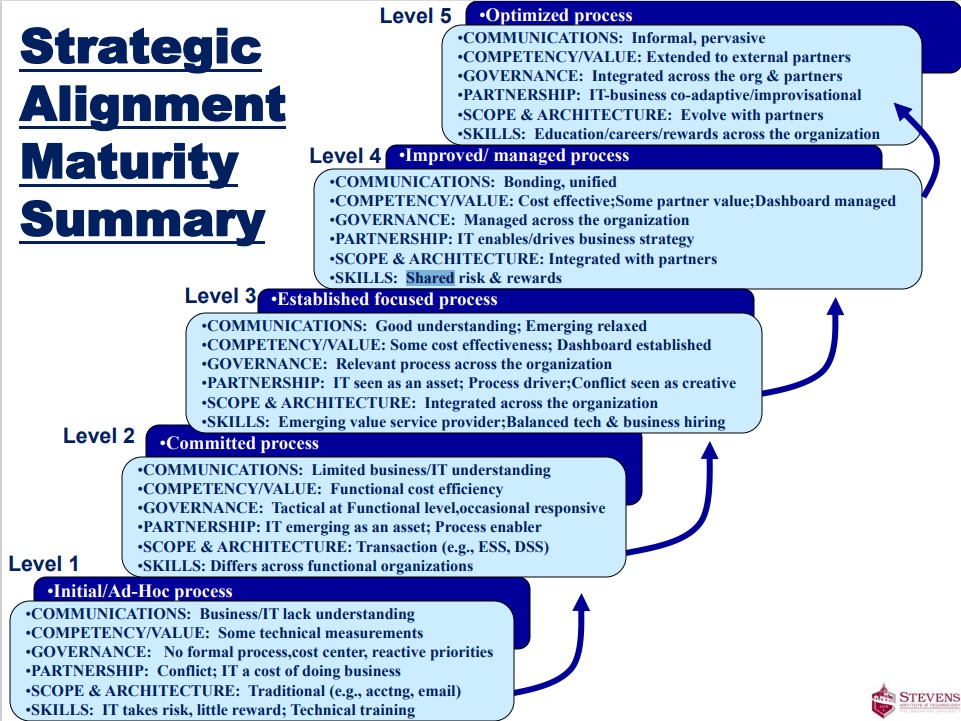 level 1:
level 1:

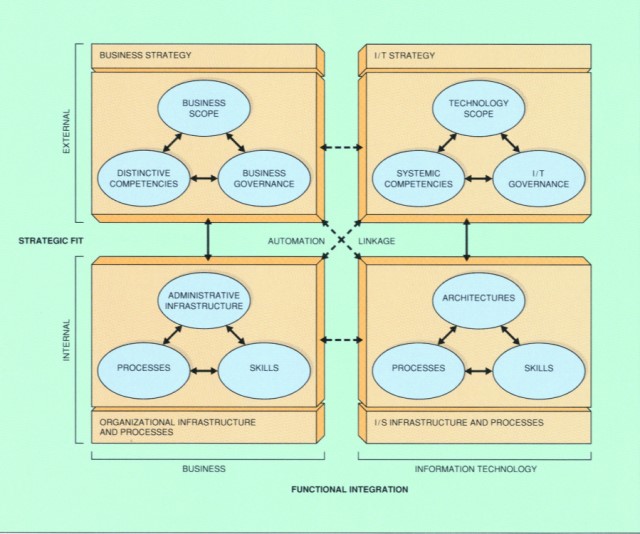
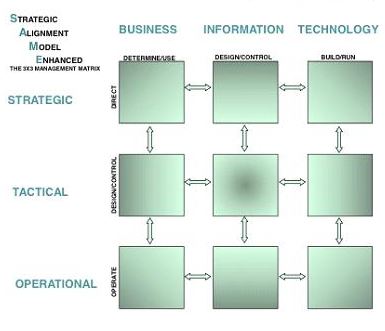
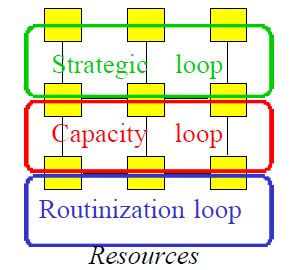 🤔 A mistake , adding the loops was not done fully, there should have been four of them.
The strategic loop should have been above the top and the tactical at what is shown as strategical.
What would got solved?
🤔 A mistake , adding the loops was not done fully, there should have been four of them.
The strategic loop should have been above the top and the tactical at what is shown as strategical.
What would got solved?
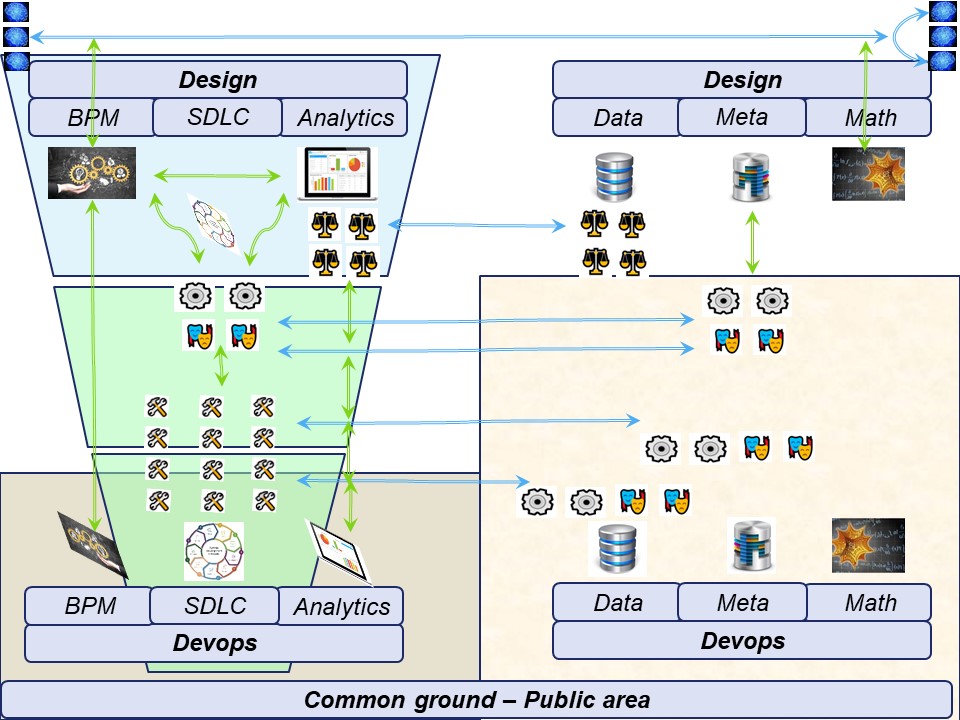

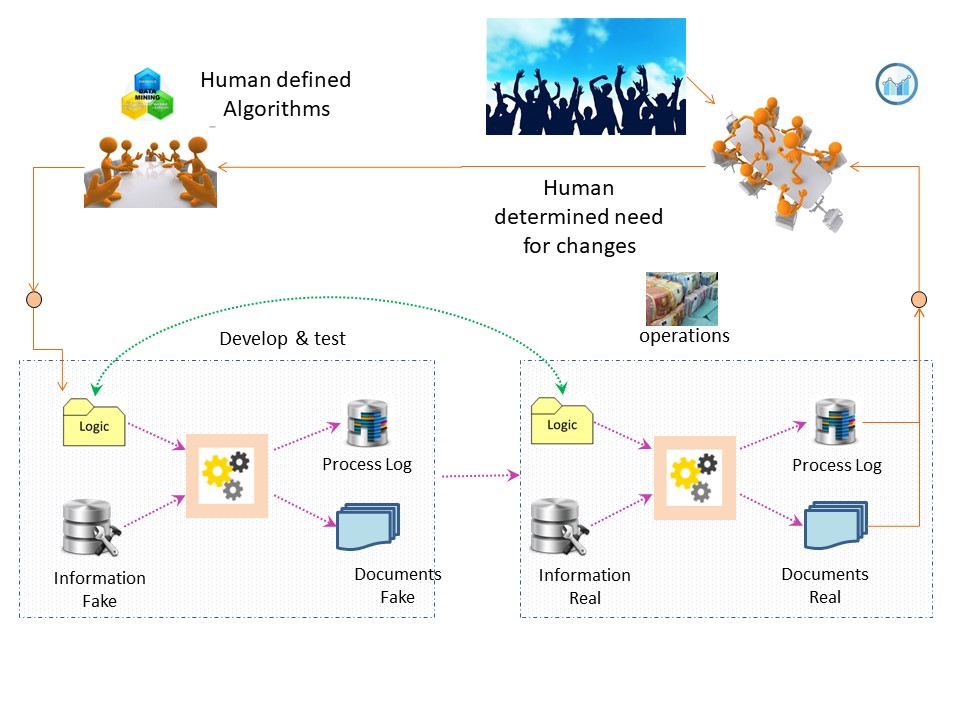
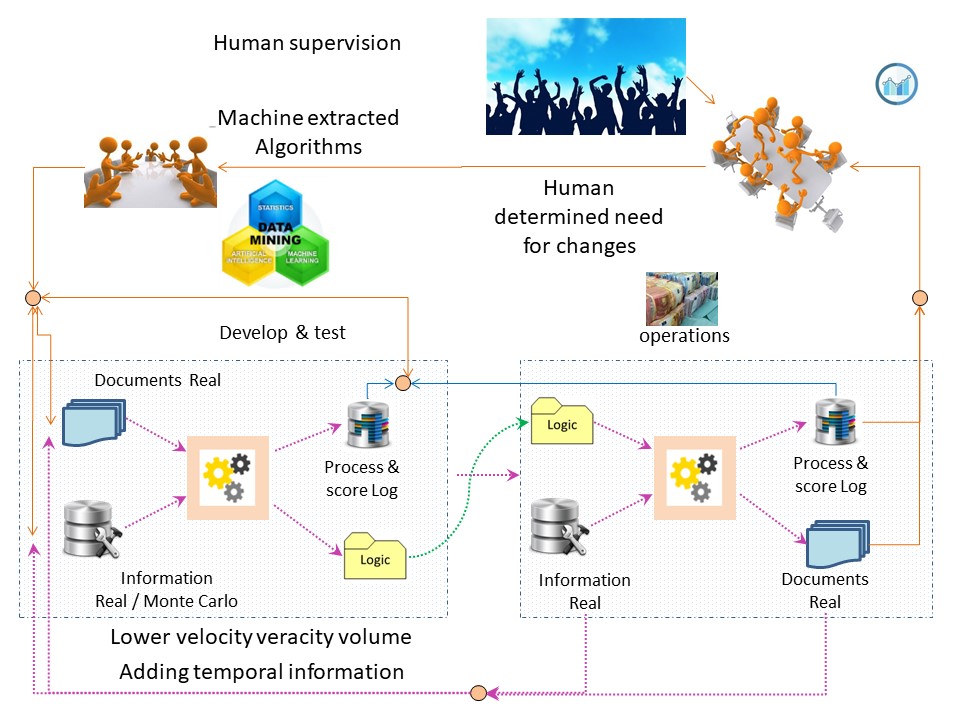
 It´s an accepted convention that the monolithic data platform hosts and owns the data that logically belong to different domains.
Instead of flowing the data from domains into a centrally owned data lake or platform, domains need to host and serve their domain datasets in an easily consumable way.
It´s an accepted convention that the monolithic data platform hosts and owns the data that logically belong to different domains.
Instead of flowing the data from domains into a centrally owned data lake or platform, domains need to host and serve their domain datasets in an easily consumable way. 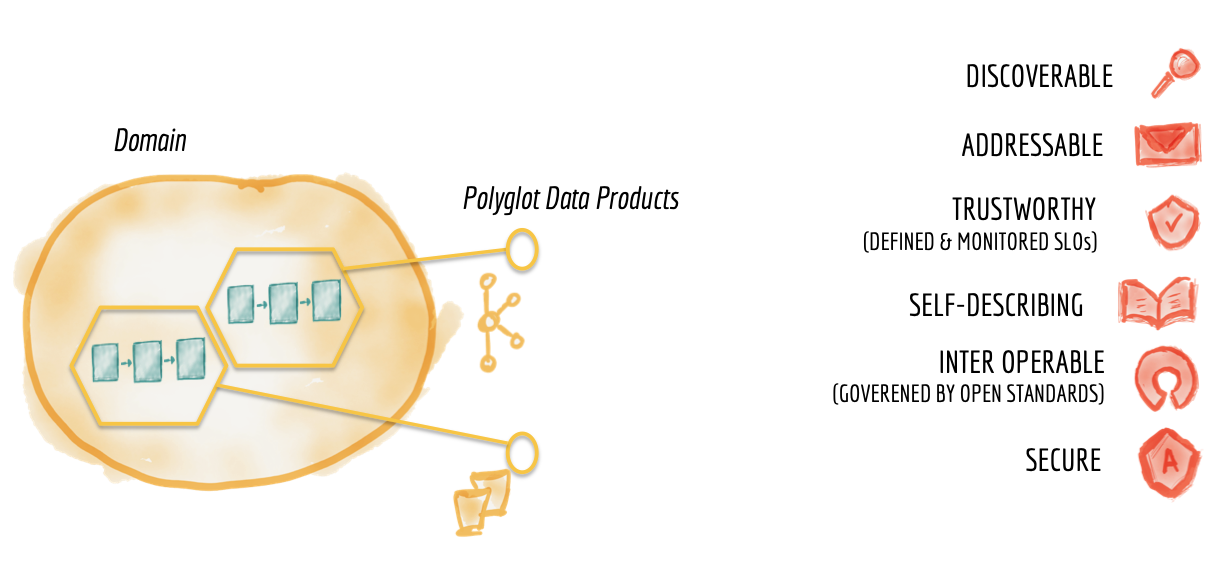

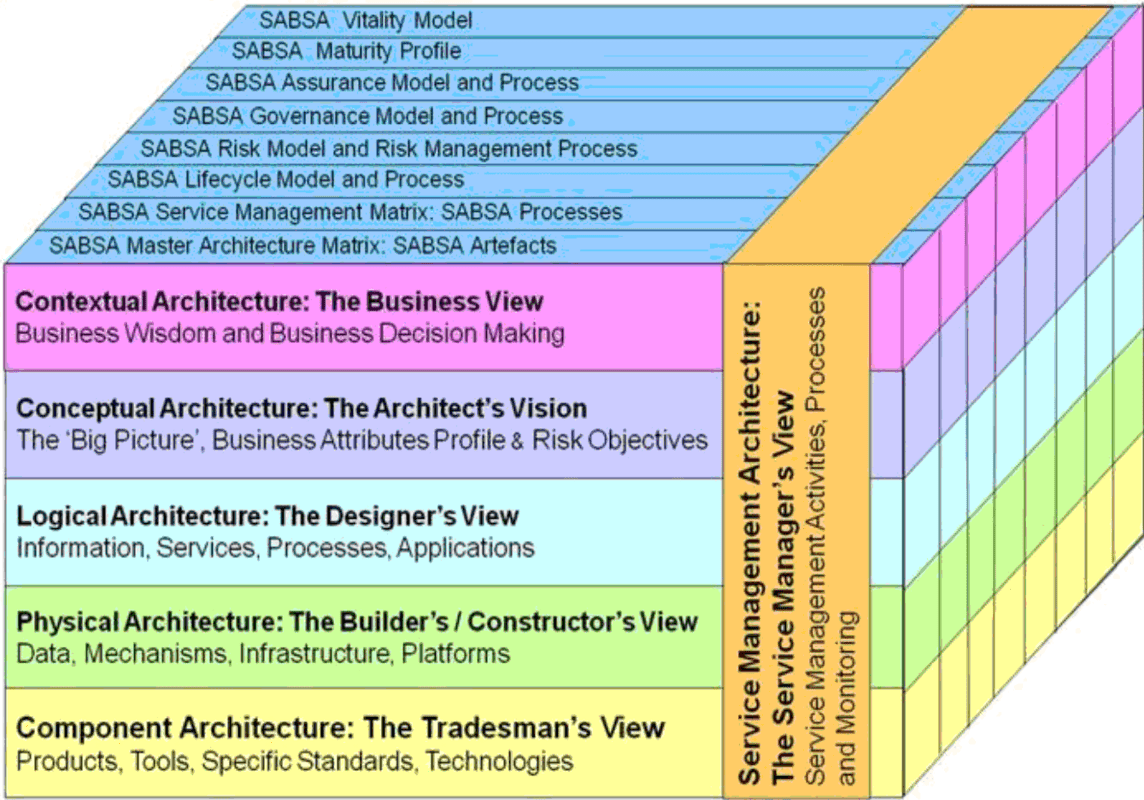
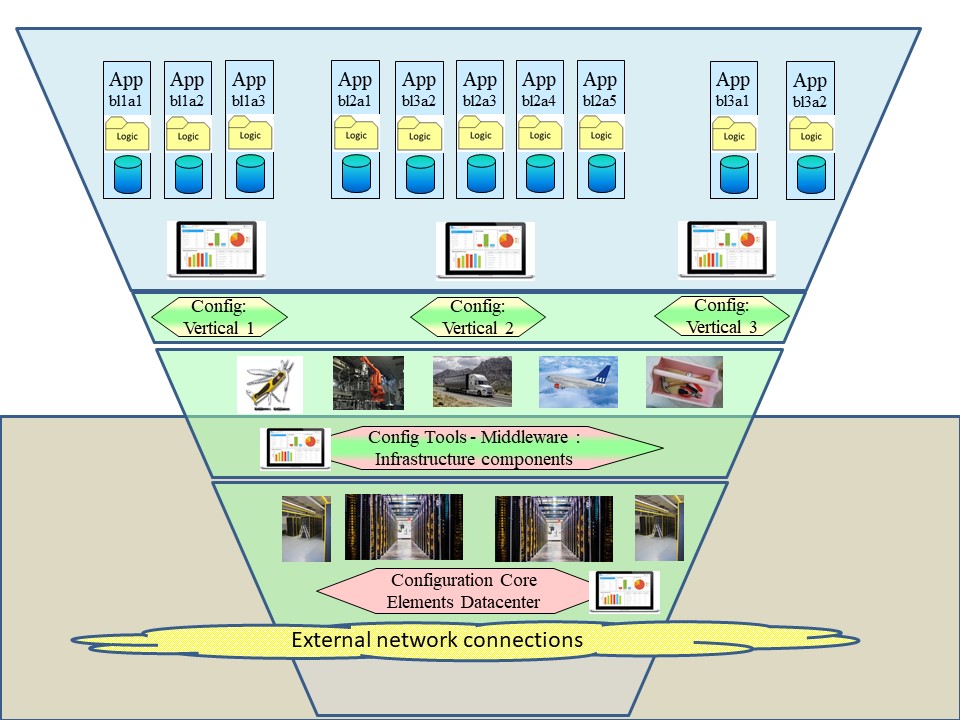
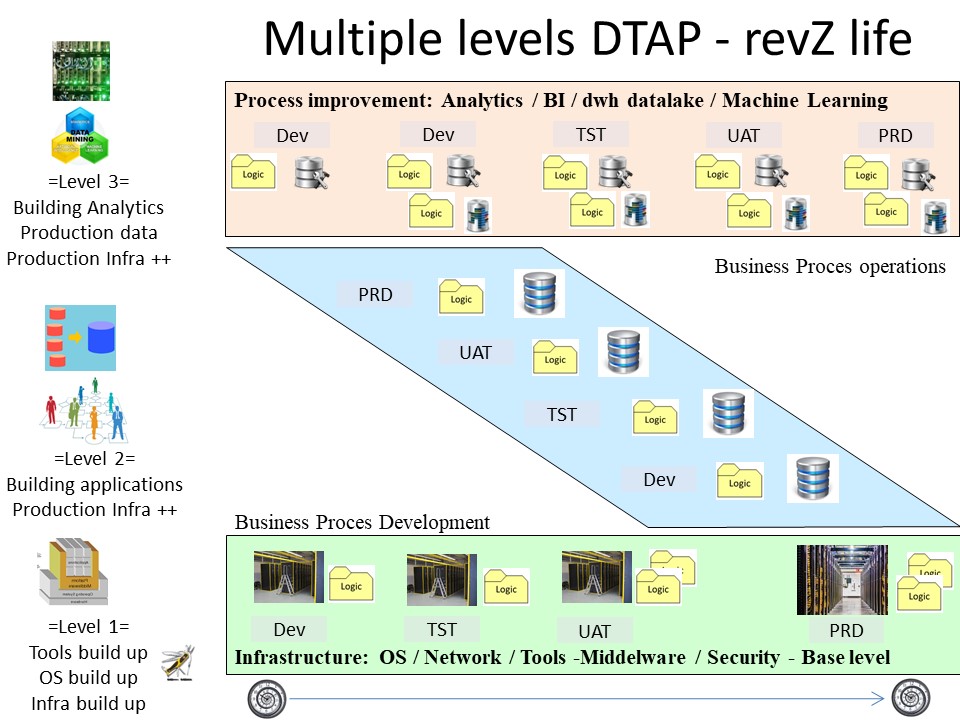
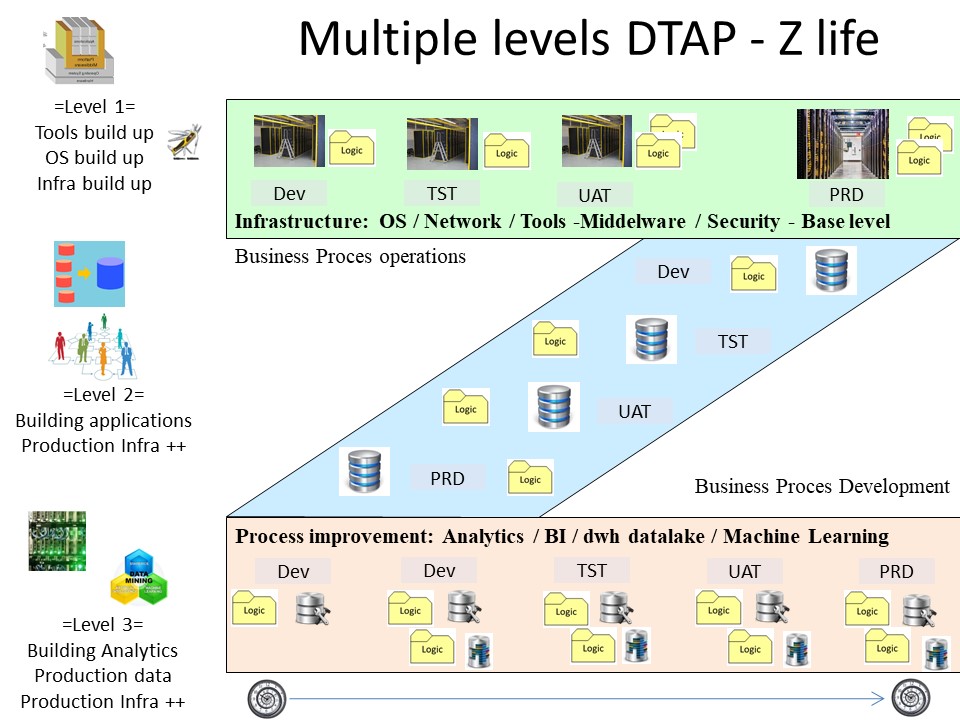
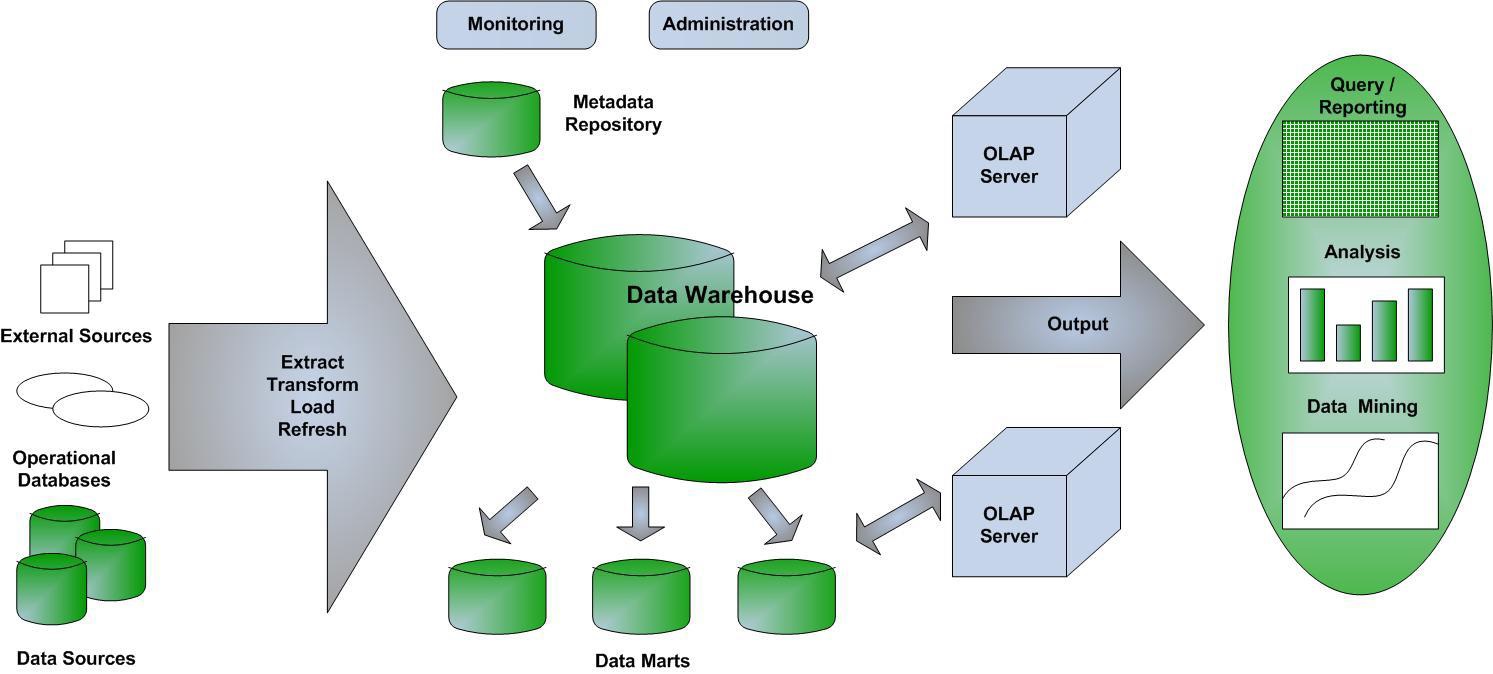

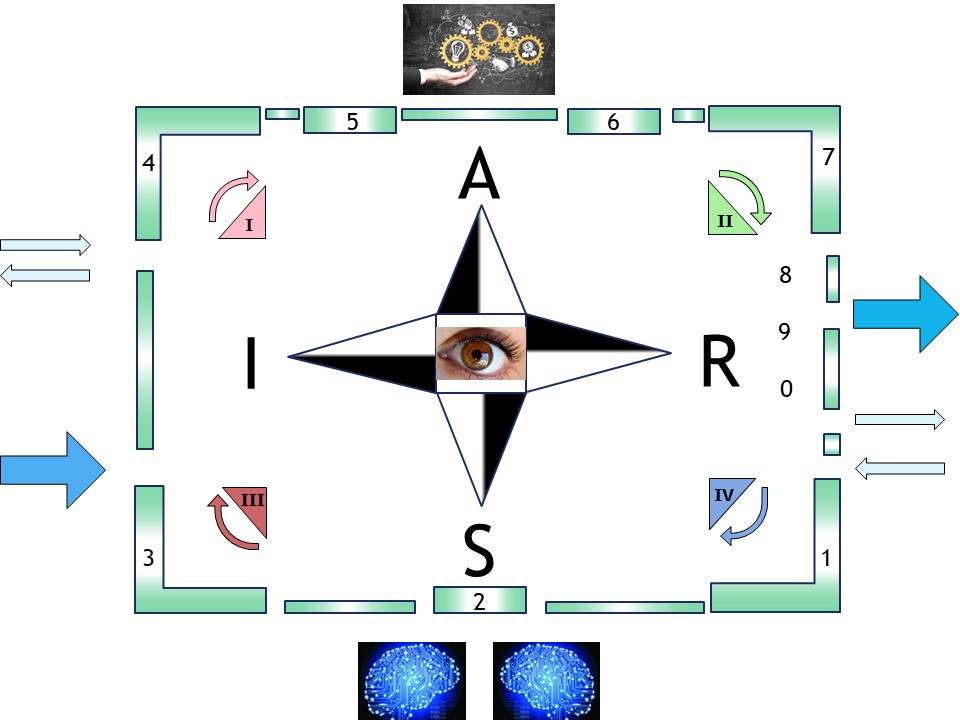
























 Indeed, this model was once characterized as being inherently conservative, because it allegedly assumed the stability and functionality of societal structures.
Indeed, this model was once characterized as being inherently conservative, because it allegedly assumed the stability and functionality of societal structures.  Using ideas from cybernetics and systems theory, Parsons orders the four components of the system hierarchically, indicated by the zigzag sequence of directed links shown in bold in the figure.
Using ideas from cybernetics and systems theory, Parsons orders the four components of the system hierarchically, indicated by the zigzag sequence of directed links shown in bold in the figure. 




 "Self-organization is a mechanism that enables almost sudden changes in the states of order in open systems consisting out of autonomous subsystems!” (Haken Schiepeck)
"Self-organization is a mechanism that enables almost sudden changes in the states of order in open systems consisting out of autonomous subsystems!” (Haken Schiepeck)  ❸
An answer:
TPS wasn't designed as a universal toolkit, it evolved in a specific cultural and operational context.
After 80+ years, it's clear that simply adopting Toyota's methods doesn't guarantee success.
❸
An answer:
TPS wasn't designed as a universal toolkit, it evolved in a specific cultural and operational context.
After 80+ years, it's clear that simply adopting Toyota's methods doesn't guarantee success. 



 ❹ Failures in the homomorphic model understanding:
❹ Failures in the homomorphic model understanding:




 ❸
The Logical Framework Approach elegantly weaves together top-down and bottom-up approaches to project management. It brings together the classical, top-down for identifying the activities in a project, with a rigorous bottom-up checking process to make sure that these activity lists are comprehensive.
❸
The Logical Framework Approach elegantly weaves together top-down and bottom-up approaches to project management. It brings together the classical, top-down for identifying the activities in a project, with a rigorous bottom-up checking process to make sure that these activity lists are comprehensive.

 Micromanagement is excessive and unhealthy need of control, where a manager closely observes and monitors the work of their subordinates, often with a lack of delegation.
It involves constant surveillance and making decisions without consultation, leading to a direct impact on the autonomy and creativity of the team.
Micromanagement is excessive and unhealthy need of control, where a manager closely observes and monitors the work of their subordinates, often with a lack of delegation.
It involves constant surveillance and making decisions without consultation, leading to a direct impact on the autonomy and creativity of the team.  See figure.
See figure. 


 Sub-strategy steps result into value:
Sub-strategy steps result into value:
 Properties shared with other approaches:
Properties shared with other approaches:


 Penta concept Co-invented by Al Shalloway and Tom Gilb, 2022 PENTA: Purposely Efficient Nodes for Top Attributes.
Penta concept Co-invented by Al Shalloway and Tom Gilb, 2022 PENTA: Purposely Efficient Nodes for Top Attributes. 






 🚧 The "DevOps" model:
🚧 The "DevOps" model:

 🚧 The "Pro-visionBuyer" model:
🚧 The "Pro-visionBuyer" model:


 Just using the technology mindset is missing the purpose provision and the enablement in supply.
There are only two dichotomous where the system (SIMF SIAR) using flow has four.
Just using the technology mindset is missing the purpose provision and the enablement in supply.
There are only two dichotomous where the system (SIMF SIAR) using flow has four.

 Cons:
Cons: 







 The key lies in balancing structure and flexibility.
Organizations need to remain agile enough to pivot when conditions change, while also leveraging technology and frameworks to provide a baseline of order.
This often requires:
The key lies in balancing structure and flexibility.
Organizations need to remain agile enough to pivot when conditions change, while also leveraging technology and frameworks to provide a baseline of order.
This often requires: